TFT LCD Display (Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display) is a cornerstone of modern display technology, widely used in smartphones, TVs, industrial control panels, and more. This article delves into the TFT LCD Display technology, its core classifications (e.g., TN-type and IPS-type), technical advantages, and future trends, helping you understand this critical innovation.
1. What is a TFT LCD Display?
A TFT LCD Display is a liquid crystal display that uses Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) technology to control each pixel individually. This design enables high-resolution, fast response times, and vibrant color reproduction, making it a dominant choice in the display industry.
1.1 Core Structure
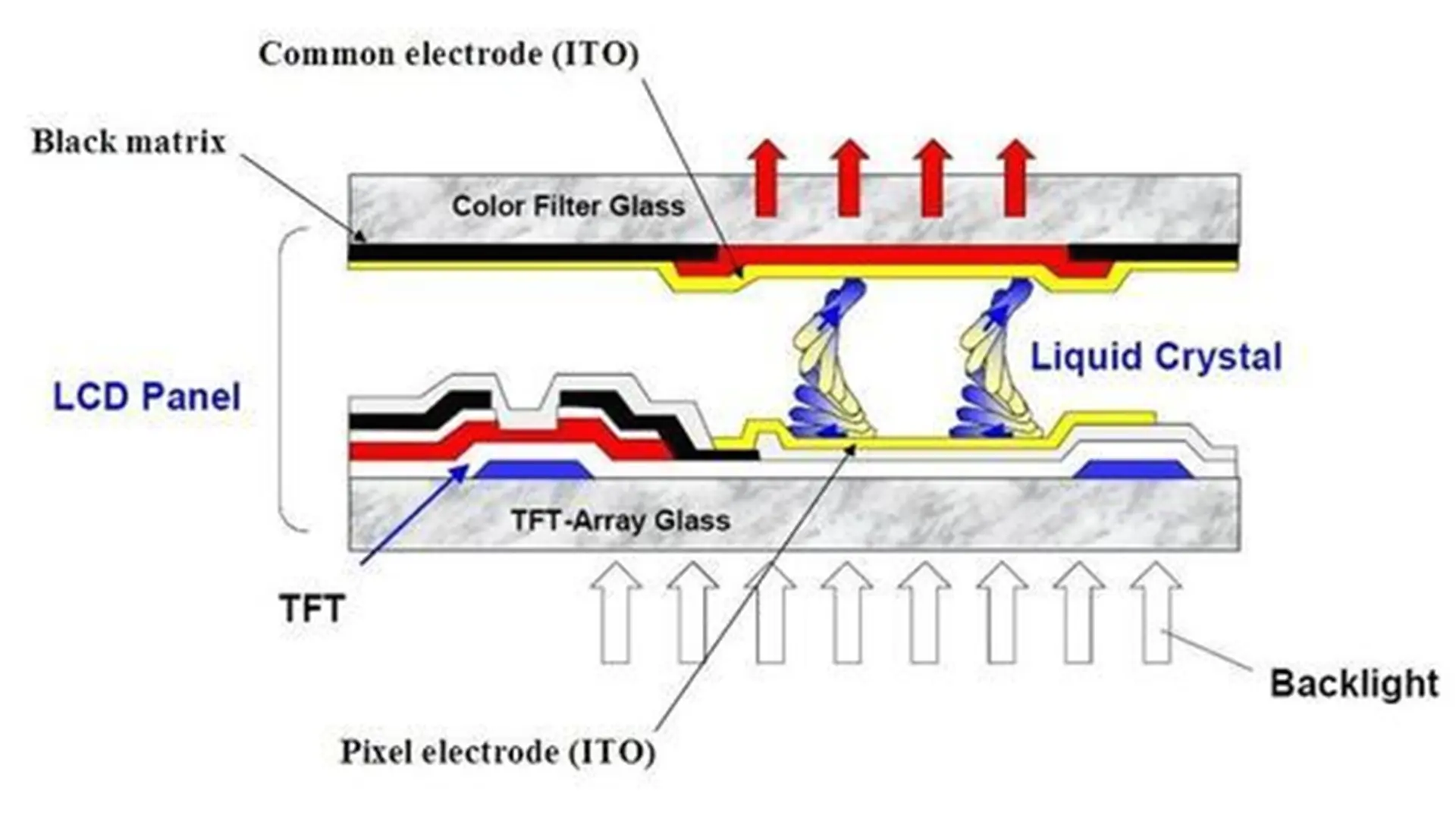
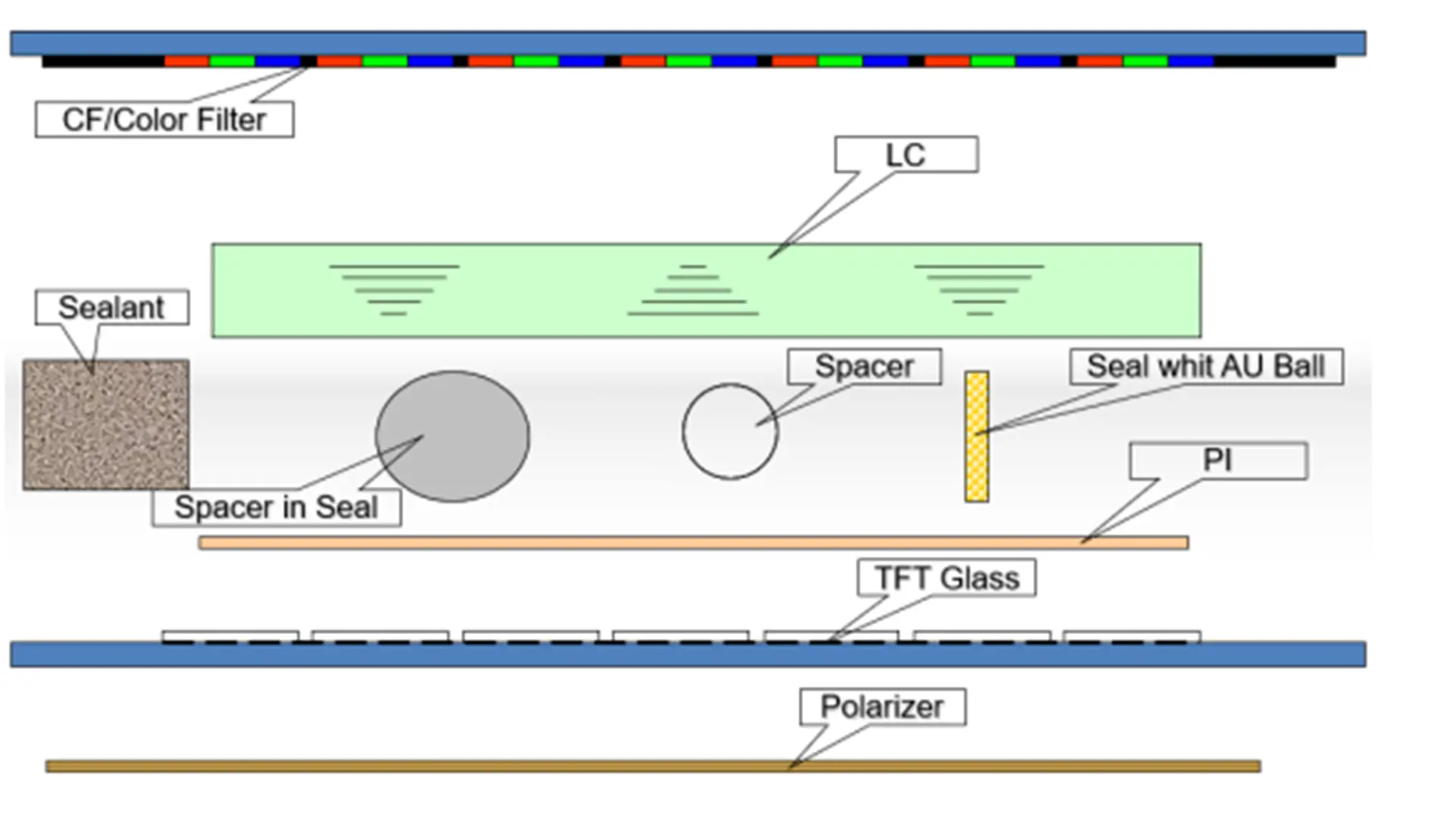
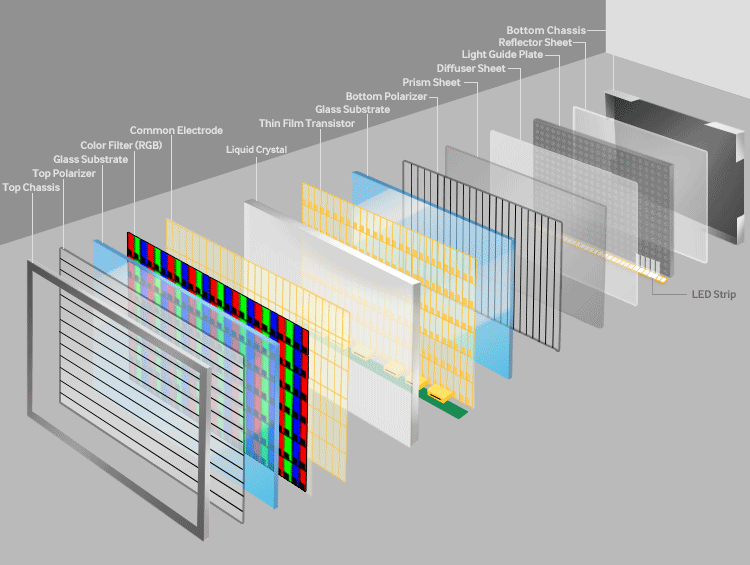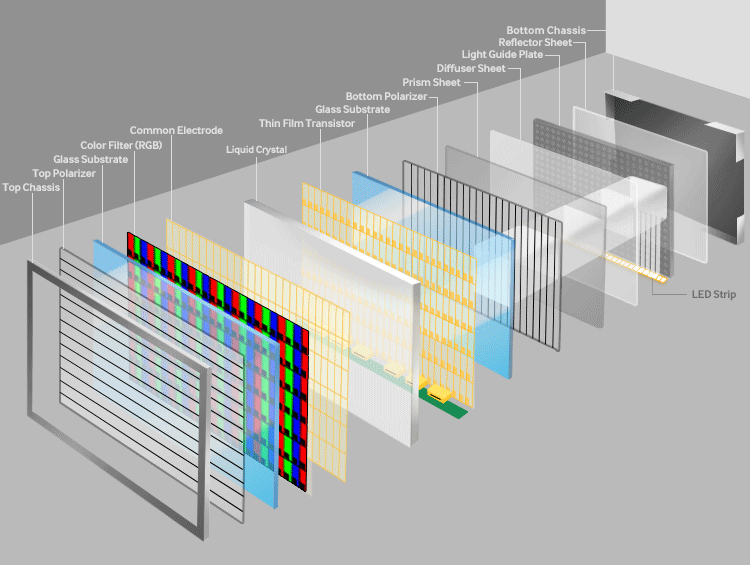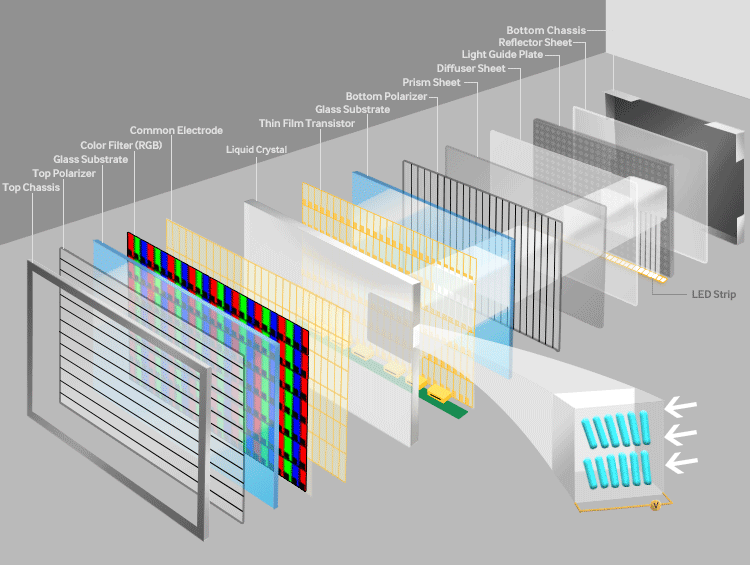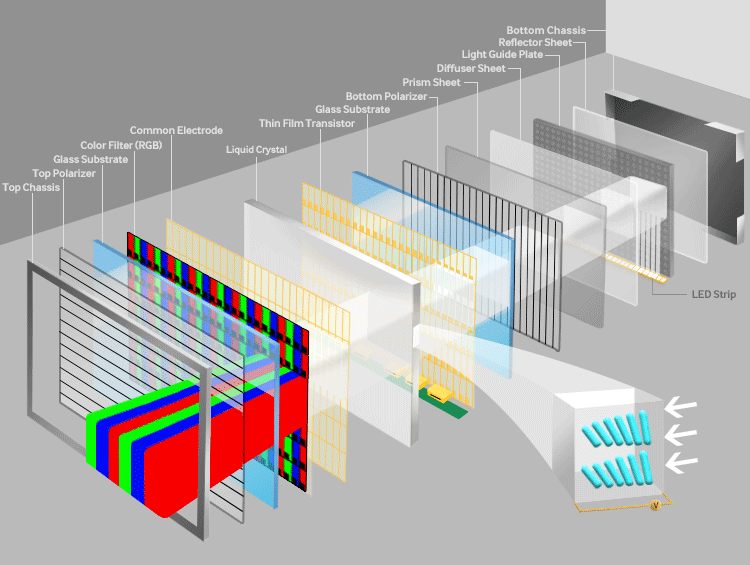
The structure of a TFT LCD Display consists of multiple precision-engineered layers:
Glass Substrates: Upper and lower glass layers, with the lower one integrated with TFT arrays and the upper one bonded to a color filter (CF).
Liquid Crystal Layer: Positioned between the two substrates, this layer modulates light based on electric field changes.
Polarizers (POL): Two polarizing films with perpendicular optical axes (90° phase difference) filter light direction to control brightness.
Color Filters (CF): Divide each pixel into red, green, and blue subpixels for full-color display.
Backlight Module: Provides illumination, typically using LED or CCFL technology.
Diffuser and Light Guide Plate: Ensures even light distribution for uniform brightness.
Driver Circuits: Row and column drivers control TFT switching for pixel-level image rendering.
The layered structure works synergistically to convert electrical signals into optical modulation, producing sharp, high-contrast images.
2. How a TFT LCD Display Works
2.1 Light Modulation Process
Since liquid crystals do not emit light, TFT LCD Displays rely on a backlight source. The process involves:
Backlight Illumination: LED or CCFL light passes through the lower polarizer (POL) into the liquid crystal layer.
Liquid Crystal Alignment: TFTs adjust voltage to reorient liquid crystal molecules, altering their optical properties.
Polarization Filtering: Light exiting the liquid crystal layer passes through the upper polarizer, allowing only specific light directions to pass, thus regulating brightness.
Color Display: Color filters (CF) combine RGB subpixel brightness to create full-color images.
2.2 Voltage and Transmittance Relationship
The core of TFT LCD Displays lies in voltage-controlled liquid crystal alignment. The dielectric anisotropy of liquid crystals causes them to align with the electric field. TFT switches regulate pixel voltage via gate voltage, enabling grayscale and color control. Matrix-driven scanning (gate/data lines) ensures precise pixel-by-pixel rendering.
3. Classification of TFT LCD Displays: TN vs. IPS
3.1 TN-Type TFT LCD Display (Twisted Nematic)
Structure:
Liquid crystals twist by ~90° in the absence of an electric field.
Apply voltage to realign molecules along the field, reducing light rotation.
Advantages:
Ultra-fast response time (<1ms), ideal for dynamic content (e.g., gaming monitors).
Low power consumption, suitable for portable devices (e.g., smartphones).
Disadvantages:
Narrow viewing angle (<160°), causing color distortion when viewed sideways.
Lower color saturation, unsuitable for professional design or medical imaging.
Applications:
Gaming monitors, automotive dashboards, consumer-grade laptops.
3.2 IPS-Type TFT LCD Display (In-Plane Switching)
Structure:
Liquid crystals align horizontally to the substrate in the absence of a field.
Apply voltage to rotate molecules in-plane (~90°), altering light polarization.
Advantages:
Wide viewing angle (>178°), perfect for collaborative work (e.g., meeting room displays).
High color accuracy, ideal for design, medical imaging, and premium TVs.
Disadvantages:
Slower response time (>4ms), less suitable for high-speed motion.
Higher power consumption, slightly higher cost than TN-type.
Applications:
Professional design monitors, medical imaging equipment, high-end TVs.
3.3 TN vs. IPS Comparison Table
| Feature | TN-Type TFT LCD | IPS-Type TFT LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | <1ms (Ultra-fast) | >4ms (Slower) |
| Viewing Angle | <160° (Narrow) | >178° (Extremely Wide) |
| Color Accuracy | Low Saturation | High Color Fidelity (sRGB>98%) |
| Power Consumption | Low | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Ideal Use Cases | Gaming, Automotive, Consumer Electronics | Design, Medical, Premium TVs |
4. Key Advantages of TFT LCD Displays
High Resolution: Supports 4K/8K for ultra-detailed visuals.
Fast Response Time: TN-type <1ms for dynamic content.
Vivid Colors: IPS-type delivers sRGB>98% color gamut.
Low Power Consumption: LED backlights reduce energy use by 50%.
Slim Design: Thickness <3mm for portable and embedded applications.
5. Typical Applications of TFT LCD Displays
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Industrial Control: Command centers, traffic management, and medical devices.
Commercial Displays: Digital signage, retail kiosks, and POS terminals.
Automotive: Dashboards, infotainment systems, and HUDs.
6. Future Trends in TFT LCD Display Technology
6.1 Mini LED Backlighting
Mini LED backlighting uses micrometer-scale LEDs to enhance brightness and contrast. Combined with TFT LCD Displays, it powers 8K TVs and high-end monitors. Example: Apple’s Pro Display XDR.
6.2 Oxide Semiconductor TFTs
Oxide semiconductors (e.g., IGZO) replace traditional a-Si TFTs, boosting electron mobility and reducing power consumption.
6.3 Flexible and Foldable Displays
Flexible substrates and ultra-thin packaging enable foldable/flexible TFT LCD Displays for next-gen smartphones and wearables.
7. How to Choose the Right TFT LCD Display
Resolution Requirements: 4K/8K for professional or cinematic use.
Application Context: Industrial use prioritizes durability; consumer electronics balance thinness and color.
Backlight Type: Mini LED for premium displays; standard LED for everyday use.
Type Selection:
TN-Type: Prioritize response time (e.g., gaming monitors).
IPS-Type: Prioritize color accuracy and viewing angles (e.g., design monitors).
Brand & Certification: Opt for ISO 9001/RoHS-certified providers like Brownopto.
8. TFT LCD Display vs. Other Display Technologies
| Feature | TFT LCD Display | OLED | Micro LED |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brightness | High (requires backlight) | Self-emissive, Ultra High | Self-emissive, Ultra High |
| Contrast Ratio | Medium | Infinite | Infinite |
| Response Time | 1-5ms (TN-type) | <0.1ms | <0.1ms |
| Lifespan | >50,000 hours | ~10,000 hours | >100,000 hours |
| Cost | Low | High | Extremely High |
9. Why Choose Brownopto for Your TFT LCD Display Needs?
At Brownopto, we specialize in designing and manufacturing cutting-edge TFT LCD Display solutions tailored to your requirements. Whether you need industrial control panels, high-resolution monitoring screens, or custom video walls, we deliver precision-engineered displays with unmatched reliability.
Our Commitment to You:
Expertise in TFT LCD Technology: From TN to IPS panels, our products are engineered for diverse applications.
Custom Solutions: Tailored to your specifications—resolution, size, color accuracy, and more.
Global Support: 24/7 technical assistance and post-sale service to ensure your success.
10. Take Action Now
If you’re looking for high-performance TFT LCD Display solutions, contact Brownopto today!
Contact Us:
Email: info@blhlcd.com
Phone: +86 177-4857-4559
Website: www.blhlcd.com
Elevate your business with Brownopto’s advanced display technology—visit our website or reach out directly to explore how we can meet your needs.
Latest articles
-
Why 1–2" AMOLEDs Are Key to AR/XR in 2025
Why 1–2 Inch AMOLED Displays Are Becoming Essential in the AR/XR Boom (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
Discover how stretched bar LCD displays enhance supermarket shelf-edge marketing, drive sales, reduc
-
Stretched LCD Solutions for Restaurants and Hospitality Venues
Stretched LCDs offer sleek, high-brightness displays perfect for restaurant menus and hospitality si
Recommended products
-
9.0 inch Standard TFT without Touchscreen
BR090WIE3053-A4 V.2 IntroductionThe BR090WIE3053-A4 V.2 is a 9.0-inch LCD screen that operates at a
-
4.3 inch Standard High brightness TFT without Touchscreen
BR043RIE1028-A4 V.1 IntroductionThis 4.3-inch LCD screen, utilizing a-Si TFT drive elements, showcas
-
7 inch IPS TFT LCD with LVDS Interface
BR070800480AF-V1 | 7" IPS LCD 800×480 | 1000-Nits High Brightness | LVDS Interface | Non-TouchEngine
-
10.1 inch For HDMI Signal TFT Display With Resistive Touch Screen Size:10.1" HDMI | 1024x600 P
BR101JII3650-A3 V.1 HDMI Display Module OverviewProduct Name: BR101JII3650-A3 V.1 HDMI Display
-
5.0 inch For HDMI Signal TFT Display With Resistive Touch Screen
BR050WIG1230-B5 V.1 HDMI Display Module OverviewProduct Name: BR050WIG1230-B5 V.1 HDMI Display