In the rapidly evolving world of display technologies, TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) and SEI (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) stand out as pivotal innovations driving the global market. China, as a powerhouse in flat panel display (FPD) manufacturing, has become a leader in producing TFTESEI panels. This article delves into the intricacies of TFTESEI technologies, exploring their applications, key manufacturers, and factory landscapes in China. Based on extensive open-source intelligence (OSINT) research, we'll cover historical developments, capacities, and future trends to provide a detailed overview for enthusiasts, investors, and industry professionals.
Whether you're researching TFT LCD screens for consumer electronics or the latest SEI advancements for smartphones, this guide offers in-depth insights. Stay tuned as we break down the ecosystem of China's TFTESEI panel factories. We'll examine how these technologies are shaping everything from everyday gadgets to high-end automotive displays, with a focus on production scales that make China a global hub. The industry's growth is fueled by massive investments, technological breakthroughs, and a competitive landscape that continues to innovate.
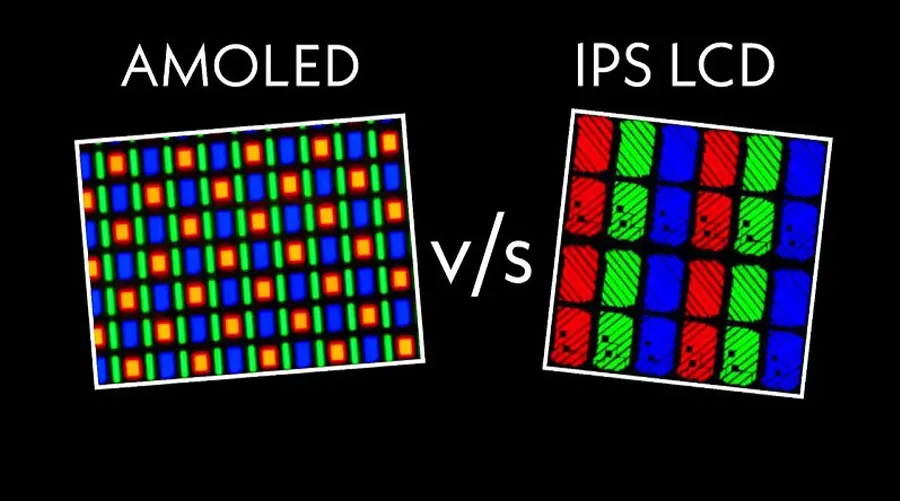
The Fundamentals of TFT and OLED Technologies
Before diving into China's manufacturing landscape, it's essential to understand the core differences and synergies between TFTESEI. These technologies form the backbone of modern displays, each with unique strengths that cater to different market needs. In this section, we'll explore their technical foundations, advantages, and how they complement each other in hybrid applications.
What is TFT Technology?
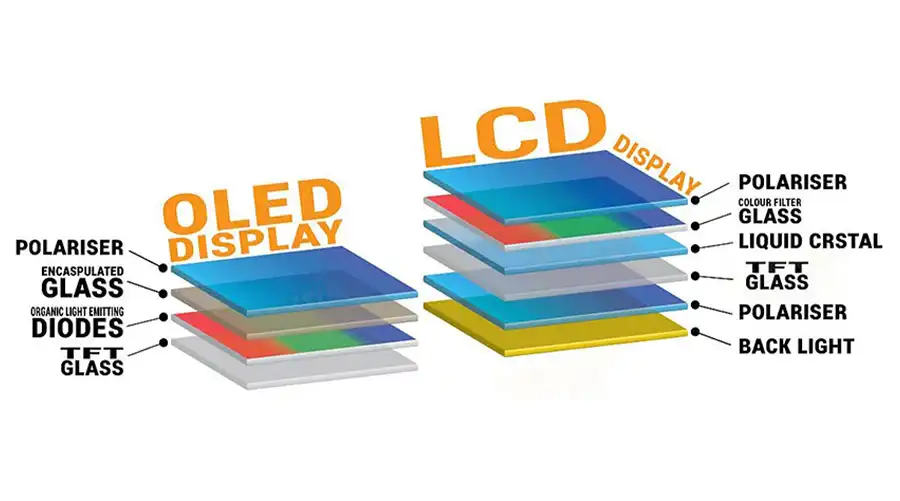
TFT technology refers to Thin-Film Transistor active-matrix displays, which are widely used in LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panels. TFT acts as a switch to control individual pixels, enabling high-resolution images with excellent color accuracy. In China, TFT has been the backbone of large-scale production for TVs, monitors, and mobile devices. The technology relies on a thin film of transistors deposited on a glass substrate, allowing for precise control over liquid crystals that modulate light from a backlight source.
TFT panels come in various generations (e.g., G8.5, G10.5), where higher generations mean larger glass substrates and greater efficiency. China's adoption of TFT has led to massive production capacities, with factories optimizing for a-Si (amorphous silicon) and LTPS (Low-Temperature Poly-Silicon) variants. For example, a-Si TFT is cost-effective for large TVs, while LTPS TFT offers higher electron mobility for mobile screens. Advantages include affordability, scalability, and energy efficiency in backlit setups, though it lacks the self-emissive properties of other technologies.
The evolution of TFT in China dates back to the early 2000s, with rapid advancements in the 2010s. Factories have incorporated copper wiring and oxide semiconductors to enhance performance, reducing power consumption and improving refresh rates. This makes TFT ideal for applications like laptops and industrial monitors, where reliability and cost are paramount.
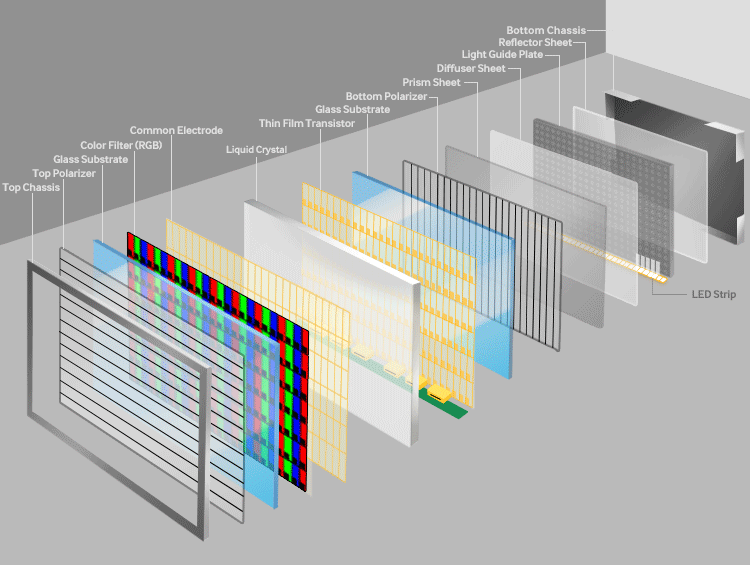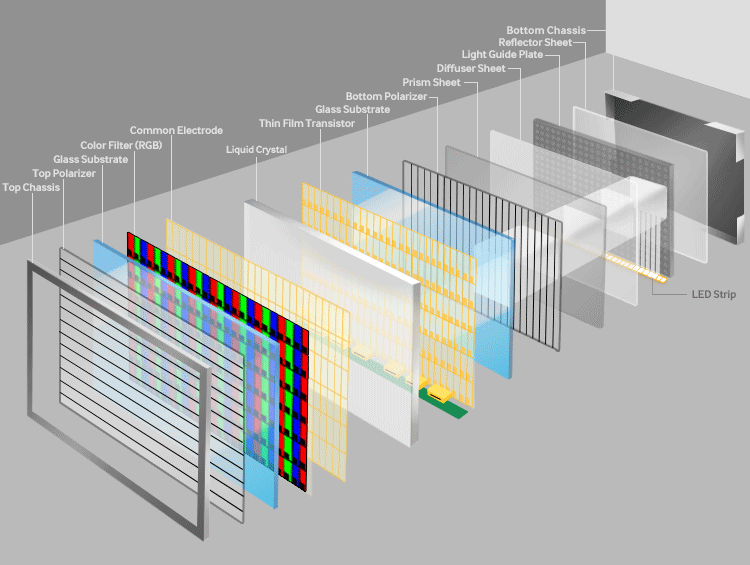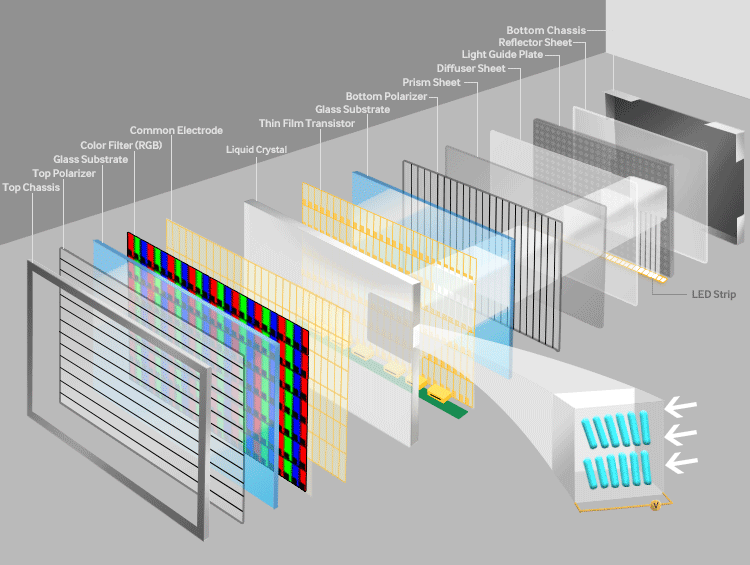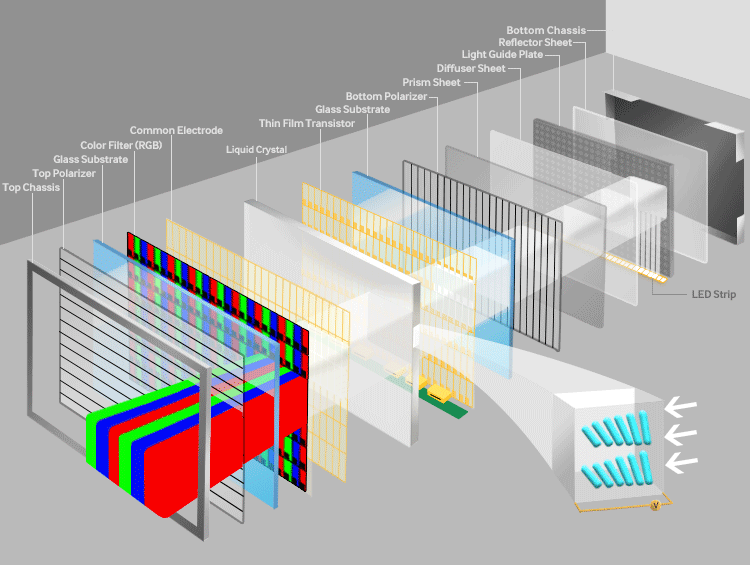
Capire i display OLED
SEI technology, on the other hand, uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Unlike TFT LCD, which requires backlighting, SEI panels are self-emissive, offering superior contrast, deeper blacks, and flexibility for curved or foldable screens. Subtypes like AMOLED (Active-Matrix OLED) and WOLED (White OLED) dominate the market, with AMOLED being particularly popular for its vibrant colors and thin profiles.
In China, SEI production has surged, particularly for smartphones and wearables, with innovations in LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide) for energy efficiency. SEI pixels light up individually, eliminating the need for backlights and enabling true blacks by turning off pixels completely. This results in infinite contrast ratios and wider viewing angles, making SEI perfect for premium TVs and mobile devices. However, challenges include burn-in risks and higher manufacturing costs due to organic material degradation.
China's SEI journey began in the mid-2010s, with factories scaling up from small pilots to full production lines. Technologies like vapor deposition and inkjet printing are key, allowing for flexible substrates that bend without breaking. The self-emissive nature also supports thinner designs, revolutionizing wearables and automotive dashboards.
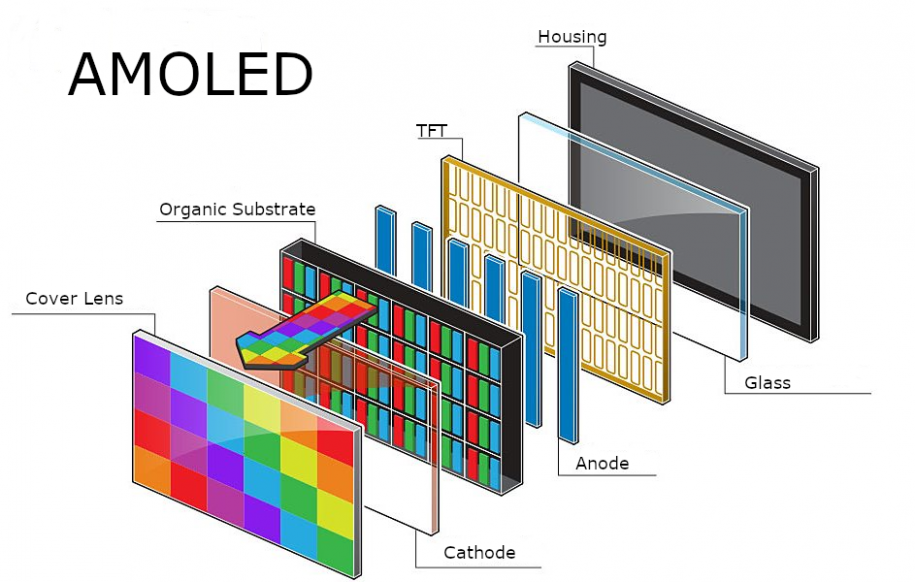
Synergies Between TFT and OLED
Many modern displays combine TFT backplanes with SEI emitters, creating hybrid solutions like LTPO-OLED. This integration enhances performance, and China's factories are at the forefront of scaling these technologies. TFTfornisce la matrice di transistor stabile, mentreSEIgestisce l'emissione luminosa, dando vita a display efficienti dal punto di vista energetico e visivamente sorprendenti.
Indirizzo ibridiTFTlimitazioni della retroilluminazione eSEIproblemi di longevità, con LTPO che riduce il consumo energetico fino al 30% in scenari con frequenza di aggiornamento variabile. In Cina, questa sinergia è evidente nelle fabbriche che producono pannelli per marchi globali, combinando efficienza dei costiTFTscalando conSEICaratteristiche premium. Con il passare del tempo, ci aspettiamo ulteriori innovazioni, come i sistemi ibridi Micro-LED, che uniscono ulteriormente queste tecnologie.
Panorama della produzione di TFT e OLED in Cina
L'industria cinese degli FPD è dominata da giganti come BOE, TCL CSOT e Visionox, con stabilimenti in città come Pechino, Shenzhen e Hefei. Le sezioni seguenti descrivono in dettaglio i principali attori e le loroTFTESEIstrutture, tratte da un elenco del 2023 compilato dall'analista di settore Li Chase. Questo panorama è caratterizzato da ingenti investimenti, rapide espansioni e un focus sulle linee ad alta generazione per soddisfare la domanda globale.
Principali fabbriche e capacità di pannelli TFT
China's TFTLa produzione si concentra su linee ad alta generazione per una produzione economicamente vantaggiosa. Ecco una ripartizione delle principaliTFTfabbriche, compresa una tabella riepilogativa delle capacità principali.
Il predominio di BOE nella produzione di TFT LCD
BOE (Beijing Orient Electronics) gestisce piùTFTfabbriche in tutta la Cina. Ad esempio, la fabbrica B17 di Wuhan è una G10.5TFTLinea a-Si-LCD con una capacità di 180.000 substrati al mese. La costruzione è iniziata nel 2016 con un investimento di 460 miliardi di CNY e, dopo gli ampliamenti, raggiungerà la piena produzione entro il 2021. Questa fabbrica integra processi interamente in rame, consentendo la produzione di grandi volumi per TV di grandi dimensioni.
A Hefei, il B9 della BOE è un altro G10.5TFTlinea, a partire da 90K/m e in espansione a 155K/m attraverso gli aggiornamenti nel 2017 e nel 2021. QuestiTFTGli stabilimenti puntano sui processi in rame (Cu) per una migliore conduttività, supportando i televisori ad altissima definizione. Il B3 di BOE a Hefei (LCD a-Si G6, 86K/m) diversifica ulteriormente il proprio portfolio, con trasformazioni dai processi in alluminio a quelli in argento che migliorano l'integrazione dei sensori.
BOETFTL'ecosistema comprende anche linee innovative come la B5 di Hefei, che ospita i piloti WOLED e IJP-OLED insieme ai tradizionaliTFTLCD. Gli sviluppi storici mostrano che BOE investe molto in ricerca e sviluppo, con progetti che incorporano strutture ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) per una produzione sostenibile.

Innovazioni TFT di TCL CSOT
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology (CSOT) eccelle inTFTCon stabilimenti come T6 e T7 a Shenzhen, entrambi con linee LCD a-Si G10.5 a 90.000/m ciascuna. Annunciati nel 2016 con investimenti per 427 miliardi di CNY, questi impianti hanno raggiunto la produzione di massa entro il 2019-2021, concentrandosi sui TV LCD ultra-large.
A Guangzhou, T9 è un G8.6TFTFabbrica di a-Si-LCD con capacità di 180K/m, focalizzata sui display IT. CSOTTFTLe linee integrano il taglio MMG (Multi-Model Glass) avanzato per l'efficienza, con espansioni previste per aumentare ulteriormente la capacità. I loro T1 e T2 a Shenzhen (G8.5, 160K/m ciascuno) evidenziano i primiTFTsuccessi, evolvendosi dai progetti iniziali da 100K/m attraverso molteplici aggiornamenti.
Per illustrare le capacità, ecco una tabella delle principaliTFTfabbriche in Cina:
| Produttore | Fabbrica | Generazione | Technology | Capacità (K/m) | Posizione | Investimento (miliardi di CNY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOE | B17 | G10.5 | LCD TFT a-Si | 180 | Wuhan | 460 |
| BOE | B9 | G10.5 | LCD TFT a-Si | 155 | Hefei | 400 |
| TCL CSOT | T6 | G10.5 | LCD TFT a-Si | 90 | Shenzhen | 427 |
| TCL CSOT | T9 | G8.6 | LCD TFT a-Si | 180 | Canton | 350 |
| HKC | H5 | G8.6 | LCD TFT a-Si | 200 | Liuyang | 320 |
| Tianma | TM19 | G8.6 | LCD TFT a-Si/IGZO | 120 | Xiamen | 330 |
Questa tabella evidenzia la scala diTFTproduzione, con investimenti per un totale di migliaia di miliardi di CNY in queste strutture.

Progressi OLED e attori chiave
SEILa produzione in Cina è cresciuta esponenzialmente, con pannelli flessibili e ad alta frequenza di aggiornamento in testa. Le fabbriche stanno spingendo i limiti nei design AMOLED e ibridi.
Rete di fabbriche OLED di Visionox
Visionox è leader inSEI, con stabilimenti come V3 a Hefei (G6 LTPO-OLED, 30K/m). Annunciato nel 2018 con un fatturato di 440 miliardi di CNY, ha raggiunto la produzione di massa nel 2021, incorporando aggiornamenti al rame per frequenze di aggiornamento più elevate. Le espansioni del 2023 hanno aggiunto apparecchiature per 4525 milioni di pezzi/anno, concentrandosi sui dispositivi indossabili a basso consumo.
Il V2 in Gu'an è un altro G6SEIlinea a 15K/m (espandibile a 30K/m), specializzata in AMOLED flessibili. Vistar di Visionox a Chengdu si concentra su ibridi Micro-LED conSEI, con una capacità produttiva di 460 wafer al mese nella Fase 1 e di 540 wafer al mese nella Fase 2. Queste strutture integrano linee di produzione di moduli come la M4 di Guangzhou (5.222 milioni di moduli AMOLED all'anno), supportando le esportazioni globali.
L'approccio di Visionox include centri di ricerca e sviluppo a Kunshan, con linee pilota per tecnologie avanzateSEImateriali, garantendo un'innovazione continua.

Linee di produzione OLED di Tianma
Tianma Microelectronics gestisce TM17 a Wuhan (G6 LTPO-OLED, 37,5K/m), evolvendosi dai piani LTPS-LCD del 2014 a quelli completiSEIentro il 2015. Gli investimenti hanno raggiunto un totale di 265 miliardi di CNY, con espansioni che hanno aggiunto capacità flessibili attraverso le apparecchiature di evaporazione Ulvac.
Il TM18 di Xiamen è un G6 LTPO-OLED a 48K/m, annunciato nel 2018 con un budget di 480 miliardi di CNY, destinato agli smartphone e suddiviso in fasi per un incremento graduale. Il TM15 di Shanghai (G5.5 AMOLED, 30K/m) funge da backend per schermi rigidi e flessibili.SEI, con capacità ampliate da 15K/m nel 2016 per includere esposizioni di auto.

Ecco una tabella riassuntiva della chiaveSEIfabbriche:
| Produttore | Fabbrica | Generazione | Technology | Capacità (K/m) | Posizione | Caratteristiche principali |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visionox | Versione 3 | G6 | Schermo OLED LTPO | 30 | Hefei | Tecnologia Cu per un elevato refresh |
| Visionox | Versione 2 | G6 | AMOLED | 15 (espandibile a 30) | SÌ | Messa a fuoco flessibile |
| Tianma | TM17 | G6 | Schermo OLED LTPO | 37.5 | Wuhan | Evoluto da LCD |
| Tianma | TM18 | G6 | Schermo OLED LTPO | 48 | Xiamen | Orientato allo smartphone |
| BOE | B7 | G6 | Schermo OLED LTPO | 48 | Chengdu | Integrazione touch |
| E Hui | EDOG6 | G6 | AMOLED | 45 | Shanghai | Transizione da rigida a flessibile |
Questa tabella sottolinea la CinaSEIpredominio, con particolare attenzione alla flessibilità e all'efficienza.
Integrazione di TFT e OLED nei display ibridi
La fusione diTFTESEILe tecnologie stanno trasformando i display, con la Cina leader nelle innovazioni ibride. Questa sezione esplora come queste tecnologie si fondono per creare prodotti di qualità superiore, rispondendo alle richieste del mercato di prestazioni migliori e consumi energetici ridotti.
LTPO-OLED: una svolta ibrida TFT-OLED
LTPO (ossido policristallino a bassa temperatura) combinaTFT backplanes with SEIemettitori per frequenze di aggiornamento variabili, riducendo il consumo energetico. Il B7 di BOE a Chengdu (G6 LTPO-OLED, 48K/m) ne è un esempio, avviato nel 2015 con un investimento di 465 miliardi di CNY e con aggiornamenti per l'integrazione touch nel 2018-2020. La costruzione in due fasi dello stabilimento (24K/m ciascuna) ha incorporato tecnologie di incapsulamento e COE.
Analogamente, il T4 di CSOT a Wuhan (G6 LTPO-OLED, 48K/m) è stato avviato nel 2017, espandendosi da 45K/m per supportare dispositivi di fascia alta come quelli di Apple. Investimenti per 393 miliardi di CNY hanno incluso linee di ricerca e sviluppo per i test AMOLED. Questi ibridi sfruttanoTFTla stabilità conSEIproprietà emissive, raggiungendo frequenze di aggiornamento fino a 120 Hz, preservando al contempo la durata della batteria.
In pratica, i pannelli LTPO-OLED vengono utilizzati negli smartphone di punta, doveTFTgestisce la commutazione dei pixel eSEIFornisce colori vividi. Le fabbriche cinesi hanno rapidamente adottato questa tecnologia, con rendimenti migliorati grazie alle ottimizzazioni basate su OSINT.
Sfide nel ridimensionamento TFT e OLED
ScalabilitàTFTESEIcomporta ostacoli come i tassi di rendimento e i costi dei materiali. PerTFT, le linee più vecchie come la B4 della BOE (G8.5, 150K/m) affrontano transizioni verso processi di ossido, con espansioni da 90K/m nel 2009 ai livelli attuali tramite aggiornamenti di Cu. InSEI, le apparecchiature di evaporazione (ad esempio, Tokki) limitano le capacità, come si vede nel TM15 di Tianma (G5.5 AMOLED, 30K/m), che è passato da rigido a flessibile nel 2020.
La Cina affronta queste problematiche attraverso ingenti investimenti e supporto governativo, con fabbriche come l'H5 di HKC (G8.6 a-Si-TFT, 200K/m) che ottimizzano la produzione di LCD ad alto volume tramite obiettivi MTD e ricerca e sviluppo sugli ossidi. Le sfide legate alla sostenibilità, come la gestione dei rifiuti, vengono mitigate grazie alle integrazioni ESG.
Tendenze future nelle tecnologie TFT e OLED
Guardando al futuro, la CinaTFTESEII settori puntano all'integrazione di Micro-LED e QLED. Il BMOT di BOE a Kunming si concentra sui Micro-OLED (linee da 8/12 pollici) per AR/VR, con una capacità di 523 milioni di pezzi/anno introdotta gradualmente a partire dal 2019. Vistar di Visionox spinge sui Mini/Micro-LED, passando da 460 wafer/mese nel 2020 a 540 nella Fase 2.
Le tendenze emergenti includono la stampa a getto d'inchiostroSEI(IJP-OLED) nei miglioramenti B5 e quantum-dot di BOE per una gamma cromatica più ampia. Con la crescente domanda globale, le fabbriche cinesi stanno investendo nella produzione basata sull'intelligenza artificiale per aumentare la produttività e ridurre i costi, posizionando il Paese come epicentro dell'innovazione dei display.

Casi di studio dettagliati di fabbriche TFT e OLED
Per approfondire ulteriormente, esaminiamo nel dettaglio alcune fabbriche specifiche, evidenziandone la storia, le tecnologie e l'impatto.
B17 di BOE: l'apice dell'ingegneria TFT LCD
Il B17 della BOE a Wuhan esemplifica la diffusione su larga scalaTFTProduzione. Questa linea di produzione di pannelli LCD a-Si G10.5 è partita da 120.000 m/m nel 2016 (con un investimento di 460 miliardi di CNY), con l'obiettivo di raggiungere i 180.000 m/m entro il 2021 grazie a upgrade per 37 miliardi di CNY. Le caratteristiche principali includono processi completi al rame e ottimizzazione MMG, per la produzione di pannelli per TV da 65 a 85 pollici. La struttura dello stabilimento include centri di riciclaggio delle risorse e stoccaggio di prodotti chimici per garantire l'efficienza operativa.
Tappe storiche: pianificazione iniziale nel 2016, prima espansione nel 2020 per l'ottimizzazione della pipeline e un importante aumento della capacità nel 2021 con nuove macchine di esposizione. Il successo di B17 ha contribuito alla quota di mercato del 43% di BOE nei grandiTFT LCDpannelli, esportati in oltre 100 paesi.
Visionox V3: flessibilità OLED avanzata
La V3 di Visionox a Hefei è una fabbrica G6 LTPO-OLED con una capacità di 30K/m, in cui sono stati investiti 440 miliardi di CNY dal 2018. Gli aggiornamenti del 2020 (16 miliardi di CNY) hanno migliorato le frequenze di aggiornamento, con modifiche tecnologiche al Cu nel 2023 (50 milioni di CNY) che puntano a 4525 milioni di pezzi/anno, tra cui 1500 milioni di AMOLED a basso aggiornamento e 3025 milioni di dispositivi indossabili.
Lo stabilimento integra linee di produzione di moduli (M3/M4), producendo 25,99 milioni di moduli AMOLED all'anno. Le sfide includono miglioramenti della resa, ma l'approccio OSINT di Visionox lo ha posizionato come un'azienda flessibile.SEIleader nella fornitura di pannelli per telefoni pieghevoli e smartwatch.
Tianma TM19: TFT per IT e Automotive
Il TM19 di Tianma a Xiamen è una linea di LCD TFT a-Si/IGZO G8.6 (120K/m), annunciata nel 2022 con un budget di 330 miliardi di CNY. Suddivisa in fasi (Fase 1 da 70K/m, Fase 2 da 50K/m), si concentra su display per auto e pannelli IT, combinando a-Si (80K/m) e IGZO (40K/m) per una maggiore versatilità. Le espansioni enfatizzano la riduzione delle maschere per rendimenti più elevati, in linea con le esigenze globali.TFTrichieste nel settore automobilistico.
L'integrazione di IGZO nel TM19 migliora la trasmittanza, rendendolo adatto ai monitor ad alta risoluzione. Con una domanda del settore automobilistico in crescita del 20% annuo, questo stabilimento è fondamentale per l'espansione di Tianma.
Impatto economico e influenza globale dell'industria cinese dei TFT e OLED
China's TFTESEII settori contribuiscono in modo significativo all'economia, con le esportazioni che trainano la crescita. Il settore impiega milioni di persone e genera migliaia di miliardi di fatturato, alimentato da sussidi e incentivi alla ricerca e sviluppo.
Quota di mercato e investimenti in TFT
La Cina detiene oltre il 50% del mercato globaleTFT LCDcapacità produttiva, guidata da BOE e CSOT. Gli investimenti totali superano i trilioni di CNY, con stabilimenti come l'H4 di Hong Kong (G8.6 TFT, 210.000 m/m) che sono passati dai 120.000 m/m del 2018 per soddisfare la domanda IT. Le esportazioni verso Europa e Stati Uniti rappresentano il 40% della produzione, con un conseguente incremento del PIL.
Crescita OLED e dinamiche di esportazione
SEILe spedizioni dalla Cina sono aumentate del 30% nel 2023, con Visionox e Tianma che esportano verso marchi come Samsung e Apple. Fabbriche come EDOG6 (G6 AMOLED di Everd, 45.000 m²) evidenziano la transizione da rigido a flessibile, con espansioni che hanno aggiunto 15.000 m² nel 2021. L'influenza globale è evidente nelle catene di fornitura per i dispositivi premium.
Sostenibilità nella produzione di TFT e OLED
Le considerazioni ambientali sono fondamentali, con integrazioni ESG nei layout (ad esempio, i centri di riciclaggio dei rifiuti di BOE). La spinta della Cina verso il verdeTFTESEIla produzione è in linea con gli standard globali, riducendo le emissioni attraverso un riciclaggio avanzato e progetti a basso consumo energetico.

Conclusione: il futuro di TFT e OLED in Cina
China's TFTESEIle industrie sono pronte per una crescita esponenziale, combinando innovazione e scala. Dalla vasta BOETFTreti flessibili di VisionoxSEIOltre alle sue capacità, il panorama offre infinite opportunità. Con l'evoluzione di tecnologie come LTPO-OLED, è fondamentale rimanere informati tramite risorse come la Directory FPD 2023.
L'integrazione diTFTESEIguiderà i display di nuova generazione, con la Cina in testa grazie a enormi fabbriche e ricerca e sviluppo. Per gli investitori, il settore promette alti rendimenti grazie alla crescente domanda. Cosa ne pensi?TFTcontroSEI? Condividilo nei commenti!
Latest articles
-
Perché gli AMOLED da 1-2" sono fondamentali per AR/XR nel 2025
Perché i display AMOLED da 1-2 pollici stanno diventando essenziali nel boom AR/XR (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Display LCD a barra allungata per la vendita al dettaglio: aumenta le vendite e il coinvolgimento nei supermercati
Scopri come i display LCD a barre allungate migliorano il marketing sugli scaffali dei supermercati, aumentano le vendite e riducono
-
Soluzioni LCD allungate per ristoranti e strutture ricettive
Gli LCD allungati offrono display eleganti e ad alta luminosità, perfetti per i menu dei ristoranti e per i servizi di ospitalità
Prodotti consigliati
-
LCD TFT ad alta risoluzione IPS da 3,5 pollici + interfaccia MIPI DSI
Progettato per condizioni di illuminazione difficili, questo schermo offre una visibilità eccezionale con elevata luminosità
-
LCD TFT IPS da 7 pollici con interfaccia LVDS
BR070800480AF-V1 | LCD IPS da 7" 800×480 | Alta luminosità 1000 nit | Interfaccia LVDS | Non-TouchEngine
-
Display TFT da 10,1 pollici per segnale HDMI con touch screen resistivo Dimensioni: 10,1" HDMI | 1024x600 P
Panoramica del modulo display HDMI BR101JII3650-A3 V.1Nome prodotto: Display HDMI BR101JII3650-A3 V.1
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Specifiche del prodotto: BRO392001ARisoluzione: 1080x1024Intervallo di tensione di funzionamento: 28VDimensioni dello schermo: 3,92
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Specifiche del prodotto: BRO601001AModalità di visualizzazione: AMOLED Dimensioni dello schermo (pollici): 6,01 Risoluzione: 1080x2
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Specifiche del prodotto: BRO548001ARisoluzione: 1080x1920Intervallo di tensione di funzionamento: 2,8VDimensioni dello schermo: 5,4