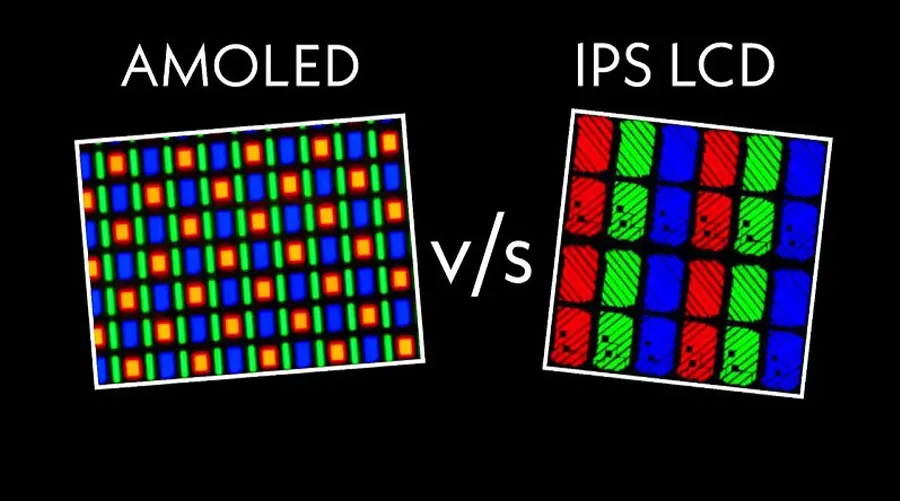
I. What is OLED Display Technology?
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are "self-emissive", meaning each pixel generates light independently. This technology eliminates the need for a backlight, enabling:
True black & infinite contrast ratio
Thinner & lighter form factors
Flexible, foldable & transparent displays
Ultra-fast response for AR/VR and gaming
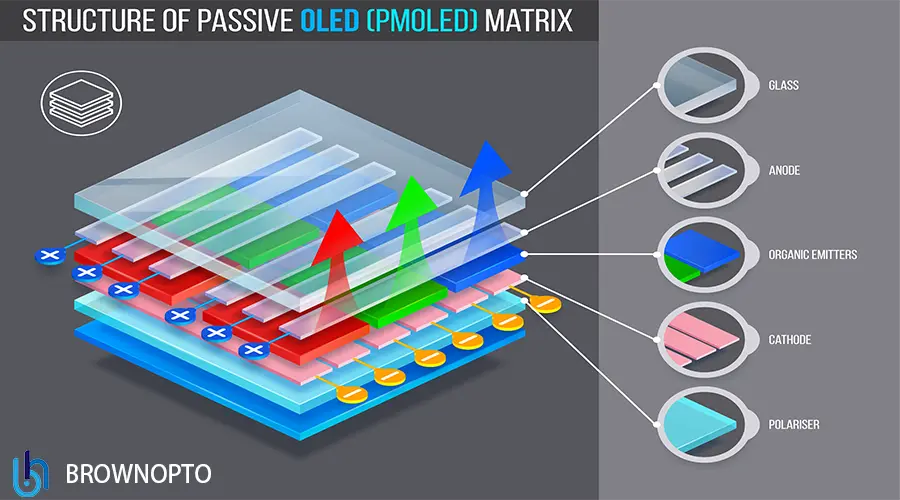
OLED has become the benchmark in premium devices (phones, wearables, TVs), and now expanding into "industrial, medical, transportation & retail electronics".
II. How OLED Pixels Work
Electroluminescence principle
Organic molecules emit light when electrons and holes recombine. People see the light directly from each pixel — no backlight, no light leakage.
OLED Device Layer Structure
Encapsulation layer (protects from moisture/O₂)
Optik çıkarma katmanı
Yayıcı tabaka (RGB ışık yayan moleküller)
Yük taşıma katmanları (ETL/HTL)
Şeffaf anot + Metal katot
TFT aktif matris (LTPS veya IGZO)
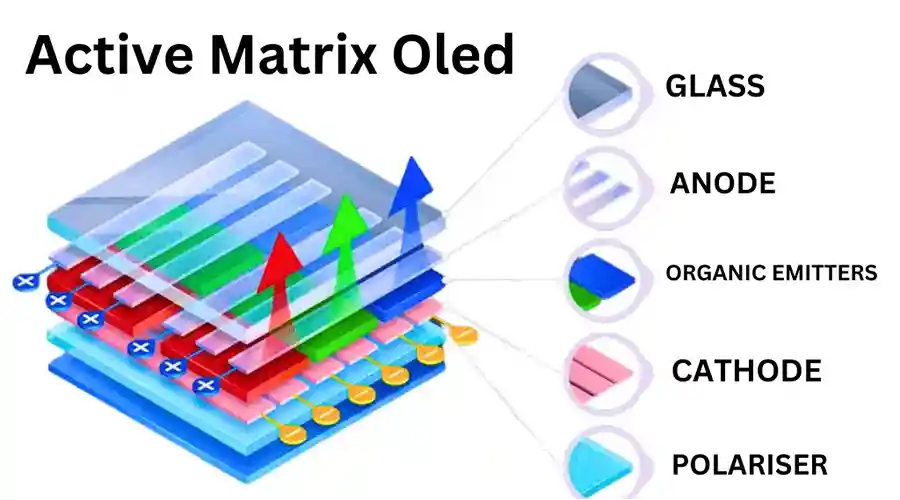
III. Temel Malzemeler ve Bileşenler
Yayıcılar — Floresan, Fosforesan ve TADF
Modern AMOLED'ler, %100'e yakın IQE sağlayan "fosforesan yayıcılar" (kırmızı/yeşil) kullanırken, "mavi TADF", ömür boyu iyileştirme için en sıcak Ar-Ge odak noktasıdır.
Şeffaf elektrotlar
| Malzeme | Kullanım Örneği | Esneklik |
|---|---|---|
| BU | Sert OLED | Düşük |
| Grafen | Esnek OLED | Yüksek |
| Gümüş nanotel | Kavisli giyilebilir ekranlar | Yüksek |
İnce Film Kapsülleme (TFE)
Gerekli WVTR: Çok yıllık operasyonel istikrarı garantilemek için "< 10⁻⁶ g/m²/gün".
IV. OLED Üretim Teknolojisi
OLED üretimi, yarı iletken, kimya ve hassas optiği bir araya getirir. En yaygın teknik:
Buharlaşma + İnce Metal Maske (FMM)
Akıllı telefonlarda, giyilebilir cihazlarda kullanılır
Yüksek PPI (>500), hassas RGB hizalaması
>10 inç boyutlarıyla sınırlı ölçeklendirme
Mürekkep Püskürtmeli Baskı OLED (IJP-OLED)
Malzeme kullanım verimliliği >%90
Büyük ekranlar (TV, tabela) için uygundur
Maliyet azaltma yol haritası hızla geliştiriliyor
V. OLED Performans Mühendisliği
Mühendisler parlaklık, kullanım ömrü, güç ve termal kararlılığı dengeleyerek tasarımı optimize ediyor.
Parlaklık ve Dış Mekan Görünürlüğü
Tipik: 300–900 nit (APL'ye bağlı)
MLA'lar / tandem yığını ile: 2000 nit'e kadar +
Tıbbi ve otomotiv için önemlidir
Ömür Boyu Güvenilirlik
| Renk | Tipik LT97 Ömrü | Notlar |
|---|---|---|
| Yeşil | 50k–120k saat | Güçlü istikrar |
| Kırmızı | 40k–80k saat | Mükemmel verimlilik |
| Mavi | 10k–25k saat | TADF aracılığıyla hala gelişiyor |
Kullanıcı arayüzü tasarımıÖnemli olan: Statik ikonlar diferansiyel yaşlanmayı (burn-in) hızlandırır.
Tepki Süresi
OLED'in tepkisi "1 μs" kadar hızlıdır, LCD'den 100 kat daha hızlıdır — VR/AR ve HUD'lar için idealdir.
VI. Başlıca OLED Ekran Türleri
Sert AMOLED (Cam Alt Tabaka)
Maliyet etkin, olgun tedarik zinciri
Endüstriyel el cihazları, HMI modülleri, tıbbi
Esnek ve Katlanabilir OLED
Poliimid alt tabakalar eğrilere ve kıvrımlara izin verir
Giyilebilir cihazlar, akıllı aksesuarlar, araç içi
Şeffaf OLED
%40'tan fazla şeffaflığa sahip efektleri sergileyin
Perakende, müzeler, fütüristik kullanıcı deneyimi
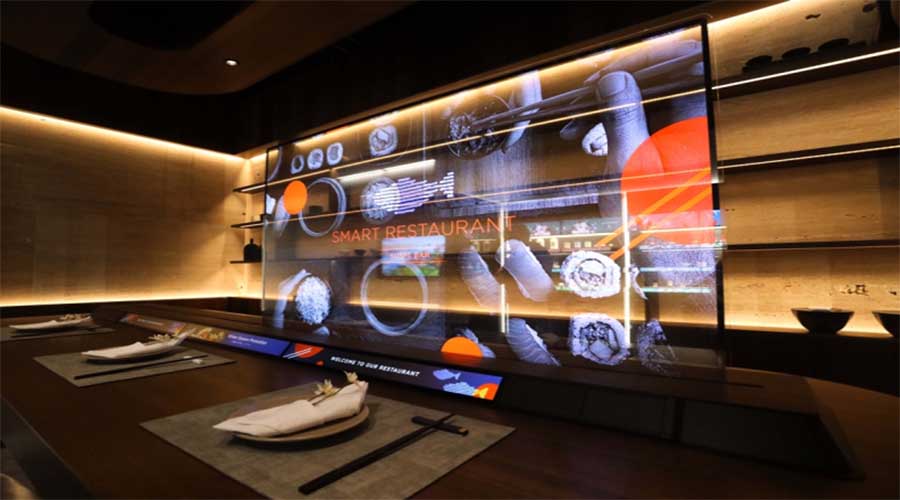

VII. OLED Ekranların Endüstriyel Uygulamaları
1) Giyilebilir Teknoloji
Düşük güç AOD modları
Konfor için kavisli form
Açık havada okunabilirlik iyileştirmeleri
2) Endüstriyel İnsan-Makine Arayüzleri
Yüksek kontrast + geniş görüş açıları
Sağlam dokunmatik sistemler için optik bağlama
Uzun ömürlü kullanıcı arayüzü stratejisi gereklidir
3) Perakende ve Şeffaf Tabela
Premium grafik sürücüsü dönüşümleri
Yüzen bilgi ekranı
4) Tıbbi ve Enstrümantasyon
Yakından okuma için yüksek veri netliği
Yansıma önleyici/bakteri önleyici kaplamalar isteğe bağlıdır
VIII. OLED, LCD, Mini LED ve MicroLED
| Bakış açısı | SEN | Mini LED (LCD) | Standart LCD | Mikro LED |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siyah Seviye | Mükemmel siyah | Yerel karartma ile daha iyi | Parla ve kana | Mükemmel siyah |
| Zıtlık | Sonsuz | Yüksek | Düşük | Sonsuz |
| Parlaklık | İyi | Çok yüksek | Yüksek | Çok yüksek |
| Esneklik | Evet | HAYIR | HAYIR | Evet |
| Yanma Riski | Azaltmaya ihtiyaç var | Hiçbiri | Hiçbiri | En az |
| Maliyet | Daha yüksek | Üst-orta | Daha düşük | Çok yüksek |
Çözüm:Üst düzey kullanıcı deneyimi ve ince/esnek tasarıma ihtiyaç duyulduğunda OLED en iyi seçimdir.
IX. Ortaya Çıkan Trendler ve OLED'in Geleceği
QD-OLED ve Hibrit Yaklaşımlar
Kuantum noktalı OLED (QD-OLED) ve diğer hibrit yaklaşımlar, algılanan parlaklığı ve renk hacmini artırmak için OLED yayıcı katmanlarını kuantum noktalı renk dönüştürme veya iyileştirme filmleriyle birleştirir. QD-OLED, OLED'in piksel düzeyindeki kontrastını korurken, en yüksek parlaklık ve renk doygunluğunu iyileştirmeyi hedefler; bu da üst düzey TV'ler ve profesyonel monitörler için cazip bir avantajdır.
Tandem OLED ve Yığılmış Mimariler
Tandem OLED yığınları, akımı paylaşmak ve yayıcı başına stresi azaltmak için birden fazla yayıcı üniteyi seri olarak yerleştirir. Tandem mimariler, kullanım ömrünü iyileştirir, kullanılabilir parlaklığı artırır ve yanmaya neden olan farklı yaşlanmayı azaltır. Bu yığınlar, geliştirilmiş mavi kimyasallarla bir araya gelerek uzun ömürlü ticari OLED stratejilerinin merkezinde yer alır.
Sarılabilir, Baskılı ve Esnek OLED'ler
Baskılı elektronik ve ince film kapsülleme alanındaki gelişmeler, rulo haline getirilebilir televizyonlara, uyumlu tabelalara ve tekstile gömülü ekranlara olanak tanır. Baskılı OLED'ler, bazı vakum biriktirme adımlarını ortadan kaldırarak üretim sermaye giderlerini düşürürken, esnek OLED araştırmaları, ekranların cilde veya kumaşa uyum sağladığı giyilebilir ve tıbbi entegrasyonu hedefler.
MicroOLED / Göz Yakını Ekranlar ve AR
Silikon veya CMOS arka panellere sahip MicroOLED ekranlar (mikro ekranlar), AR/VR gözlükler için son derece yüksek piksel yoğunlukları sunar. OLED mikro ekranlar gecikmeyi en aza indirir ve sürükleyici göz yakını sistemleri için temel ölçüt olan yüksek dinamik aralığı destekler.
Sürdürülebilirlik ve Malzeme Verimliliği
Sektör, nadir malzeme kullanımını aktif olarak azaltıyor, alt tabakaların ve katmanların geri dönüştürülebilirliğini iyileştiriyor ve enerji tasarrufu için sürücü elektroniğini optimize ediyor. Yaşam döngüsü değerlendirmeleri ve eko-tasarım, ekranları büyük ölçekte dağıtan OEM'ler için satın alma kararlarında göz önünde bulundurulması gereken unsurlar haline geliyor.
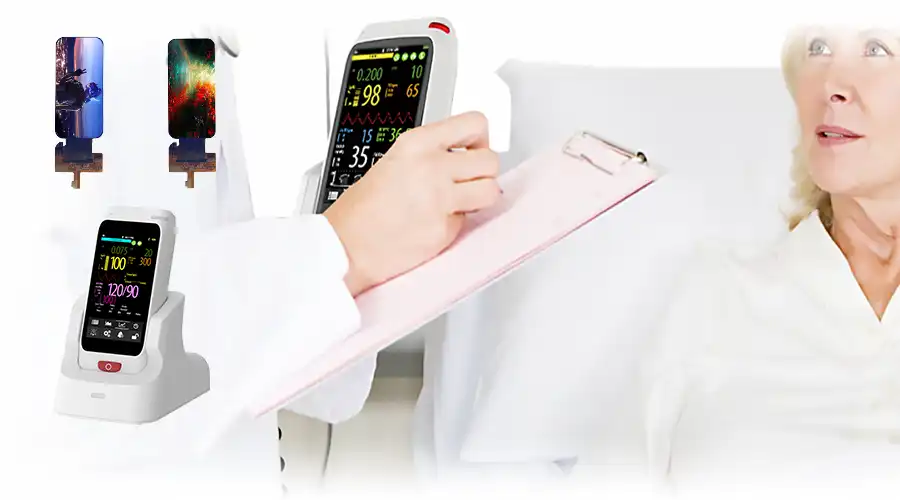
X. Vaka Çalışması — Elde Taşınabilir Tıbbi Cihazlar için BROWNOPTO 4,4" AMOLED Entegrasyonu
Proje Genel Bakışı
Bir tıbbi cihaz OEM'i, taşınabilir bir bakım noktası analizörü için kompakt, gün ışığında okunabilen bir ekrana ihtiyaç duyuyordu. Başlıca kısıtlamalar arasında ince mekanik profil, eldivenle kullanılabilen dokunmatik ekran, klinik okunabilirlik için yüksek kontrast ve -20°C ile +70°C arasında sağlam saha güvenilirliği yer alıyordu.
Mühendislik Çözümü
Panel seçimi: Parlaklık ve kullanım ömrünü dengeleyen tandem yayıcı mimariye sahip 4.40" LTPS AMOLED.
Dokunmatik entegrasyon:Nitril eldivenler ve ıslak koşullar için kalibre edilmiş hücre içi projeksiyonlu kapasitif dokunmatik.
Optik: Geliştirilmiş güneş ışığı kontrastı ve sağlamlık için yansıma önleyici polarize filtre ve optik bağlama (OCA).
Arayüz: Güvenli başlatma ve düşük güç tüketimli uyku modları için optimize edilmiş güç sıralamasına sahip MIPI DSI 2 şeritli.
Kapsülleme: İnce film kapsülleme (TFE), uzatılmış saha ömrü için WVTR < 1e-6 g/m²/gün sağlar.
Temel Özellikler Sunuldu
| Parametre | Değer |
|---|---|
| Diyagonal | 4.40 inç |
| Çözünürlük | 568 × 1210 |
| Tipik Parlaklık | 600 cd/m² |
| Zıtlık | ~100.000:1 (tipik) |
| Arayüz | MIPI DSI (2 şerit) |
| Çalışma Sıcaklığı | -20 °C ile +70 °C arası |
| Kapsülleme | İnce film kapsülleme (TFE) |
Sonuçlar ve Saha Geri Bildirimi
Cihaz, klinikler ve mobil üniteler genelinde 12 aylık bir pilot uygulamaya girdi. Geri bildirimler, farklı ışık koşullarında olağanüstü okunabilirlik ve eldivenlerle tutarlı dokunma davranışı sergilediğini vurguladı. Ekran performansıyla ilgili herhangi bir saha arızası kaydedilmedi; tandem OLED yaklaşımı ve kalibre edilmiş kullanıcı arayüzü stratejileri yanma riskini azalttı.

XI. Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
OLED ile AMOLED arasındaki fark nedir?
OLED, organik ışık yayan diyot ekranların genel sınıfıdır. AMOLED (Aktif Matris OLED), pikselleri aktif olarak adreslemek için ince film transistör (TFT) arka paneli kullanır ve akıllı telefonlar, televizyonlar ve endüstriyel ekranlar için uygun yüksek çözünürlüklü ve geniş formatlı panelleri destekler; PMOLED ise küçük ve düşük maliyetli ekranlar için uygun pasif matris çeşididir.
OLED ekranlar genellikle ne kadar dayanır?
Ömür, yayıcı kimyasına, panel parlaklığına, termal tasarıma ve çalışma düzenlerine bağlıdır. Tipik ticari AMOLED ömürleri, mavi dışındaki renkler için on binlerce ila 100.000+ saat arasında değişir; mavi yayıcı ömrü sınırlayıcı faktör olmaya devam etmekte olup, malzeme araştırmaları ve tandem yapılar aracılığıyla aktif olarak iyileştirilmektedir.
OLED ekranlar dış mekan tabelaları için uygun mudur?
OLED'ler, yüksek tepe parlaklığı için tasarlanıp yansıma önleyici optiklerle eşleştirildiğinde dış mekanlarda kullanılabilir. Ancak, aşırı doğrudan güneş ışığı senaryoları için, daha yüksek sürekli tepe parlaklığı ve güneş ışığının etkisine karşı daha düşük duyarlılıkları nedeniyle yüksek parlaklıklı LCD/mini LED çözümleri yine de tercih edilebilir.
Yanma neden olur ve nasıl önlenir?
Yanma, statik yüksek kontrastlı içerik uzun süreler boyunca görüntülendiğinde organik yayıcıların düzensiz yaşlanmasından kaynaklanır. Bu azaltma stratejileri arasında statik öğeleri azaltmak için kullanıcı arayüzü tasarımı, piksel kayması, kalıcı kullanıcı arayüzü öğeleri için parlaklık sınırları, zamanlanmış içerik hareketi ve daha uzun ömür için tandem yayıcı yığınların kullanılması yer alır.
OLED ekranlar dokunmatik ve sert kullanım desteği sunabilir mi?
Evet. Hücre içi ve hücre üstü dokunmatik mimariler yaygındır. Dayanıklı ekipmanlarda, çevresel ve mekanik özellikleri karşılamak için optik bağlama ve dayanıklı kapak lensleri (kimyasal olarak güçlendirilmiş cam, AR/AG kaplamalar) ve konformal sızdırmazlık kullanılır.
OLED, MicroLED ile nasıl karşılaştırılır?
Özel bir OLED ekran çözümüne mi ihtiyacınız var?BROWNOPTO mühendisleri, giyilebilir, tıbbi, endüstriyel ve perakende ürünler için özel AMOLED modülleri sunmak üzere OEM'lerle ortaklık kuruyor.Bize Ulaşınörnekler, veri sayfaları ve NPI desteği için.
Son makaleler
-
2025'te AR/XR için 1-2 inç AMOLED'lerin Neden Önemli Olduğu
AR/XR Patlamasında 1-2 İnç AMOLED Ekranların Neden Vazgeçilmez Hale Geldiği (2025 Sektör İçgörüsü)
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Perakende için Gerilmiş Çubuk LCD Ekranlar: Süpermarketlerde Satışları ve Etkileşimi Artırın
Gerilmiş çubuk LCD ekranların süpermarket raf kenarı pazarlamasını nasıl geliştirdiğini, satışları nasıl artırdığını ve
-
Restoranlar ve Misafirperverlik Mekanları için Gerilmiş LCD Çözümleri
Gerilmiş LCD'ler, restoran menüleri ve misafirperverlik hizmetleri için mükemmel, şık ve yüksek parlaklıkta ekranlar sunar
Önerilen ürünler
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Ürün Özellikleri: BRO392001A Çözünürlük: 1080x1024 Çalışma Voltaj Aralığı: 28V Ekran Boyutu: 3.92
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Ürün Özellikleri: BRO601001ADisplayMode: AMOLED Ekran Boyutu (inç): 6.01 Çözünürlük: 1080x2
-
1.43 INCH Circular OLED 466x466 MIPI for Smartwatches/Industrial
1,43 inç AMOLED ekran1,43 inç AMOLED dairesel ekran modülü, kompakt akıllı telefonlar için tasarlanmıştır
-
6.39 INCH Outdoor AMOLED, 1080x2340, HD, High Brightness
Ürün Özellikleri: BRO639001A Çözünürlük: 1080x2340 Voltaj: 2.8V Boyut: 6.39 inç Sürücü IC: SD52
-
4.39 INCH OLED display module I2C Interface 568×1210 Resolution
Shenzhen Brownopto Technology tarafından tanıtılan 4,39 inçlik AMOLED ekran modülü (model BR439102-A1)
-
2.08 INCH AMOLED Display 320×680 MIPI LTPS Module
2.08 INCH AMOLED 320×680 display, MIPI interface, 600nit brightness, wide viewing angle. Ideal for w