目次
1. Introduction to TFT and OLED
Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) and Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technologies are the cornerstones of modern display innovation. TFT-LCDs dominate the market for large-format screens like TVs and monitors, while OLEDs lead in high-end smartphones, wearables, and flexible displays. This article explores the science, manufacturing, and real-world applications of these technologies, leveraging insights from leading Chinese manufacturers such as BOE, CSOT, and Visionox.
Key Differences at a Glance
| 特徴 | TFT液晶 | あなたは |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight Required | Yes (LED/CCFL) | No (self-emissive) |
| コントラスト比 | ~500:1 | Up to 1,000,000:1 |
| 柔軟性 | Rigid panels | Flexible/foldable designs |
| 電力効率 | 適度 | High for dark content |
| 料金 | $15–$30/cm² | $30–$50/cm² |
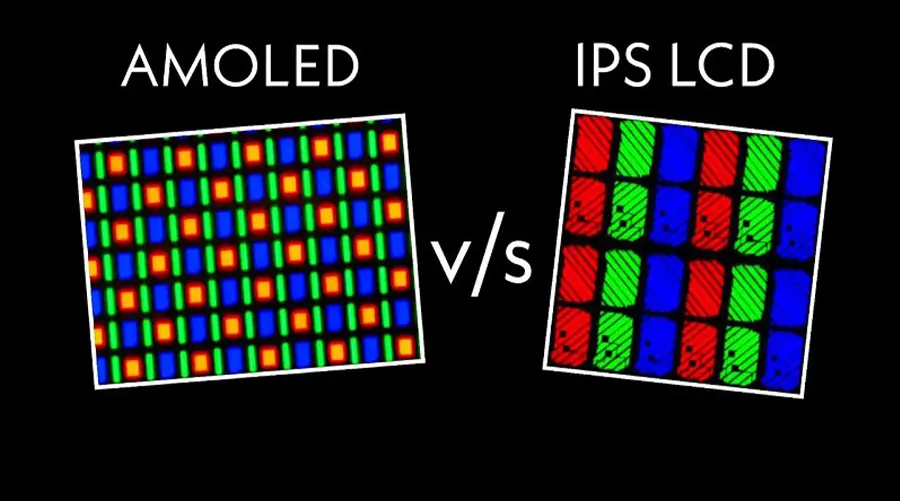
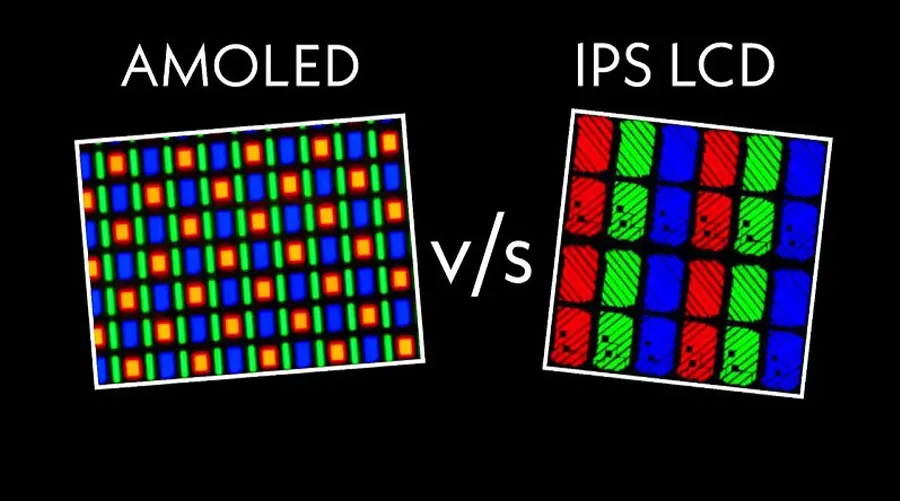
2. TFT Technology: Principles and Applications
What is TFT?
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) is a semiconductor technology used in LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) to control individual pixels. TFT-LCDs combine a liquid crystal layer with a backlight and a TFT array to produce high-resolution images.
Key Components of TFT-LCDs
-
Glass Substrates: Typically 700–1200mm in size, made of soda-lime or alkali-free glass.
-
Thin-Film Deposition: Layers of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), silicon nitride (SiN), and indium tin oxide (ITO) are deposited via chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
-
Photolithography: A multi-step process using 4–6 masks to pattern the TFT array.
-
Cell Assembly: Liquid crystals are sealed between two substrates with spacers to maintain uniform thickness.
Applications of TFT-LCDs
-
Television and Monitor Manufacturing: Dominates the TV market due to cost-effectiveness.
-
Industrial Automation: Used in medical devices (e.g., diagnostic equipment) and industrial control panels.
-
自動車用ディスプレイ: Integrated into car dashboards and infotainment systems.
Case Study: BOE's B7 Line
BOE’s B7 line in Chengdu produces 48K/M AMOLED panels using LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon) technology. This line achieves 1000 cd/m² brightness and supports 120Hz refresh rates, making it ideal for high-end smartphones.
3. OLED Technology: Advantages and Challenges
What is OLED?
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) uses organic compounds that emit light when electrically stimulated. Unlike TFT-LCDs, OLEDs do not require a backlight, enabling ultra-thin, flexible displays with perfect blacks and wide viewing angles.
OLEDの利点
-
高コントラスト比: Achieves 1,000,000:1 due to self-emissive pixels.
-
Flexibility: Enables foldable phones (e.g., Huawei Mate X3) and curved TVs.
-
エネルギー効率: Consumes less power for dark scenes compared to TFT-LCDs.
Challenges in OLED Manufacturing
-
Blue OLED Lifespan:青色の有機材料は赤色/緑色よりも早く劣化するため、高度なリン光発光体が必要になります。
-
生産コスト:真空蒸着プロセスは高価で、コストは 1cm² あたり 30 ~ 50 ドルに達します。
-
利回り率:TFT-LCD よりも低い (材料の欠陥により通常は 60~70%)。
ケーススタディ:VisionoxのV2ライン
Visionoxの広州V2ラインは、Cu(銅)およびLTPO(低温多結晶酸化物)技術を用いたAMOLED生産に特化しています。このラインはFDA認証の医療機器および車載ディスプレイに対応し、2023年までに月産3万枚の生産能力を実現します。
4. Manufacturing Processes of TFT and OLED
TFT-LCDの製造工程
-
ガラス基板の準備:洗浄と化学強化。
-
Thin-Film Deposition:SiO₂、SiN、および ITO の層。
-
Photolithography:ピクセル配列を定義する 4 ~ 6 個のマスク。
-
Cell Assembly:液晶注入・封止。
-
バックライト統合:照明用に LED または CCFL バックライトを追加しました。
OLEDの製造工程
-
基質の選択:柔軟性のためのガラスまたはポリマーフィルム。
-
真空蒸着:インクジェット印刷または熱蒸着により堆積された有機材料(例:TADF エミッター)。
-
カプセル化:水分の浸入を防ぐために薄膜バリアで密封します。
-
ドライバー IC 統合:TFT アレイはピクセルの明るさと色を制御します。
比較指標
| パラメータ | TFT液晶 | あなたは |
|---|---|---|
| 輝度 | 300~800 cd/m² | 500~1000 cd/m² |
| 応答時間 | 5~8ミリ秒 | 0.1ミリ秒 |
| 消費電力 | 3~5 W(10インチ画面) | 2~4 W(10インチ画面) |
| 利回り率 | ~75% | ~60% |
5. Leading Factories and Case Studies
BOEのB1ライン(北京)
プロジェクト:LCD バックライト用のミニ LED 統合。
結果:9K/M ミニ LED 変換により 100K/M TFT-LCD 容量を達成し、バックライト効率が 30% 向上しました。
CSOTのT4ライン(武漢)
集中:車載ディスプレイ向けAMOLED生産。
容量:48K/M、1000 cd/m²の明るさ。
テクノロジー:導電性を向上させるためにCuベースのTFT回路を使用しています。
VisionoxのV3ライン(成都)
革新:インクジェット技術を使用して印刷された OLED。
コスト削減:大量市場への導入を目指し、材料の無駄を40%削減します。
6. TFT vs OLED: A Detailed Comparison
パフォーマンスメトリック
| 特徴 | TFT液晶 | あなたは |
|---|---|---|
| 色の正確さ | わずかに低い(8ビット) | スーペリア(10ビット) |
| 視野角 | 120–140° | 170°+ |
| リフレッシュレート | 60~120Hz | 60~120Hz |
| 耐久性 | 寿命が延びる | 焼き付きやすい |
市場シェア(2023年)
TFT液晶:世界のディスプレイ出荷量の65%(テレビ、モニターに使用)。
あなたは:出荷の35%はスマートフォンとウェアラブルに集中しています。

7. Future Trends and Innovations
マイクロLEDディスプレイ
BOEのB1ライン:LCD用ミニLEDバックライトを生産しており、年間生産量20,000m²を達成しています。
サムスンのQD-OLED:量子ドットと OLED を組み合わせて明るさを向上します。
AMOLED用LTPO
CSOTのT6ライン:120Hz のリフレッシュ レートと動的なフレーム レート調整を実現する LTPO (低温多結晶酸化物) を実装します。
印刷型OLED
Visionox の Vistar ライン:コストを削減し、生産規模を拡大するためにインクジェット印刷を試みます。
8. FAQs About TFT and OLED
Q1: a-Si TFT と LTPS TFT の違いは何ですか?
a-Si(アモルファスシリコン):大型パネル(テレビなど)にコスト効率が優れています。
LTPS(低温多結晶シリコン):小型で高解像度のディスプレイ (例: スマートフォン) 向けの高い電子移動度。
Q2: OLED は TFT-LCD よりもなぜ高価なのですか?
真空蒸着:有機材料を扱う複雑でコストのかかるプロセス。
材料費:リン光発光体と封止材料により経費が増加します。
Q3: Cu プロセスは OLED のパフォーマンスをどのように向上させるのでしょうか?
TFT 回路のアルミニウム (Al) を銅 (Cu) に置き換えることで、高リフレッシュ レート ディスプレイの導電性と安定性が向上します。
最新記事
-
2025年のAR/XRにおいて1~2インチAMOLEDが鍵となる理由
AR/XRブームで1~2インチAMOLEDディスプレイが不可欠になる理由(2025年業界インサイト)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
ストレッチバーLCDディスプレイがスーパーマーケットの棚端マーケティングを強化し、売上を促進し、コストを削減する方法をご覧ください。
-
Stretched LCD Solutions for Restaurants and Hospitality Venues
ストレッチLCDは、レストランのメニューやホスピタリティサービスに最適な、洗練された高輝度ディスプレイを提供します。
おすすめ商品
-
7.0インチ IPS 高輝度 TFT タッチスクリーンなし
BR070JII 2757-B4 V.1 紹介この優れた7.0インチTFT LCDモジュールは、a-Si TFTを搭載しており、
-
10.1 インチ IPS LVDS インターフェース TFT タッチスクリーンなし
BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1 紹介BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1は、先進的なTFT LCDモジュールです。
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
製品仕様: BRO392001A解像度: 1080x1024動作電圧範囲: 28V画面サイズ: 3.92
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
製品仕様: BRO548001A解像度: 1080x1920動作電圧範囲: 2.8V画面サイズ: 5.4