Inhoudsopgave
1. Introduction to TFT and OLED
Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) and Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technologies are the cornerstones of modern display innovation. TFT-LCDs dominate the market for large-format screens like TVs and monitors, while OLEDs lead in high-end smartphones, wearables, and flexible displays. This article explores the science, manufacturing, and real-world applications of these technologies, leveraging insights from leading Chinese manufacturers such as BOE, CSOT, and Visionox.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Functie | TFT-LCD | JIJ BENT |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight Required | Yes (LED/CCFL) | No (self-emissive) |
| Contrastverhouding | ~500:1 | Up to 1,000,000:1 |
| Flexibiliteit | Rigid panels | Flexible/foldable designs |
| Energie-efficiëntie | Gematigd | High for dark content |
| Kosten | $15–$30/cm² | $30–$50/cm² |
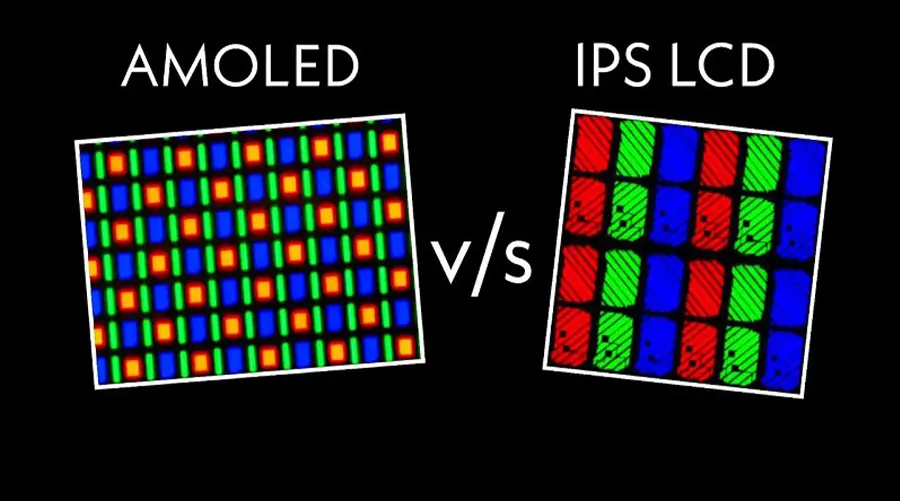
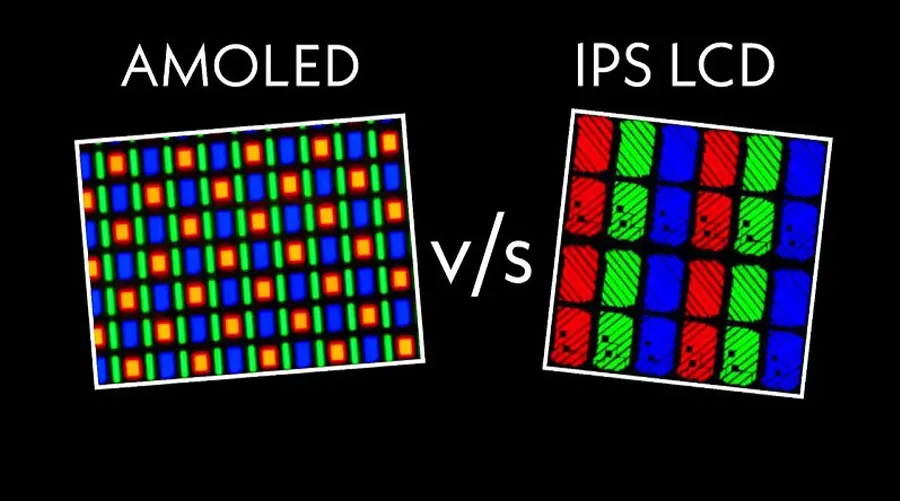
2. TFT Technology: Principles and Applications
What is TFT?
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) is a semiconductor technology used in LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) to control individual pixels. TFT-LCDs combine a liquid crystal layer with a backlight and a TFT array to produce high-resolution images.
Key Components of TFT-LCDs
-
Glass Substrates: Typically 700–1200mm in size, made of soda-lime or alkali-free glass.
-
Thin-Film Deposition: Layers of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), silicon nitride (SiN), and indium tin oxide (ITO) are deposited via chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
-
Photolithography: A multi-step process using 4–6 masks to pattern the TFT array.
-
Cell Assembly: Liquid crystals are sealed between two substrates with spacers to maintain uniform thickness.
Applications of TFT-LCDs
-
Television and Monitor Manufacturing: Dominates the TV market due to cost-effectiveness.
-
Industrial Automation: Used in medical devices (e.g., diagnostic equipment) and industrial control panels.
-
Autodisplays: Integrated into car dashboards and infotainment systems.
Case Study: BOE's B7 Line
BOE’s B7 line in Chengdu produces 48K/M AMOLED panels using LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon) technology. This line achieves 1000 cd/m² brightness and supports 120Hz refresh rates, making it ideal for high-end smartphones.
3. OLED Technology: Advantages and Challenges
What is OLED?
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) uses organic compounds that emit light when electrically stimulated. Unlike TFT-LCDs, OLEDs do not require a backlight, enabling ultra-thin, flexible displays with perfect blacks and wide viewing angles.
Voordelen van OLED
-
Hoge contrastverhouding: Achieves 1,000,000:1 due to self-emissive pixels.
-
Flexibility: Enables foldable phones (e.g., Huawei Mate X3) and curved TVs.
-
Energie-efficiëntie: Consumes less power for dark scenes compared to TFT-LCDs.
Challenges in OLED Manufacturing
-
Blue OLED Lifespan:Blauwe organische materialen degraderen sneller dan rode/groene materialen, waarvoor geavanceerde fosforescerende emitters nodig zijn.
-
Productiekosten:Vacuümdepositieprocessen zijn duur: de kosten kunnen oplopen tot $ 30–$ 50/cm².
-
Opbrengstpercentages:Lager dan TFT-LCD's (doorgaans 60–70% vanwege materiaalfouten).
Case Study: Visionox's V2-lijn
De V2-lijn van Visionox in Guangzhou richt zich op AMOLED-productie met Cu (koper) en LTPO (lagetemperatuurpolykristallijnoxide)-technologieën. Deze lijn ondersteunt FDA-gecertificeerde medische apparaten en autodisplays en bereikt in 2023 een capaciteit van 30.000 m³/m³.
4. Manufacturing Processes of TFT and OLED
TFT-LCD-productiestappen
-
Voorbereiding van het glazen substraat:Reinigend en chemisch versterkend.
-
Thin-Film Deposition:Lagen van SiO₂, SiN en ITO.
-
Photolithography:4–6 maskers om pixelarrays te definiëren.
-
Cell Assembly:Injectie en afdichting van vloeibare kristallen.
-
Integratie van achtergrondverlichting:LED- of CCFL-achtergrondverlichting toegevoegd voor verlichting.
OLED-productiestappen
-
Substraatselectie:Glas- of polymeerfolies voor flexibiliteit.
-
Vacuümdepositie:Organische materialen (bijvoorbeeld TADF-stralers) die via inkjetprinten of thermische verdamping worden afgezet.
-
Inkapseling:Afdichten met dunne-filmbarrières om vochtinfiltratie te voorkomen.
-
Driver IC-integratie:TFT-arrays regelen de helderheid en kleur van pixels.
Vergelijkende statistieken
| Parameter | TFT-LCD | JIJ BENT |
|---|---|---|
| Helderheid | 300–800 cd/m² | 500–1000 cd/m² |
| Reactietijd | 5–8 ms | 0,1 ms |
| Stroomverbruik | 3–5 W (10-inch scherm) | 2–4 W (10-inch scherm) |
| Opbrengstpercentage | ~75% | ~60% |
5. Leading Factories and Case Studies
BOE's B1-lijn (Peking)
Project:Mini LED-integratie voor LCD-achtergrondverlichting.
Resultaat:Bereikte een capaciteit van 100K/M TFT-LCD met 9K/M Mini LED-conversie, waardoor de achtergrondverlichtingsefficiëntie met 30% werd verhoogd.
CSOT's T4-lijn (Wuhan)
Focus:AMOLED-productie voor autodisplays.
Capaciteit:48K/M met 1000 cd/m² helderheid.
Technologie:Maakt gebruik van op koper gebaseerde TFT-circuits voor verbeterde geleiding.
Visionox's V3-lijn (Chengdu)
Innovatie:Geprint OLED met inkjettechnologie.
Kostenreductie:Vermindert materiaalverspilling met 40% en richt zich op massamarktacceptatie.
6. TFT vs OLED: A Detailed Comparison
Prestatiegegevens
| Functie | TFT-LCD | JIJ BENT |
|---|---|---|
| Kleurnauwkeurigheid | Iets lager (8-bit) | Superieur (10-bits) |
| Kijkhoek | 120–140° | 170°+ |
| Vernieuwingsfrequentie | 60–120 Hz | 60–120 Hz |
| Duurzaamheid | Langere levensduur | Gevoelig voor inbranden |
Marktaandeel (2023)
TFT-LCD:65% van de wereldwijde displayleveringen (gebruikt in tv's en monitoren).
JIJ BENT:35% van de zendingen bestaat uit smartphones en wearables.

7. Future Trends and Innovations
MicroLED-schermen
B1-lijn van BOE:Produceert Mini LED-achtergrondverlichting voor LCD's, met een jaarlijkse productie van 20.000 m².
De QD-OLED van Samsung:Combineert quantum dots met OLED voor verbeterde helderheid.
LTPO voor AMOLED
De T6-lijn van CSOT:Implementeert LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide) voor vernieuwingsfrequenties van 120 Hz en dynamische aanpassingen van de framesnelheid.
Gedrukte OLED
De Vistar-lijn van Visionox:Experimenten met inkjetprinten om kosten te verlagen en de productie op te schalen.
8. FAQs About TFT and OLED
V1: Wat is het verschil tussen a-Si en LTPS TFT's?
a-Si (amorf silicium):Kosteneffectief voor grote panelen (bijv. tv's).
LTPS (Lage-temperatuur polykristallijn silicium):Hogere elektronenmobiliteit voor kleine, hoge-resolutie displays (bijv. smartphones).
Vraag 2: Waarom zijn OLED's duurder dan TFT-LCD's?
Vacuümdepositie:Complex en kostbaar proces voor organische materialen.
Materiaalkosten:Fosforescerende emitters en inkapselingsmaterialen verhogen de kosten.
Vraag 3: Hoe verbeteren Cu-processen de OLED-prestaties?
Koper (Cu) vervangt aluminium (Al) in TFT-circuits en verbetert de geleiding en stabiliteit van beeldschermen met een hoge verversingssnelheid.
Laatste artikelen
-
Waarom 1-2" AMOLED's de sleutel zijn tot AR/XR in 2025
Waarom 1-2 inch AMOLED-schermen essentieel worden in de AR/XR-hausse (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
LCD-schermen met uitgerekte staven voor de detailhandel: verhoog de omzet en betrokkenheid in supermarkten
Ontdek hoe LCD-schermen met uitgerekte staven de marketing in de supermarktschappen verbeteren, de verkoop stimuleren en de kosten verlagen.
-
Uitgerekte LCD-oplossingen voor restaurants en horecagelegenheden
Uitgerekte LCD's bieden strakke, zeer heldere displays die perfect zijn voor restaurantmenu's en horecagelegenheden.
Aanbevolen producten
-
7,0 inch IPS TFT met hoge helderheid zonder touchscreen
BR070JII 2757-B4 V.1 InleidingDeze uitzonderlijke 7,0-inch TFT LCD-module, aangedreven door een a-Si TFT-act
-
10,1 inch IPS LVDS-interface TFT zonder touchscreen
BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1 Inleiding Zeker. BR101DHI3625-A4 V.1 is een geavanceerde TFT LCD-module die
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Productspecificaties: BRO392001A Resolutie: 1080x1024 Bedrijfsspanningsbereik: 28V Schermgrootte: 3,92
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Productspecificaties: BRO548001A Resolutie: 1080x1920 Bedrijfsspanningsbereik: 2,8V Schermgrootte: 5,4