목차
1. Introduction to TFT and OLED
Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) and Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technologies are the cornerstones of modern display innovation. TFT-LCDs dominate the market for large-format screens like TVs and monitors, while OLEDs lead in high-end smartphones, wearables, and flexible displays. This article explores the science, manufacturing, and real-world applications of these technologies, leveraging insights from leading Chinese manufacturers such as BOE, CSOT, and Visionox.
Key Differences at a Glance
| 특징 | TFT-LCD | 당신은 |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight Required | Yes (LED/CCFL) | No (self-emissive) |
| 대비율 | ~500:1 | Up to 1,000,000:1 |
| 유연성 | Rigid panels | Flexible/foldable designs |
| 전력 효율 | 보통의 | High for dark content |
| 비용 | $15–$30/cm² | $30–$50/cm² |
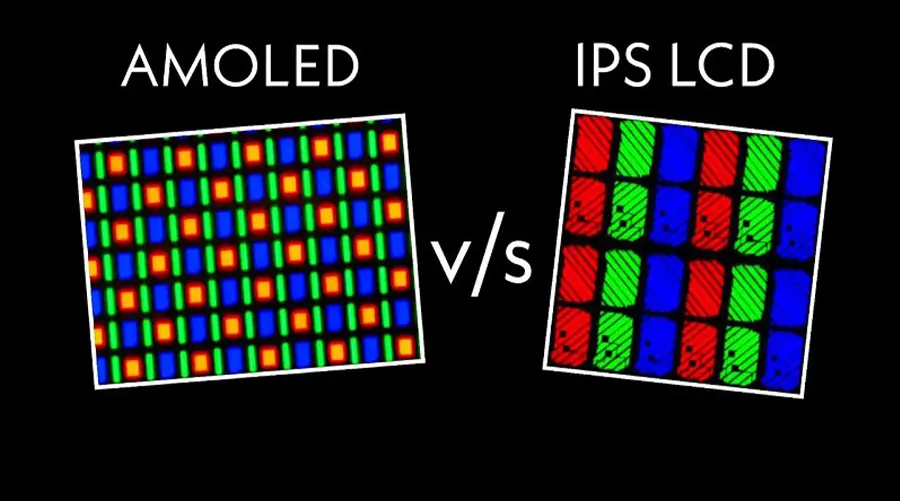
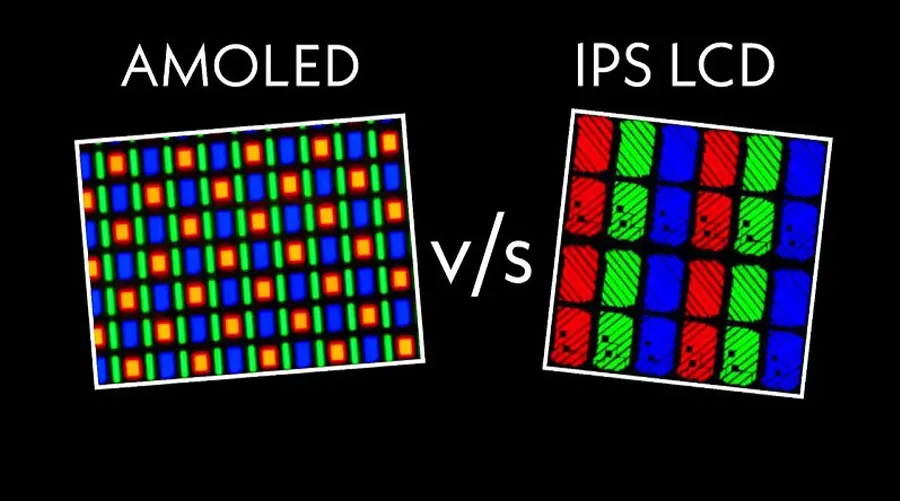
2. TFT Technology: Principles and Applications
What is TFT?
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) is a semiconductor technology used in LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) to control individual pixels. TFT-LCDs combine a liquid crystal layer with a backlight and a TFT array to produce high-resolution images.
Key Components of TFT-LCDs
-
Glass Substrates: Typically 700–1200mm in size, made of soda-lime or alkali-free glass.
-
Thin-Film Deposition: Layers of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), silicon nitride (SiN), and indium tin oxide (ITO) are deposited via chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
-
Photolithography: A multi-step process using 4–6 masks to pattern the TFT array.
-
Cell Assembly: Liquid crystals are sealed between two substrates with spacers to maintain uniform thickness.
Applications of TFT-LCDs
-
Television and Monitor Manufacturing: Dominates the TV market due to cost-effectiveness.
-
Industrial Automation: Used in medical devices (e.g., diagnostic equipment) and industrial control panels.
-
자동차용 디스플레이: Integrated into car dashboards and infotainment systems.
Case Study: BOE's B7 Line
BOE’s B7 line in Chengdu produces 48K/M AMOLED panels using LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon) technology. This line achieves 1000 cd/m² brightness and supports 120Hz refresh rates, making it ideal for high-end smartphones.
3. OLED Technology: Advantages and Challenges
What is OLED?
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) uses organic compounds that emit light when electrically stimulated. Unlike TFT-LCDs, OLEDs do not require a backlight, enabling ultra-thin, flexible displays with perfect blacks and wide viewing angles.
OLED의 장점
-
높은 대비율: Achieves 1,000,000:1 due to self-emissive pixels.
-
Flexibility:폴더블 폰(예: Huawei Mate X3)과 곡면 TV를 지원합니다.
-
에너지 효율성:TFT-LCD에 비해 어두운 장면에서 전력을 적게 소모합니다.
OLED 제조의 과제
-
Blue OLED 수명:파란색 유기 물질은 빨간색/녹색 유기 물질보다 더 빨리 분해되므로 고급 인광 방출체가 필요합니다.
-
생산 비용:진공 증착 공정은 비용이 많이 들며, 비용은 cm²당 30~50달러에 이릅니다.
-
수확률:TFT-LCD보다 낮음(일반적으로 재료 결함으로 인해 60~70%)
사례 연구: Visionox의 V2 라인
Visionox의 광저우 V2 라인은 Cu(구리) 및 LTPO(저온 다결정 산화물) 기술을 활용한 AMOLED 생산에 중점을 두고 있습니다. 이 라인은 FDA 인증 의료기기 및 자동차용 디스플레이를 지원하며, 2023년까지 30K/M 생산능력을 달성할 예정입니다.
4. Manufacturing Processes of TFT and OLED
TFT-LCD 제조 단계
-
유리 기판 준비:세척 및 화학적 강화.
-
Thin-Film Deposition:SiO2, SiN 및 ITO 층.
-
Photolithography:픽셀 배열을 정의하기 위한 4~6개의 마스크.
-
Cell Assembly:액정 주입 및 밀봉.
-
백라이트 통합:조명을 위해 LED 또는 CCFL 백라이트가 추가되었습니다.
OLED 제조 단계
-
기질 선택:유연성을 위해 유리나 폴리머 필름을 사용합니다.
-
진공 증착:잉크젯 인쇄나 열 증발을 통해 증착된 유기 물질(예: TADF 방출기).
-
캡슐화:얇은 필름 장벽으로 밀봉하여 습기가 침투하는 것을 방지합니다.
-
드라이버 IC 통합:TFT 어레이는 픽셀의 밝기와 색상을 제어합니다.
비교 지표
| 매개변수 | TFT-LCD | 당신은 |
|---|---|---|
| 명도 | 300~800cd/m² | 500~1000cd/m² |
| 응답 시간 | 5~8밀리초 | 0.1밀리초 |
| 전력 소비 | 3~5W(10인치 화면) | 2~4W(10인치 화면) |
| 수율 | ~75% | ~60% |
5. Leading Factories and Case Studies
BOE의 B1 라인(베이징)
프로젝트:LCD 백라이트를 위한 미니 LED 통합.
결과:9K/M Mini LED 변환으로 100K/M TFT-LCD 용량을 달성하여 백라이트 효율을 30% 향상시켰습니다.
CSOT의 T4 노선(우한)
집중하다:자동차용 디스플레이용 AMOLED 생산.
용량:1000 cd/m² 밝기의 48K/M.
기술:향상된 전도성을 위해 Cu 기반 TFT 회로를 사용합니다.
Visionox의 V3 라인(청두)
혁신:잉크젯 기술을 사용하여 인쇄된 OLED.
비용 절감:대량 시장 도입을 목표로 재료 낭비를 40% 줄였습니다.
6. TFT vs OLED: A Detailed Comparison
성과 지표
| 특징 | TFT-LCD | 당신은 |
|---|---|---|
| 색상 정확도 | 약간 낮음(8비트) | 우수(10비트) |
| 시야각 | 120–140° | 170°+ |
| 새로 고침 빈도 | 60~120Hz | 60~120Hz |
| 내구성 | 더 긴 수명 | 번인에 취약함 |
시장 점유율(2023년)
TFT-LCD:전 세계 디스플레이 출하량의 65%(TV, 모니터에 사용).
당신은:출하량의 35%는 스마트폰과 웨어러블 기기에 집중되어 있습니다.

7. Future Trends and Innovations
마이크로LED 디스플레이
BOE의 B1 라인:LCD용 미니 LED 백라이트를 생산하며, 연간 생산량은 20,000m²입니다.
삼성의 QD-OLED:OLED와 양자점을 결합하여 밝기를 향상시켰습니다.
AMOLED용 LTPO
CSOT의 T6 노선:120Hz 화면 재생 빈도와 동적 프레임 속도 조정을 위해 LTPO(저온 다결정 산화물)를 구현했습니다.
인쇄형 OLED
Visionox의 Vistar 제품군:비용을 절감하고 생산 규모를 확대하기 위해 잉크젯 인쇄를 실험합니다.
8. FAQs About TFT and OLED
Q1: a-Si와 LTPS TFT의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
a-Si(비정질 실리콘):대형 패널(예: TV)에 비용 효율적입니다.
LTPS(저온 다결정 실리콘):소형, 고해상도 디스플레이(예: 스마트폰)의 경우 더 높은 전자 이동도가 필요합니다.
Q2: OLED가 TFT-LCD보다 비싼 이유는 무엇입니까?
진공 증착:유기물질을 처리하는 복잡하고 비용이 많이 드는 과정입니다.
재료비:인광 발광체와 캡슐화 소재는 비용을 증가시킨다.
Q3: Cu 공정은 어떻게 OLED 성능을 향상시키나요?
구리(Cu)는 TFT 회로에서 알루미늄(Al)을 대체하여 높은 재생률 디스플레이의 전도성과 안정성을 향상시킵니다.
최신 기사
-
2025년 AR/XR의 핵심은 1~2인치 AMOLED
AR/XR 붐에서 1~2인치 AMOLED 디스플레이가 필수가 되는 이유(2025년 산업 통찰력) 본문 {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
스트레치 바 LCD 디스플레이가 슈퍼마켓 선반 가장자리 마케팅을 향상시키고 매출을 늘리고 비용을 절감하는 방법을 알아보세요.
-
레스토랑 및 호스피탈리티 장소를 위한 스트레치 LCD 솔루션
스트레치 LCD는 레스토랑 메뉴와 호스피탈리티 서비스에 적합한 세련되고 고휘도 디스플레이를 제공합니다.
추천 상품
-
터치스크린 없는 7.0인치 IPS 고휘도 TFT
BR070JII 2757-B4 V.1 소개 a-Si TFT 액트로 구동되는 이 뛰어난 7.0인치 TFT LCD 모듈
-
터치스크린 없는 10.1인치 IPS LVDS 인터페이스 TFT
BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1 소개 물론입니다. BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1은 고급 TFT LCD 모듈입니다.
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
제품 사양: BRO392001A 해상도: 1080x1024 작동 전압 범위: 28V 화면 크기: 3.92
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
제품 사양: BRO548001A 해상도: 1080x1920 작동 전압 범위: 2.8V 화면 크기: 5.4