Змест
1. Introduction to TFT and OLED
Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) and Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technologies are the cornerstones of modern display innovation. TFT-LCDs dominate the market for large-format screens like TVs and monitors, while OLEDs lead in high-end smartphones, wearables, and flexible displays. This article explores the science, manufacturing, and real-world applications of these technologies, leveraging insights from leading Chinese manufacturers such as BOE, CSOT, and Visionox.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Асаблівасць | TFT-LCD | ТЫ ЁСЦЬ |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight Required | Yes (LED/CCFL) | No (self-emissive) |
| Каэфіцыент кантраснасці | ~500:1 | Up to 1,000,000:1 |
| Гнуткасць | Rigid panels | Flexible/foldable designs |
| Энергаэфектыўнасць | Умераны | High for dark content |
| Кошт | $15–$30/cm² | $30–$50/cm² |
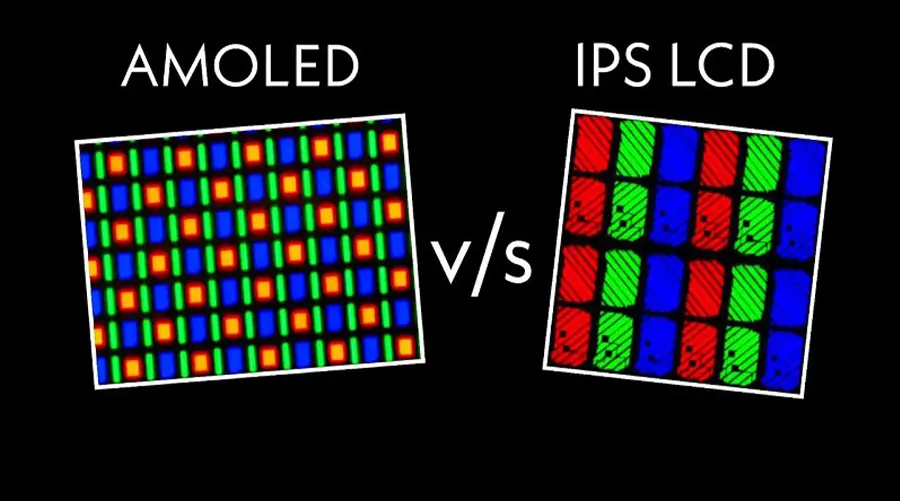
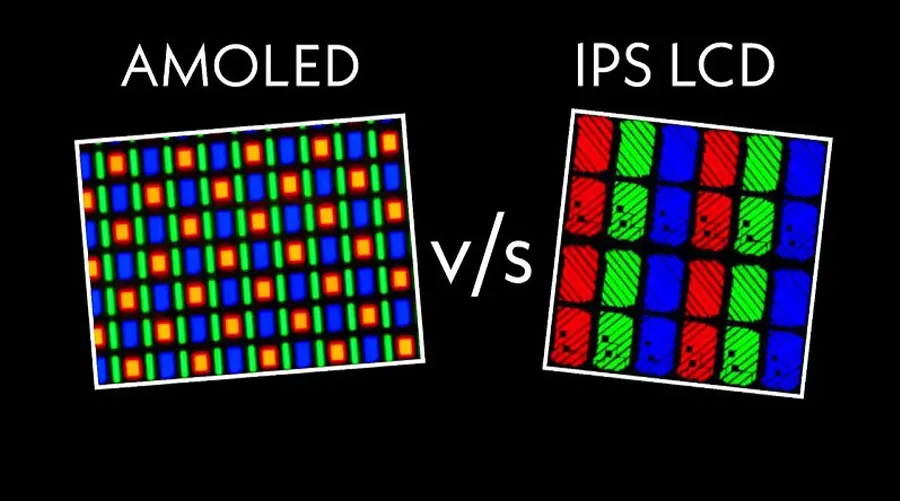
2. TFT Technology: Principles and Applications
What is TFT?
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) is a semiconductor technology used in LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) to control individual pixels. TFT-LCDs combine a liquid crystal layer with a backlight and a TFT array to produce high-resolution images.
Key Components of TFT-LCDs
-
Glass Substrates: Typically 700–1200mm in size, made of soda-lime or alkali-free glass.
-
Thin-Film Deposition: Layers of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), silicon nitride (SiN), and indium tin oxide (ITO) are deposited via chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
-
Photolithography: A multi-step process using 4–6 masks to pattern the TFT array.
-
Cell Assembly: Liquid crystals are sealed between two substrates with spacers to maintain uniform thickness.
Applications of TFT-LCDs
-
Television and Monitor Manufacturing: Dominates the TV market due to cost-effectiveness.
-
Industrial Automation: Used in medical devices (e.g., diagnostic equipment) and industrial control panels.
-
Аўтамабільныя дысплеі: Integrated into car dashboards and infotainment systems.
Case Study: BOE's B7 Line
BOE’s B7 line in Chengdu produces 48K/M AMOLED panels using LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon) technology. This line achieves 1000 cd/m² brightness and supports 120Hz refresh rates, making it ideal for high-end smartphones.
3. OLED Technology: Advantages and Challenges
What is OLED?
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) uses organic compounds that emit light when electrically stimulated. Unlike TFT-LCDs, OLEDs do not require a backlight, enabling ultra-thin, flexible displays with perfect blacks and wide viewing angles.
Перавагі OLED-дысплеяў
-
Высокі каэфіцыент кантраснасці: Achieves 1,000,000:1 due to self-emissive pixels.
-
Flexibility: Enables foldable phones (e.g., Huawei Mate X3) and curved TVs.
-
Энергаэфектыўнасць: Consumes less power for dark scenes compared to TFT-LCDs.
Challenges in OLED Manufacturing
-
Тэрмін службы сіняга OLED-дысплея:Сінія арганічныя матэрыялы раскладаюцца хутчэй, чым чырвоныя/зялёныя, і патрабуюць перадавых фасфарэсцэнтных выпраменьвальнікаў.
-
Выдаткі на вытворчасць:Працэсы вакуумнага нанясення з'яўляюцца дарагімі, іх кошт дасягае 30–50 долараў/см².
-
Паказчыкі прыбытковасці:Ніжэй, чым у TFT-LCD (звычайна 60–70% з-за дэфектаў матэрыялу).
Тэматычнае даследаванне: лінейка V2 ад Visionox
Лінія V2 кампаніі Visionox у Гуанчжоу сканцэнтравана на вытворчасці AMOLED-дысплеяў з выкарыстаннем тэхналогій Cu (медзі) і LTPO (нізкатэмпературнага полікрышталічнага аксіду). Гэтая лінія падтрымлівае сертыфікаваныя FDA медыцынскія прылады і аўтамабільныя дысплеі, дасягнуўшы магутнасці 30 тыс./млн да 2023 года.
4. Manufacturing Processes of TFT and OLED
Этапы вырабу TFT-LCD
-
Падрыхтоўка шкляной падкладкі:Ачыстка і хімічнае ўмацаванне.
-
Thin-Film Deposition:Пласты SiO₂, SiN і ITO.
-
Photolithography:4–6 масак для вызначэння піксельных масіваў.
-
Cell Assembly:Упырскванне і герметызацыя вадкіх крышталяў.
-
Інтэграцыя падсветкі:Для падсветкі дададзеныя святлодыёдныя або CCFL-падсветкі.
Этапы вытворчасці OLED
-
Выбар субстрата:Шкляныя або палімерныя плёнкі для гнуткасці.
-
Вакуумнае нанясенне:Арганічныя матэрыялы (напрыклад, эмітэры TADF), нанесеныя з дапамогай струменевага друку або тэрмічнага выпарэння.
-
Інкапсуляцыя:Герметызацыя тонкаплёнкавымі бар'ерамі для прадухілення траплення вільгаці.
-
Інтэграцыя мікрасхемы драйвера:TFT-матрыцы кантралююць яркасць і колер пікселяў.
Параўнальныя паказчыкі
| Параметр | TFT-LCD | ТЫ ЁСЦЬ |
|---|---|---|
| Яркасць | 300–800 кд/м² | 500–1000 кд/м² |
| Час водгуку | 5–8 мс | 0,1 мс |
| Спажыванне энергіі | 3–5 Вт (10-цалевы экран) | 2–4 Вт (10-цалевы экран) |
| Ураджайнасць | ~75% | ~60% |
5. Leading Factories and Case Studies
Лінія B1 кампаніі BOE (Пекін)
Праект:Інтэграцыя міні-святлодыёдаў для падсветкі ВК-дысплеяў.
Вынік:Дасягнута ёмістасць TFT-LCD 100 тыс./м² з пераўтварэннем Mini LED 9 тыс./м², што павысіла эфектыўнасць падсветкі на 30%.
Лінія Т4 CSOT (Ухань)
Фокус:Вытворчасць AMOLED-дысплеяў для аўтамабільных дысплеяў.
Ёмістасць:48 тыс./м² з яркасцю 1000 кд/м².
Тэхналогія:Выкарыстоўвае TFT-схемы на аснове Cu для паляпшэння праводнасці.
Лінейка Visionox V3 (Чэнду)
Інавацыі:Надрукаваныя OLED-дысплеі з выкарыстаннем тэхналогіі струменевай друку.
Зніжэнне выдаткаў:Скарачае колькасць адходаў матэрыялаў на 40%, арыентуючыся на масавае ўкараненне на рынку.
6. TFT vs OLED: A Detailed Comparison
Паказчыкі прадукцыйнасці
| Асаблівасць | TFT-LCD | ТЫ ЁСЦЬ |
|---|---|---|
| Дакладнасць колеру | Крыху ніжэй (8 біт) | Палепшаны (10-бітны) |
| Кут агляду | 120–140° | 170°+ |
| Частата абнаўлення | 60–120 Гц | 60–120 Гц |
| Даўгавечнасць | Большы тэрмін службы | Схільны да выгарання |
Доля рынку (2023 г.)
TFT-ВК-дысплей:65% сусветных паставак дысплеяў (выкарыстоўваюцца ў тэлевізарах, маніторах).
ВЫ:35% паставак сканцэнтравана на смартфонах і носных прыладах.

7. Future Trends and Innovations
Мікрасвятлодыёдныя дысплеі
Лінія B1 Банка Англіі:Вырабляе мініяцюрныя святлодыёдныя падсветкі для ВК-дысплеяў, дасягаючы 20 000 м² у год.
QD-OLED ад Samsung:Спалучае квантавыя кропкі з OLED для павышэння яркасці.
LTPO для AMOLED
Лінія Т6 ад CSOT:Рэалізуе LTPO (нізкатэмпературны полікрышталічны аксід) для частаты абнаўлення 120 Гц і дынамічнай карэкціроўкі частаты кадраў.
Друкаваны OLED-дысплей
Лінейка Vistar ад Visionox:Эксперыменты са струменевым друкам для зніжэння выдаткаў і маштабавання вытворчасці.
8. FAQs About TFT and OLED
Пытанне 1: У чым розніца паміж TFT-трафікамі a-Si і LTPS?
a-Si (аморфны крэмній):Эканамічна выгадны для вялікіх панэляў (напрыклад, тэлевізараў).
LTPS (нізкатэмпературны полікрышталічны крэмній):Больш высокая рухомасць электронаў для невялікіх дысплеяў з высокім разрозненнем (напрыклад, смартфонаў).
Пытанне 2: Чаму OLED-дысплеі даражэйшыя за TFT-LCD-дысплеі?
Вакуумнае нанясенне:Складаны і дарагі працэс атрымання арганічных матэрыялаў.
Выдаткі на матэрыялы:Фасфарэсцэнтныя выпраменьвальнікі і матэрыялы для інкапсуляцыі павялічваюць выдаткі.
Пытанне 3: Як працэсы вытворчасці Cu паляпшаюць прадукцыйнасць OLED?
Медзь (Cu) замяняе алюміній (Al) у схемах TFT, паляпшаючы праводнасць і стабільнасць дысплеяў з высокай частатой абнаўлення.
Latest articles
-
Чаму 1–2-цалевыя AMOLED-дысплеі з'яўляюцца ключавымі для AR/XR у 2025 годзе
Чаму 1-2-цалевыя AMOLED-дысплеі становяцца неабходнымі ў буме AR/XR (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Расцягнутыя ВК-дысплеі для рознічнага гандлю: павелічэнне продажаў і ўзаемадзеяння ў супермаркетах
Даведайцеся, як расцягнутыя ВК-дысплеі паляпшаюць маркетынг на паліцах супермаркетаў, павялічваюць продажы, скарачаюць
-
Расцягнутыя ВК-рашэнні для рэстаранаў і гасцінічных устаноў
Расцягнутыя ВК-дысплеі прапануюць элегантныя дысплеі высокай яркасці, ідэальна падыходзяць для меню рэстаранаў і гасцінічных устаноў.
Рэкамендаваныя прадукты
-
7,0-цалевы IPS TFT з высокай яркасцю без сэнсарнага экрана
BR070JII 2757-B4 V.1 Уводзіны Гэты выключны 7,0-цалевы TFT LCD-модуль працуе на базе a-Si TFT act
-
10,1-цалевы TFT-інтэрфейс IPS LVDS без сэнсарнага экрана
BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1 Уводзіны Вядома. BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1 - гэта ўдасканалены TFT LCD-модуль, які вылучаецца...
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Тэхнічныя характарыстыкі прадукту: BRO392001A Разрозненне: 1080x1024 Дыяпазон працоўнага напружання: 28 В Памер экрана: 3,92
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Тэхнічныя характарыстыкі прадукту: BRO548001A Разрозненне: 1080x1920 Дыяпазон працоўнага напружання: 2,8 В Памер экрана: 5,4