Table of Contents
What Is IPS Display Mode?
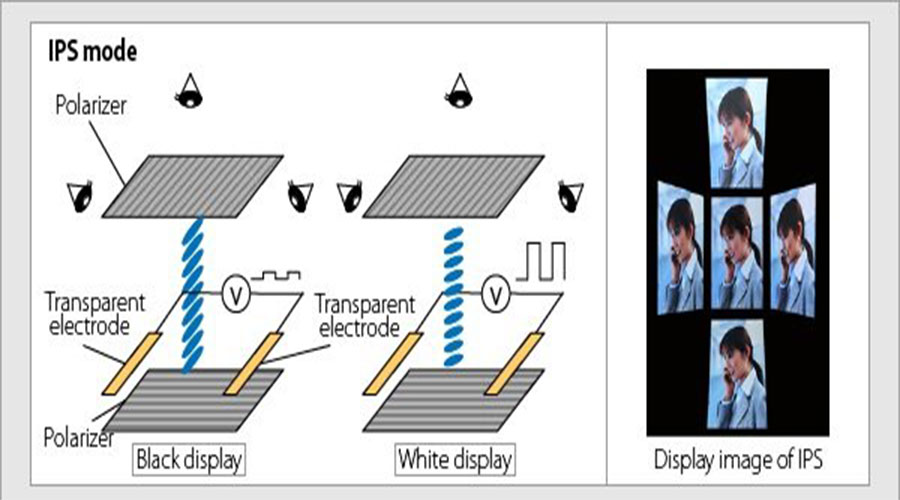
IPS display mode (In-Plane Switching) is a liquid crystal display technology that revolutionized TFT LCD performance by aligning liquid crystals parallel to the glass substrates. This innovation eliminates color inversion issues found in older TN (Twisted Nematic) panels and delivers:
Color accuracy up to 98% Adobe RGB coverage
Viewing angles exceeding 178° in all directions
Consistent grayscale rendering for professional-grade displays
As the preferred choice for design workstations, medical imaging, and high-end mobile devices, IPS technology has become synonymous with premium visual quality.
Structure of IPS TFT LCD Panels
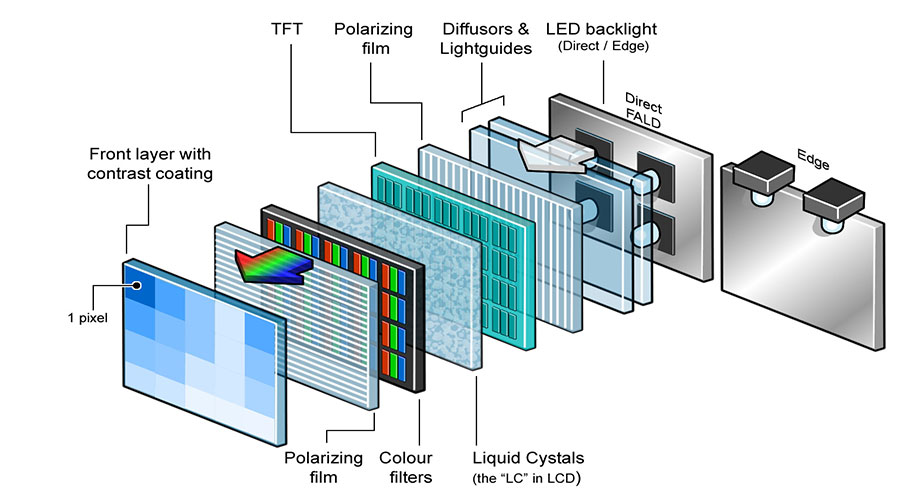
A typical IPS panel consists of three core layers working in harmony:
1. Active Matrix Substrate (TFT Array)
Contains thin-film transistors to control individual pixel behavior
Uses amorphous or low-temperature polysilicon for precise electrical control
2. Color Filter Substrate
Features red, green, and blue subpixels for color generation
Includes black matrix patterns to enhance contrast ratios
3. Liquid Crystal Layer
Horizontally aligned nematic crystals rotate in-plane with applied voltage
Eliminates vertical twisting motion of TN panels
Polarizers on both sides regulate light transmission while maintaining the horizontal crystal alignment that defines IPS technology.
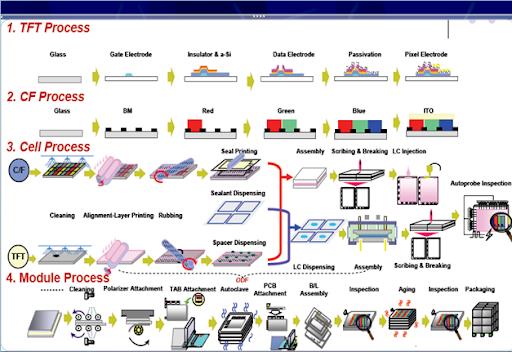
How IPS Displays Are Manufactured
The production of IPS panels involves four critical stages, each requiring precision engineering:
1. Array Fabrication
Photolithography creates gate and data lines on glass substrate
Deposition of semiconductor and insulating layers
Formation of ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) transparent electrodes
2. Color Filter Processing
Photolithography applies RGB color resins
Black matrix patterning improves contrast
Overcoat layer ensures smooth surface for subsequent steps
3. Cell Assembly
Alignment films are deposited and rubbed for precise crystal orientation
One Drop Fill (ODF) method injects liquid crystals between substrates
Vacuum bonding eliminates air bubbles for uniformity
4. Module Integration
COG (Chip-on-Glass) bonding attaches driver ICs
LED backlight integration and final optical testing
Quality assurance for brightness uniformity and color calibration
Key Advantages of IPS Technology
The IPS display mode offers unparalleled benefits for both professional and consumer applications:
1. Superior Color Consistency
Maintains ΔE < 2 color accuracy across all viewing angles
Supports wide color gamuts (sRGB, Adobe RGB, DCI-P3)
2. Wider Viewing Angles
Horizontal and vertical visibility up to 178°
No color shift or inversion at extreme angles
3. Enhanced Grayscale Performance
256-level grayscale rendering for medical imaging
Improved shadow detail in dark scenes
4. Industry Standard for Professionals
Adopted by Adobe and Pantone for color-critical workflows
Used in surgical monitors for accurate tissue visualization
Common Limitations of IPS Panels
While IPS technology excels in many areas, it also presents challenges:
1. Higher Manufacturing Costs
Complex alignment processes increase production expenses
Higher yield loss compared to TN panels
2. Response Time Trade-offs
Typical 4-8ms GTG response vs. 1-5ms in TN panels
Overdrive compensation required for gaming applications
3. Power Consumption
Horizontal crystal alignment requires higher backlight intensity
~15-20% higher power use compared to VA panels
4. Thickness Constraints
Additional alignment layers add 0.2-0.5mm to panel thickness
Challenges for ultra-thin form factors
Top Applications of IPS Display Mode
The versatility of IPS technology makes it ideal for:
1. Professional Workstations
Graphic design and photo editing (e.g., Wacom Cintiq)
Medical diagnostic equipment with DICOM calibration
2. Mobile Devices
iPhone OLED panels with IPS-derived technology
Android flagships with 120Hz refresh rates
3. Automotive Displays
Head-up displays with daylight visibility
Infotainment systems with sunlight readability
4. Industrial Monitoring
Control room displays with 24/7 operation
Ruggedized panels for factory environments

IPS vs. TN/VA Display Modes
Here's a comparative analysis of key display technologies:
| Feature | IPS | TN | VA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Viewing Angles | 178° | 160° | 178° |
| Response Time | 4-8ms | 1-5ms | 4-6ms |
| Contrast Ratio | 1000:1+ | 500:1 | 3000:1+ |
| Power Consumption | High | Low | Moderate |
Future of IPS Display Technology
Emerging innovations are addressing IPS limitations:
1. Mini-LED Backlighting
Local dimming zones improve contrast without VA trade-offs
Used in 8K TVs like LG's OLED evo
2. Quantum Dot Enhancements
Expanded color gamuts (up to 157% DCI-P3)
Improved energy efficiency in mobile devices
3. Flexible IPS Panels
Bendable displays for wearable devices
Rollable TVs with 180° folding capability
Latest articles
-
Why 1–2" AMOLEDs Are Key to AR/XR in 2025
Why 1–2 Inch AMOLED Displays Are Becoming Essential in the AR/XR Boom (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
Discover how stretched bar LCD displays enhance supermarket shelf-edge marketing, drive sales, reduc
-
Stretched LCD Solutions for Restaurants and Hospitality Venues
Stretched LCDs offer sleek, high-brightness displays perfect for restaurant menus and hospitality si
Recommended products
-
3.5 inch IPS TFT LCD Displays without Touchscreen
BR035QHH0626-A3 V.1 IntroductionThe 035QHI0626-A3 V.1 product is a high-resolution transmissive type
-
8.0 inch IPS MIPI Interface TFT without Touchscreen
BR080AII2426-A3 V.7 IntroductionThis display, with the LCD size of 8.0 inches, runs at a resolution
-
6.95 inch IPS MIPI Interface TFT without Touchscreen
BR070JIH1826-E3 V.10 IntroductionThis is an advanced 6.95-inch LCD module, featuring an IPS display
-
10.1 inch IPS TFT Display without Touchscreen
BR101JII3650-A3 V.3 IntroductionThe BR101JII3650-A3 V.3 is a 10.1-inch TFT LCD module equipped with
-
7 inch IPS TFT LCD with LVDS Interface
BR070800480AF-V1 | 7" IPS LCD 800×480 | 1000-Nits High Brightness | LVDS Interface | Non-TouchEngine