By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone displays to the foundation of a new visual era. No longer confined to flat rectangles, OLED now powers wearables, medical patches, automotive dashboards, and immersive AR interfaces. Its self-emissive pixels — producing light individually — enable ultra-thin, flexible, and energy-efficient displays that shape how humans perceive digital information.
1. The Evolution of OLED
Once a niche research subject, OLED matured through the 2010s as display giants refined materials, deposition processes, and drive electronics. The early 2020s witnessed commercialization beyond mobile devices — foldables, automotive glass panels, and transparent signage. By 2025, OLED had split into multiple specialized branches: traditional AMOLED for mobile, microOLED (OLEDoS) for AR, and hybrid printed OLED for large, sustainable fabrication.
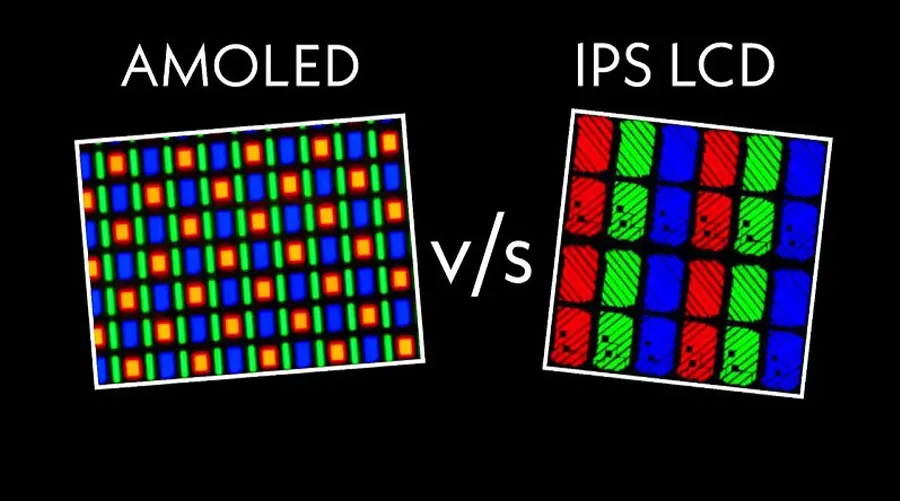
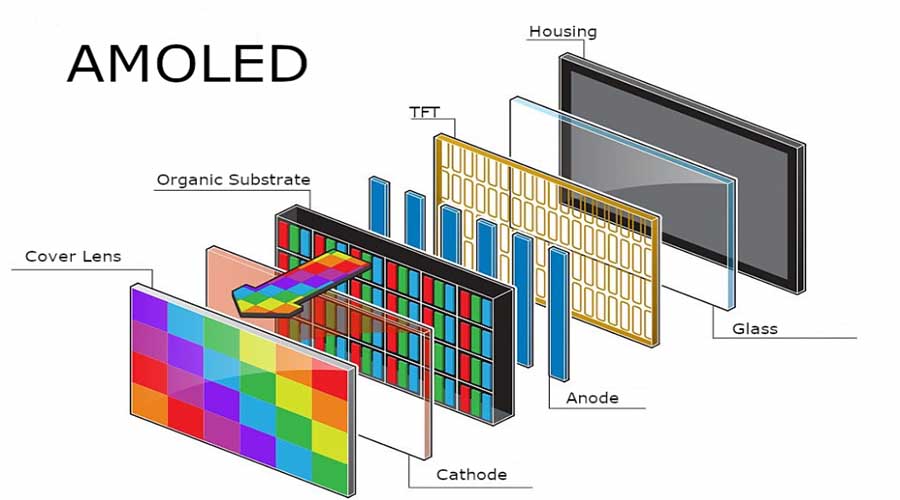
Unlike LCDs, OLED emits its own light per pixel, eliminating backlights. This reduces thickness, improves contrast (true blacks), and allows for flexible or transparent substrates. Modern OLEDs incorporate LTPO backplanes, advanced encapsulation, and AI-based compensation to mitigate burn-in. Combined, these qualities make OLED the most human-centric display medium ever created.
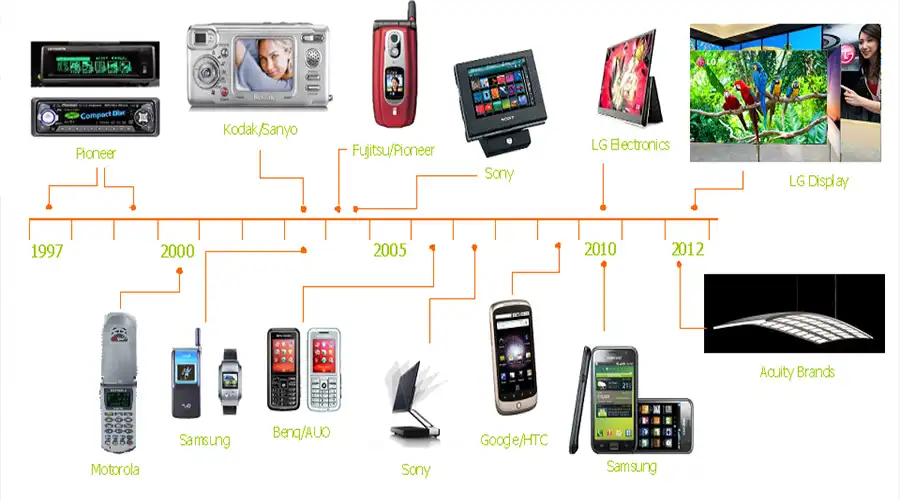
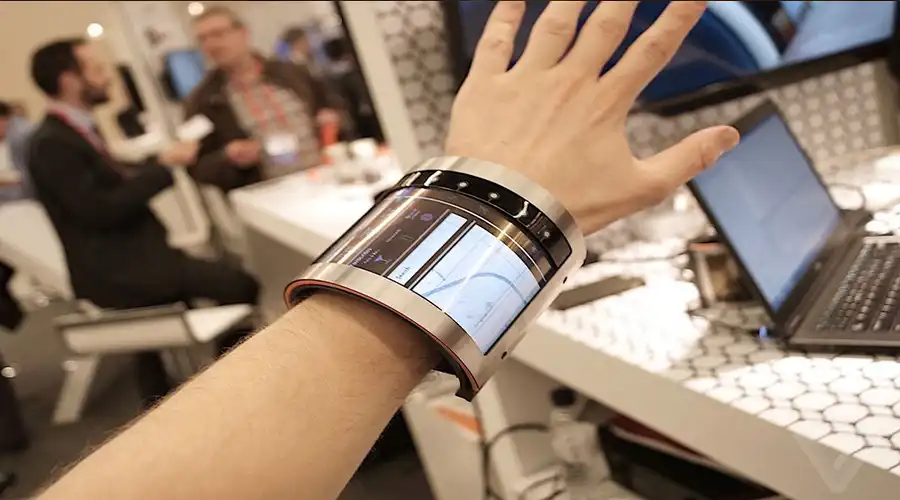
2. OLED in Wearables
Smartwatches and fitness trackers were the earliest mass-market validation for OLED. The curved, vivid, low-power displays enabled ergonomically sound devices with superb readability in outdoor settings. The flexibility and color precision of OLED perfectly fit wrist-mounted or textile-integrated use cases.
By 2025, wearable OLEDs have advanced to micro-thin modules embedded into medical sensors and skin patches. Real-time glucose, hydration, or oxygen monitoring now occurs on surfaces that breathe and flex. These displays can even remain partially transparent—showing vital data on the skin without blocking natural tone.
“OLED wearables exemplify where technology meets biology — responsive, adaptive, and almost invisible.” – Dr. Aiko Sato, Biotech Lab Tokyo

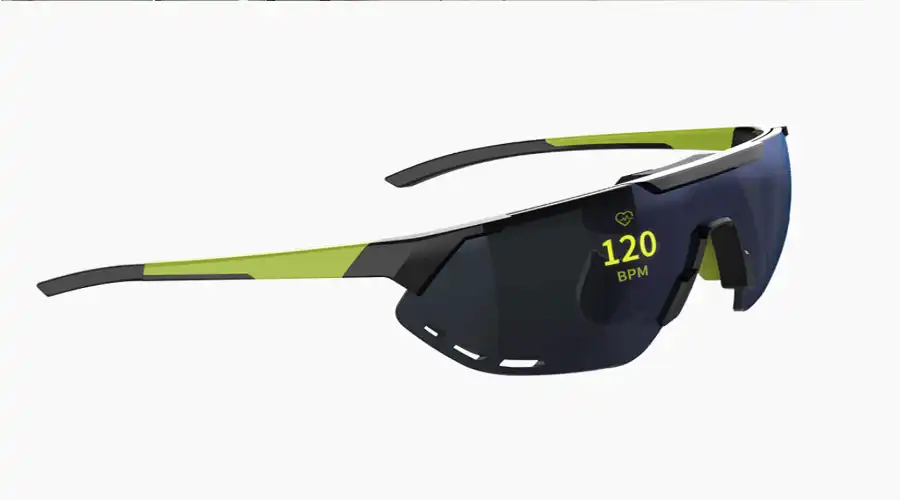
3. The Leap to AR Glasses
The 2025 AR revolution owes its realism to OLED-on-silicon (OLEDoS) technology — microdisplays with pixel densities exceeding 4000 PPI. These panels fit inside lenses mere millimeters thick, projecting crisp overlays across the user’s natural field of view. Unlike laser or LCD-based HUDs, OLED’s instantaneous contrast and deep black blending let virtual elements coexist believably with real-world objects.
The consumer market now enjoys lightweight AR eyewear capable of persistent data overlays — navigation arrows on roads, live captions in conversations, or contextual translation in travel. OLED’s self-luminous structure ensures privacy, rendering images visible only to the wearer’s pupils. Industries from surgery to engineering use similar optics for precision overlays and low-latency collaboration.

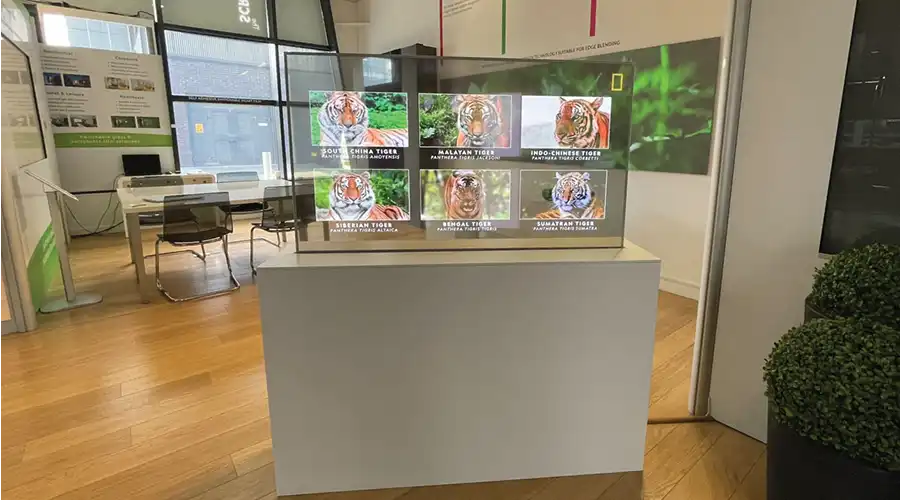
4. Transparency and Flexibility
Perhaps the hallmark of OLED design freedom lies in its material versatility. Transparent and foldable OLEDs now populate architecture, automotive dashboards, and appliances. Such displays deliver illumination and information without disturbing spatial design flows. Modern transparent OLEDs achieve over 70% light transmission, allowing unobstructed visibility behind onscreen graphics.
In industrial and vehicular design, OLED’s bendability permits dashboards and control panels to wrap around surfaces smoothly. Future concept vehicles already incorporate flexible OLED skins capable of displaying exterior signals, branding, or warnings directly on body panels. This is technology becoming texture—functional and aesthetic at once.

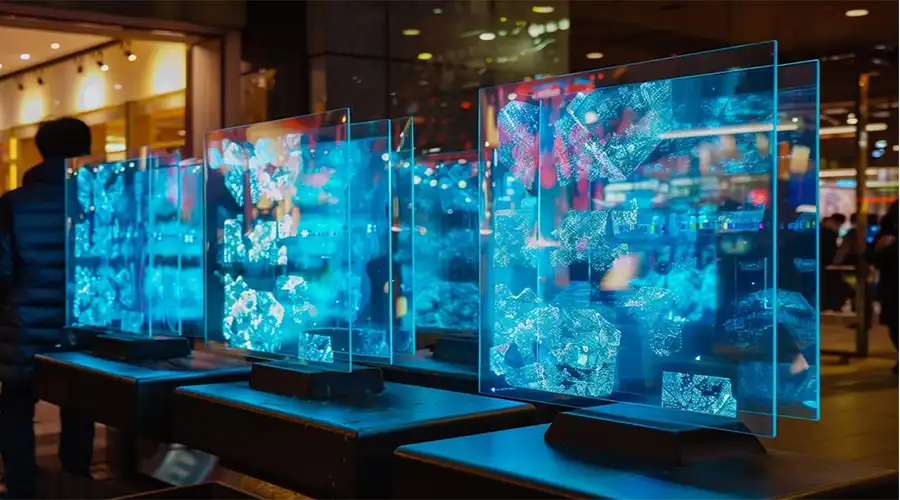
5. The Visual Aesthetics of OLED
OLED’s impact on human emotion is profound. The infinite contrast ratio—true black against vibrant hues—mimics the way our eyes perceive natural light. Designers leverage pixel-level dimming to craft interfaces that breathe rather than blink. Notice how smartwatch notifications fade in softly, or AR arrows ghost into view as if whispering directions rather than commanding attention.
In Entertainment and Storytelling
The entertainment sector harnesses OLED for cinematic AR installations, where displays serve as dynamic surfaces of storytelling. The low-latency response and near-zero motion blur elevate immersive gaming and virtual production environments, blurring boundaries between physical and digital frame rates. Artists now paint light directly — pixels as brushstrokes of imagination.

6. Sustainability and Efficiency
OLED’s environmental footprint continues to shrink as printable organic inks and recyclable substrates replace energy-intensive vacuum deposition. Without backlights and with reduced rare-metal dependency, OLED devices consume less power. Companies are exploring bio-based polymers for light-emitting layers and graphene for transparent electrodes, fostering a circular-material economy.
Meanwhile, energy management technologies—adaptive refresh, motion-triggered lighting, and deep sleep states—extend device lifecycles. Flexible OLED films also support modular repairability, reducing electronic waste. Sustainability is no longer a marketing term; it's embedded in OLED’s DNA.
7. The Future – Toward Ambient Intelligence
The “post-screen” era is dawning. OLED displays are merging into material environments, enabling ambient intelligence. Walls, mirrors, and objects now carry light-emissive logic. OLED’s adaptability transforms every surface into a contextual interface—subtle, human-centered, and reactive to presence.
Research accelerates on Quantum-dot OLED (QOLED)Emicro-OLED fotoniciche regolano luminosità e spettro in base ai singoli occhi. Immaginate occhiali che si bilanciano automaticamente in base alle temperature di colore circostanti, o livelli di realtà aumentata che regolano dinamicamente la profondità di campo. Man mano che i confini visivi si dissolvono, l'OLED diventa non solo uno schermo, ma il mezzo di percezione stesso.
"Il destino dell'OLED è l'invisibilità: quando visualizzazione e realtà diventano indistinguibili." – Hiroshi Tanaka, NEXVision Labs

Domande frequenti
Quali sono le cause del burn-in degli OLED e come si può prevenire?
Il burn-in si verifica quando i materiali organici si degradano in modo non uniforme a causa della visualizzazione prolungata di immagini statiche. Per prevenirlo, è possibile utilizzare la funzione di oscuramento automatico, il timeout dello schermo, lo spostamento dei pixel, l'oscuramento dei loghi e l'evitare livelli di luminosità elevati per i contenuti statici.
I display OLED sono adatti per ambienti esterni o ad alta luminosità?
Gli OLED standard hanno difficoltà a resistere alla luce solare diretta. Tuttavia, i modelli 2025 presentano una luminosità aumentata e rivestimenti antiriflesso. Gli OLED specializzati ad alta risoluzione stanno colmando il divario con i Mini-LED per la visibilità diurna.
Quanto durano in genere i display OLED?
La durata di vita dei moderni OLED varia dalle 50.000 alle 100.000 ore prima di raggiungere la metà della luminosità (L50). I nuovi materiali a emissione blu prolungano ulteriormente questa durata, rendendola paragonabile a quella degli schermi LCD.
Gli OLED possono essere utilizzati per display sempre accesi?
Sì, la tecnologia OLED è ideale per l'AOD (Always-On Display) perché solo i pixel accesi consumano energia. L'utilizzo di una bassa luminosità e la visualizzazione periodica dei contenuti riducono al minimo l'invecchiamento differenziale.
Qual è la differenza tra AMOLED e PMOLED?
AMOLED utilizza uno strato TFT a matrice attiva per un'alta risoluzione e un aggiornamento rapido, perfetto per smartphone e dispositivi indossabili. PMOLED gestisce passivamente righe e colonne di pixel, ideale per indicatori piccoli o statici con costi inferiori.
I display OLED supportano la funzionalità touch?
Latest articles
-
Perché gli AMOLED da 1-2" sono fondamentali per AR/XR nel 2025
Perché i display AMOLED da 1-2 pollici stanno diventando essenziali nel boom AR/XR (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Display LCD a barra allungata per la vendita al dettaglio: aumenta le vendite e il coinvolgimento nei supermercati
Scopri come i display LCD a barre allungate migliorano il marketing sugli scaffali dei supermercati, aumentano le vendite e riducono
-
Soluzioni LCD allungate per ristoranti e strutture ricettive
Gli LCD allungati offrono display eleganti e ad alta luminosità, perfetti per i menu dei ristoranti e per i servizi di ospitalità
Prodotti consigliati
-
2.0-Inch Square HD OLED AMOLED Module 460 X 460 QSPI Interface
Modulo display AMOLED da 2,0" con interfaccia QSPI per sistemi industriali e integratiSpecifiche principali
-
Display OLED da 2,06 pollici | Risoluzione 410×502 | 600 nit | Schermo SPI
Il modulo display AMOLED da 2,06 pollici è progettato specificamente per ambienti industriali difficili, dotato
-
Modulo display AMOLED da 7,0 pollici | Alta luminosità 1280×800
Il modulo display AMOLED da 7,0 pollici è una soluzione di visualizzazione ad alta risoluzione e ampia progettata per
-
Display AMOLED da 8,0 pollici 2480×1860 MIPI DSI-BROWNOPTO
Modulo AMOLED FHD da 8,0" con risoluzione 2480×1860, interfaccia MIPI DSI e touch SPI. Ideale per l'industria
-
Display AMOLED da 6,0 pollici 1080×2160 MIPI - BR600108-A1
Modulo AMOLED FHD+ da 6,0" con risoluzione 1080×2160, interfaccia MIPI a 4 corsie, luminosità di 360 nit. Ideale
-
Modulo display AMOLED da 5,5 pollici – Pannello LTPS MIPI ad alta risoluzione
Pagina del prodotto del modulo AMOLED da 5,5 pollici Il modulo display AMOLED da 5,5 pollici