In today’s digital world, display technology plays a critical role in user experience across a wide range of devices — from smartphones and laptops to televisions and gaming monitors. Two of the most popular display technologies currently available are OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) LCD.
Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different use cases and preferences. Whether you're a professional designer, a hardcore gamer, or someone who simply enjoys watching high-quality content, understanding the differences between OLED and IPS displays can help you make an informed decision when purchasing your next screen.
This article will provide a comprehensive comparison of OLED and IPS technologies, covering everything from image quality and response time to power consumption, durability, and real-world applications.

Understanding OLED Displays
OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode, and it is a self-emissive display technology. Unlike traditional LCDs, which require a backlight, each pixel in an OLED display emits its own light. This allows for perfect black levels, infinite contrast ratios, and incredibly vibrant colors.
How OLED Works
Each OLED pixel consists of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them. These pixels can be individually controlled, meaning they can be turned on or off independently. This results in:
True blacks (by turning off individual pixels)
High contrast ratio
Excellent color accuracy
Fast response times
Advantages of OLED
Perfect Blacks: Since each pixel emits its own light, black pixels are completely dark, resulting in superior contrast.
High Contrast Ratio: Infinite contrast makes images appear more vivid and realistic.
Wide Color Gamut: OLED displays often support 100% of the DCI-P3 color space, offering rich and accurate color reproduction.
Fast Response Time: Near-instantaneous pixel switching reduces motion blur and ghosting.
Thin and Flexible Design: OLED panels can be made very thin and even flexible, allowing for curved and rollable screens.
Disadvantages of OLED
Burn-In Risk: Static images displayed for long periods may cause permanent image retention.
Lower Peak Brightness: Compared to some LED-backlit IPS displays, OLEDs typically have lower peak brightness levels.
Higher Cost: OLED panels are generally more expensive than IPS due to manufacturing complexity.
Limited Lifespan: While modern OLEDs have improved significantly, blue OLED materials still degrade faster than red and green ones.
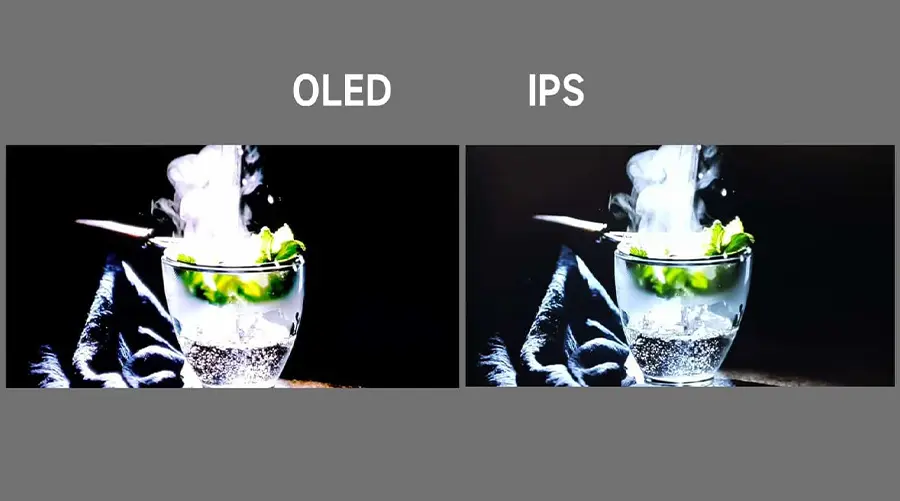
Understanding IPS Displays
IPS stands for In-Plane Switching, a type of Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) technology known for its excellent color accuracy and wide viewing angles. Unlike older TN (Twisted Nematic) panels, IPS displays maintain consistent color and brightness even when viewed from sharp angles.
How IPS Works
In an IPS panel, liquid crystals are aligned parallel to the glass substrate. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate to control how much light passes through. The backlight remains constant, and the liquid crystal layer modulates the light output.
Advantages of IPS
Excellent Color Accuracy: IPS panels are widely used in professional monitors due to their ability to reproduce accurate and consistent colors.
Wide Viewing Angles: Colors remain stable even when viewed from the side, making IPS ideal for group viewing or collaborative work.
Better Color Uniformity: Improved backlighting techniques reduce uneven lighting issues.
Affordability: IPS panels are generally more cost-effective than OLEDs.
Disadvantages of IPS
Backlight Bleeding / IPS Glow: Due to reliance on backlighting, some IPS panels suffer from light leakage, especially in darker scenes.
Lower Contrast Ratios: Black levels are not as deep as those on OLED displays.
Slower Response Times (in older models): Some budget IPS displays exhibit ghosting or motion blur, although newer "Fast IPS" models have largely resolved this issue.
Power Consumption: Constant backlight usage means higher power consumption compared to OLED in dark content.
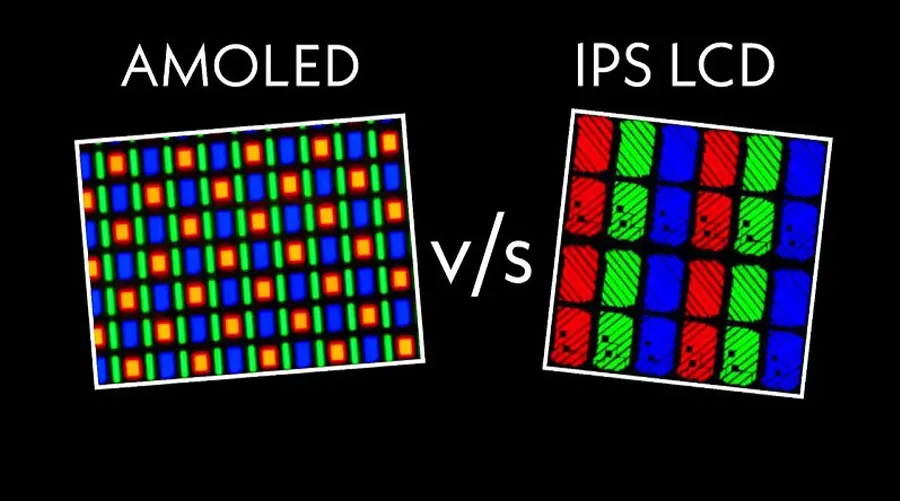
Image Quality Comparison: OLED vs IPS
The most noticeable difference between OLED and IPS lies in their image quality. Let's break down the key aspects:
Color Accuracy and Gamut
| Feature | OLED Display | IPS Display |
| Color Gamut | Up to 100% DCI-P3 | Up to ~98% sRGB or ~86% Rec. 2020 |
| Color Accuracy | Generally excellent | Excellent with proper calibration |
| Color Depth | Deeper and richer | Slightly less saturated |
Contrast Ratio and Black Levels
| Feature | OLED Display | IPS Display |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite | Typically 1000:1 – 3000:1 |
| Black Level Quality | Perfect black (pixels turned off) | Grayish black due to backlight bleed |
Brightness and HDR Performance
| Feature | OLED Display | IPS Display |
| Peak Brightness | Up to ~1000 nits (small area) | Up to ~2000+ nits with mini-LED |
| HDR Performance | Excellent dynamic range | Better peak brightness |
Response Time and Refresh Rate
Response Time
| Panel Type | Typical GtG Response Time | Ghosting/Blur Potential |
| OLED | <0.1ms | Almost none |
| IPS | 4ms – 1ms (Fast IPS) | Varies (lower in Fast IPS) |
Refresh Rate
| Panel Type | Max Available Refresh Rate | Use Case Preference |
| OLED | Up to 480Hz | Console & PC Gaming |
| IPS | Up to 500Hz+ | Competitive FPS Gaming |

Viewing Angles and Uniformity
Viewing Angles
| Panel Type | Horizontal Viewing Angle | Vertical Viewing Angle |
| OLED | >80° | >80° |
| IPS | >80° | >80° |
Screen Uniformity
| Issue | OLED | IPS |
| Backlight Bleed | None | Common in many models |
| Burn-In Risk | Moderate (modern) | None |
| Brightness Drop | Minimal | Noticeable in corners |
Power Consumption and Lifespan
Power Efficiency
| Display Type | Dark Content | Bright Content |
| OLED | Very low | High |
| IPS | Medium | Medium |
Lifespan and Durability
| Factor | OLED | IPS |
| Burn-In Risk | Present (reduced in modern models) | None |
| Pixel Degradation | Blue subpixels degrade over time | No degradation |
| Backlight Life | Not applicable | ~50,000 hours |

Use Cases and Recommendations
Here’s a breakdown of recommended use cases for each display type:
Console Gaming: OLED
Competitive FPS: IPS
Movie Watching: OLED
Photo Editing: IPS
Daytime Office Work: IPS
Nighttime Media Consumption: OLED

Conclusion
When choosing between OLED and IPS, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Both technologies have evolved significantly and serve distinct markets effectively.
OLED excels in:
Deep blacks and infinite contrast
Fast response times
Vibrant colors and wide gamut
Ideal for entertainment and creative media
IPS shines in:
Accurate color reproduction
Wide viewing angles
Higher brightness
Affordable price point
Ultimately, your choice should depend on:
Your intended usage (gaming, design, office, etc.)
Your environment (dark room vs. daylight)
Your budget
Your tolerance for potential drawbacks (burn-in vs. glow)
As both technologies continue to improve, we may soon see hybrid solutions that combine the best of both worlds. Until then, understanding the strengths and limitations of OLED and IPS will help you choose the display that best suits your needs.
Latest articles
-
Why 1–2" AMOLEDs Are Key to AR/XR in 2025
Why 1–2 Inch AMOLED Displays Are Becoming Essential in the AR/XR Boom (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
Discover how stretched bar LCD displays enhance supermarket shelf-edge marketing, drive sales, reduc
-
Stretched LCD Solutions for Restaurants and Hospitality Venues
Stretched LCDs offer sleek, high-brightness displays perfect for restaurant menus and hospitality si
Recommended products
-
2.06-inch OLED Display | 410×502 Resolution | 600 Nits | SPI Screen
The 2.06-inch AMOLED display module is designed specifically for harsh industrial environments, feat
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Product Specifications: BRO392001AResolution: 1080x1024Operating Voltage Range: 28VScreen Size: 3.92
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Product Specifications: BRO601001ADisplayMode: AMOLED Screen Size (inch): 6.01 Resolution: 1080x2
-
4.39 INCH OLED display module I2C Interface 568×1210 Resolution
The 4.39-inch AMOLED display module (model BR439102-A1) introduced by (Shenzhen Brownopto Technology
-
1.93 INCH OLED Panel I2C 368x448 Industrial-Grade Panel
Shenzhen Brownopto Technology’s 1.93-inch AMOLED module (Model BR193103-A1) features a core advantag
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Product Specifications: BRO548001AResolution: 1080x1920Operating Voltage Range: 2.8VScreen Size: 5.4