By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone displays to the foundation of a new visual era. No longer confined to flat rectangles, OLED now powers wearables, medical patches, automotive dashboards, and immersive AR interfaces. Its self-emissive pixels — producing light individually — enable ultra-thin, flexible, and energy-efficient displays that shape how humans perceive digital information.
1. The Evolution of OLED
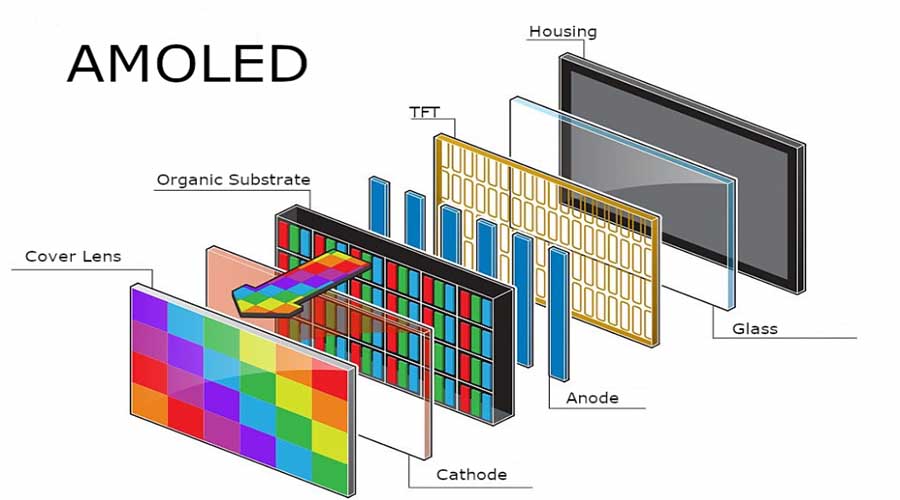
Once a niche research subject, OLED matured through the 2010s as display giants refined materials, deposition processes, and drive electronics. The early 2020s witnessed commercialization beyond mobile devices — foldables, automotive glass panels, and transparent signage. By 2025, OLED had split into multiple specialized branches: traditional AMOLED for mobile, microOLED (OLEDoS) for AR, and hybrid printed OLED for large, sustainable fabrication.
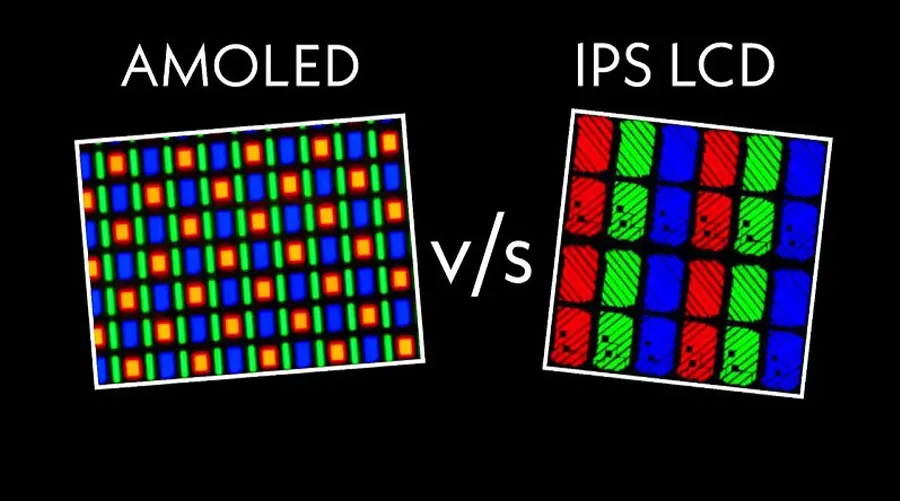
Unlike LCDs, OLED emits its own light per pixel, eliminating backlights. This reduces thickness, improves contrast (true blacks), and allows for flexible or transparent substrates. Modern OLEDs incorporate LTPO backplanes, advanced encapsulation, and AI-based compensation to mitigate burn-in. Combined, these qualities make OLED the most human-centric display medium ever created.
2. OLED in Wearables
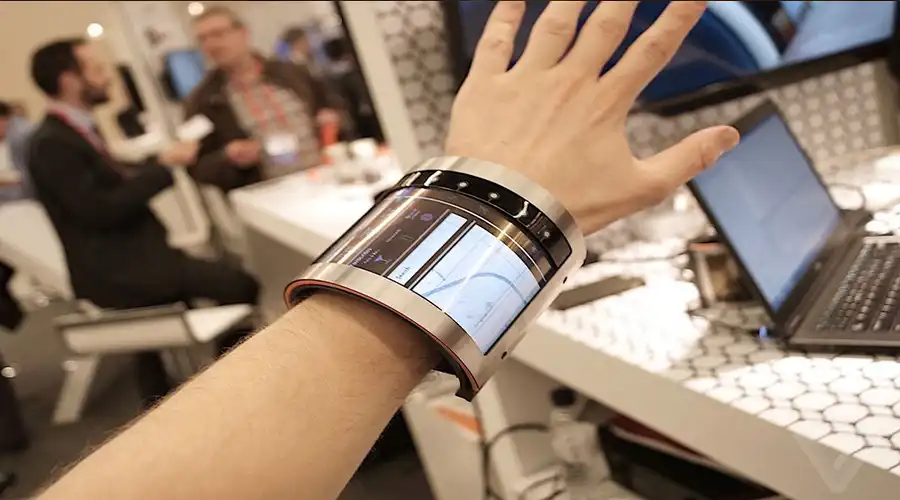
Smartwatches and fitness trackers were the earliest mass-market validation for OLED. The curved, vivid, low-power displays enabled ergonomically sound devices with superb readability in outdoor settings. The flexibility and color precision of OLED perfectly fit wrist-mounted or textile-integrated use cases.
By 2025, wearable OLEDs have advanced to micro-thin modules embedded into medical sensors and skin patches. Real-time glucose, hydration, or oxygen monitoring now occurs on surfaces that breathe and flex. These displays can even remain partially transparent—showing vital data on the skin without blocking natural tone.
“OLED wearables exemplify where technology meets biology — responsive, adaptive, and almost invisible.” – Dr. Aiko Sato, Biotech Lab Tokyo

3. The Leap to AR Glasses
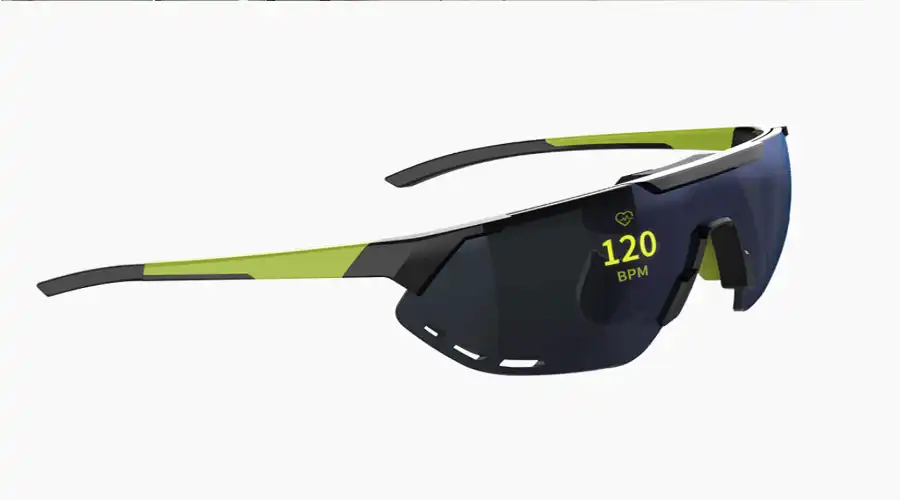
The 2025 AR revolution owes its realism to OLED-on-silicon (OLEDoS) technology — microdisplays with pixel densities exceeding 4000 PPI. These panels fit inside lenses mere millimeters thick, projecting crisp overlays across the user’s natural field of view. Unlike laser or LCD-based HUDs, OLED’s instantaneous contrast and deep black blending let virtual elements coexist believably with real-world objects.
The consumer market now enjoys lightweight AR eyewear capable of persistent data overlays — navigation arrows on roads, live captions in conversations, or contextual translation in travel. OLED’s self-luminous structure ensures privacy, rendering images visible only to the wearer’s pupils. Industries from surgery to engineering use similar optics for precision overlays and low-latency collaboration.

4. Transparency and Flexibility
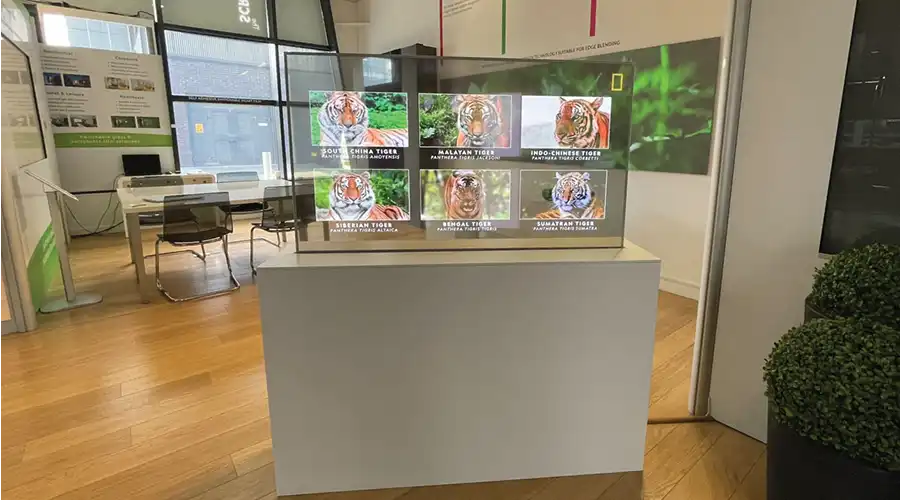
OLED 디자인 자유도의 핵심은 소재의 다양성에 있습니다. 투명 및 폴더블 OLED는 이제 건축, 자동차 대시보드, 가전제품 등에 널리 사용되고 있습니다. 이러한 디스플레이는 공간 디자인 흐름을 방해하지 않으면서 조명과 정보를 제공합니다. 최신 투명 OLED는 70% 이상의 광투과율을 달성하여 화면 그래픽 뒤편에서도 선명한 가시성을 제공합니다.
산업 및 차량 디자인에서 OLED의 뛰어난 휘어짐성은 대시보드와 제어판이 표면을 매끄럽게 감싸도록 합니다. 미래의 컨셉트카는 이미 차체 패널에 외부 신호, 브랜드 또는 경고를 직접 표시할 수 있는 유연한 OLED 스킨을 탑재하고 있습니다. 이는 기술이 기능성과 심미성을 동시에 갖춘 질감으로 진화하는 과정입니다.

5. OLED의 시각적 미학
OLED는 인간의 감정에 지대한 영향을 미칩니다. 무한한 명암비, 즉 선명한 색조에 대한 진정한 검은색은 우리 눈이 자연광을 인식하는 방식을 모방합니다. 디자이너들은 픽셀 단위의 디밍을 활용하여 깜빡임이 아닌 숨쉬는 인터페이스를 구현합니다. 스마트워치 알림이 부드럽게 사라지거나, AR 화살표가 주의를 끌기보다는 속삭이는 듯 사라지는 것을 눈여겨보세요.
엔터테인먼트와 스토리텔링에서
엔터테인먼트 업계는 OLED를 시네마틱 AR 설치에 활용하며, 디스플레이는 역동적인 스토리텔링의 표면 역할을 합니다. 낮은 지연 시간과 거의 제로에 가까운 모션 블러는 몰입감 넘치는 게임 및 가상 제작 환경을 향상시켜 물리적 프레임 속도와 디지털 프레임 속도의 경계를 모호하게 만듭니다. 이제 아티스트들은 빛을 직접 그리며, 픽셀은 상상력의 붓놀림과 같습니다.

6. 지속 가능성 및 효율성
인쇄 가능한 유기 잉크와 재활용 가능한 기판이 에너지 집약적인 진공 증착을 대체함에 따라 OLED의 환경 발자국은 지속적으로 줄어들고 있습니다. 백라이트가 없고 희귀 금속 의존도가 낮아진 OLED 장치는 전력 소모량이 적습니다. 기업들은 발광층으로 바이오 기반 폴리머를, 투명 전극으로 그래핀을 개발하여 순환형 소재 경제를 촉진하고 있습니다.
에너지 관리 기술(적응형 리프레시, 모션 트리거 조명, 딥 슬립 모드)은 기기 수명을 연장합니다. 플렉서블 OLED 필름은 모듈식 수리 기능을 지원하여 전자 폐기물을 줄입니다. 지속가능성은 더 이상 마케팅 용어가 아니라 OLED의 DNA에 내재되어 있습니다.
7. 미래 – 앰비언트 인텔리전스를 향하여
"포스트 스크린" 시대가 도래하고 있습니다. OLED 디스플레이는 물질적 환경과 융합되어 앰비언트 인텔리전스를 가능하게 합니다. 벽, 거울, 그리고 사물들은 이제 발광 논리를 지닙니다. OLED의 적응성은 모든 표면을 미묘하고, 인간 중심적이며, 존재에 반응하는 상황적 인터페이스로 변화시킵니다.
연구가 가속화됩니다양자점 OLED(QOLED)그리고광자 마이크로 OLED각 개인의 눈에 맞춰 밝기와 스펙트럼을 조절하는 기술입니다. 주변 색온도에 맞춰 자동으로 균형을 맞춰주는 안경이나 초점 심도를 동적으로 조절하는 AR 레이어를 상상해 보세요. 시각적 경계가 사라지면서 OLED는 단순한 화면을 넘어 인식의 매개체가 됩니다.
“OLED의 운명은 디스플레이와 현실을 구분할 수 없게 되는 투명성입니다.” – NEXVision Labs의 히로시 타나카

자주 묻는 질문
OLED 번인 현상은 무엇 때문에 발생하며, 어떻게 예방할 수 있나요?
번인은 정적인 이미지를 장시간 표시하면 유기물이 고르지 않게 열화되는 현상입니다. 번인 방지를 위해서는 자동 밝기 조절, 화면 시간 초과, 픽셀 이동, 로고 밝기 조절 기능을 사용하고, 정적인 콘텐츠의 밝기를 너무 밝게 하지 않는 것이 좋습니다.
OLED 디스플레이는 야외 또는 고휘도 환경에 적합합니까?
일반 OLED는 직사광선 아래에서는 성능이 떨어집니다. 그러나 2025년형 모델은 향상된 밝기와 반사 방지 코팅을 특징으로 합니다. 특수 고니트 OLED는 주간 시인성을 위해 미니 LED와의 격차를 줄이고 있습니다.
OLED 디스플레이는 일반적으로 얼마나 오래 지속되나요?
최신 OLED의 수명은 반휘도(L50)가 되기 전까지 5만 시간에서 10만 시간입니다. 새로운 청색 발광 소재는 이 수명을 더욱 연장하여 상용 수명을 LCD 화면과 유사하게 만듭니다.
OLED를 상시 켜진 디스플레이에 사용할 수 있나요?
네, OLED는 켜진 픽셀만 전력을 소모하기 때문에 AOD(Always-On Display)에 이상적입니다. 낮은 밝기를 사용하고 콘텐츠를 주기적으로 전환하면 노화 차이를 최소화할 수 있습니다.
AMOLED와 PMOLED의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
AMOLED는 고해상도와 빠른 화면 주사율을 위해 능동 매트릭스 TFT 레이어를 사용하며, 스마트폰과 웨어러블 기기에 적합합니다. PMOLED는 픽셀 행과 열을 수동적으로 구동하므로, 비용이 저렴하고 작거나 정적인 디스플레이에 적합합니다.
OLED 디스플레이는 터치 기능을 지원합니까?
최신 기사
-
2025년 AR/XR의 핵심은 1~2인치 AMOLED
AR/XR 붐에서 1~2인치 AMOLED 디스플레이가 필수가 되는 이유(2025년 산업 통찰력) 본문 {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
스트레치 바 LCD 디스플레이가 슈퍼마켓 선반 가장자리 마케팅을 향상시키고 매출을 늘리고 비용을 절감하는 방법을 알아보세요.
-
레스토랑 및 호스피탈리티 장소를 위한 스트레치 LCD 솔루션
스트레치 LCD는 레스토랑 메뉴와 호스피탈리티 서비스에 적합한 세련되고 고휘도 디스플레이를 제공합니다.
추천 상품
-
2.0인치 정사각형 HD OLED AMOLED 모듈 460 X 460 QSPI 인터페이스
산업 및 임베디드 시스템용 QSPI 인터페이스가 있는 2.0인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 모듈 핵심 사양
-
2.06인치 OLED 디스플레이 | 410×502 해상도 | 600니트 | SPI 화면
2.06인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 모듈은 특히 혹독한 산업 환경을 위해 설계되었습니다.
-
7.0인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 모듈 | 1280×800 고휘도
7.0인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 모듈은 고해상도, 광시야각 디스플레이 솔루션으로 설계되었습니다.
-
8.0인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 2480×1860 MIPI DSI-BROWNOPTO
2480×1860 해상도, MIPI DSI 인터페이스 및 SPI 터치를 갖춘 8.0인치 FHD AMOLED 모듈. 산업용에 이상적입니다.
-
6.0인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 1080×2160 MIPI - BR600108-A1
1080×2160 해상도, MIPI 4레인 인터페이스, 360니트 밝기를 갖춘 6.0인치 FHD+ AMOLED 모듈.
-
5.5인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 모듈 - 고해상도 LTPS MIPI 패널
5.5인치 AMOLED 모듈 제품 페이지 5.5인치 AMOLED 디스플레이 모듈