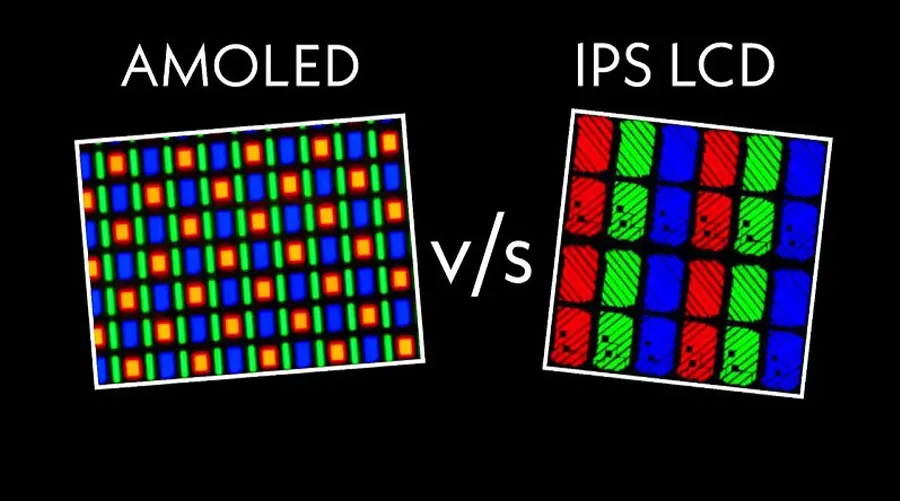
I. What is OLED Display Technology?
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are "self-emissive", meaning each pixel generates light independently. This technology eliminates the need for a backlight, enabling:
True black & infinite contrast ratio
Thinner & lighter form factors
Flexible, foldable & transparent displays
Ultra-fast response for AR/VR and gaming
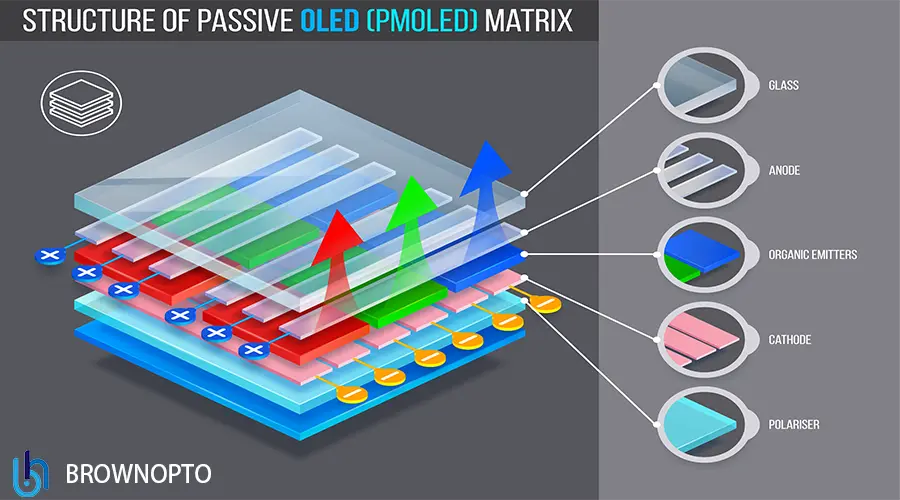
OLED has become the benchmark in premium devices (phones, wearables, TVs), and now expanding into "industrial, medical, transportation & retail electronics".
II. How OLED Pixels Work
Electroluminescence principle
Organic molecules emit light when electrons and holes recombine. People see the light directly from each pixel — no backlight, no light leakage.
OLED Device Layer Structure
Encapsulation layer (protects from moisture/O₂)
Optical extraction layer
Emissive layer (RGB light-emitting molecules)
Mga layer ng transport charge (ETL/HTL)
Transparent anode + Metal cathode
TFT active matrix (LTPS o IGZO)
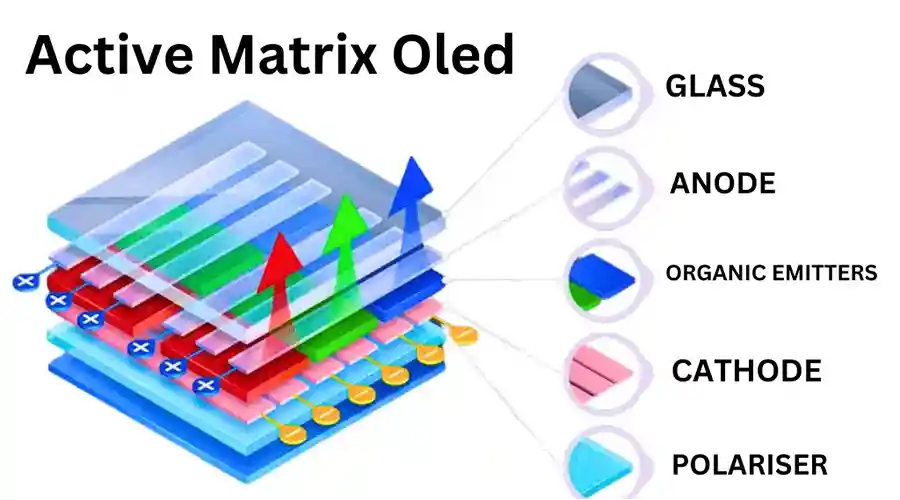
III. Mga Pangunahing Materyales at Bahagi
Mga Emitter — Fluorescent vs Phosphorescent vs TADF
Gumagamit ang mga modernong AMOLED ng "phosphorescent emitters" (pula/berde) na nakakamit ng malapit sa 100% IQE, habang ang "asul na TADF" ay ang pinakamainit na focus ng R&D para sa panghabambuhay na pagpapabuti.
Mga transparent na electrodes
| materyal | Use Case | Kakayahang umangkop |
|---|---|---|
| ITO | Matibay na OLED | Mababa |
| Graphene | Flexible na OLED | Mataas |
| Silver nanowire | Mga curved na naisusuot na display | Mataas |
Thin-Film Encapsulation (TFE)
Kinakailangang WVTR: "< 10⁻⁶ g/m²/araw" para magarantiya ang multi-year na katatagan ng pagpapatakbo.
IV. Teknolohiya sa Paggawa ng OLED
Pinagsasama ng pagmamanupaktura ng OLED ang semiconductor, chemistry, at precision optics. Ang pinakakaraniwang pamamaraan:
Pagsingaw + Fine Metal Mask (FMM)
Ginagamit sa mga smartphone, naisusuot
Mataas na PPI (>500), tumpak na pagkakahanay ng RGB
Limitadong pag-scale sa >10-pulgadang laki
Inkjet Printing OLED (IJP-OLED)
kahusayan sa paggamit ng materyal >90%
Angkop para sa malalaking display (TV, signage)
Roadmap ng pagbabawas ng gastos sa ilalim ng mabilis na pag-unlad
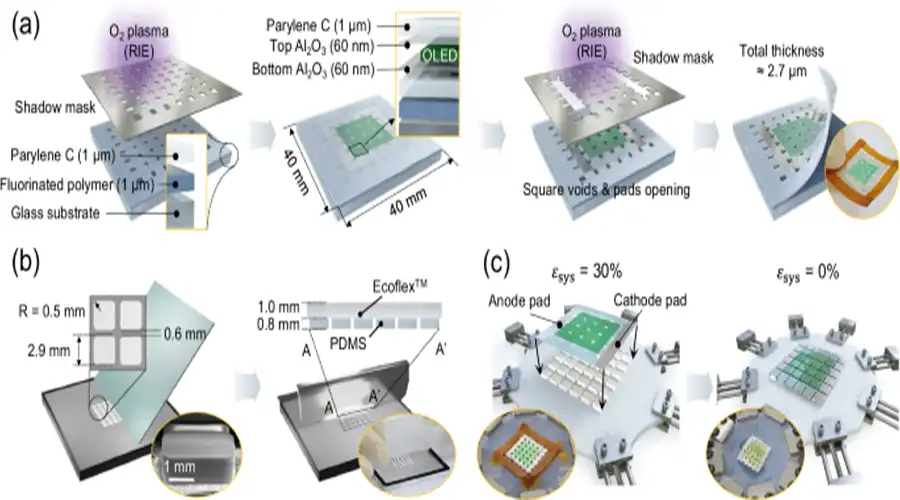
V. OLED Performance Engineering
Ino-optimize ng mga inhinyero ang disenyo sa pamamagitan ng pagbabalanse ng liwanag, panghabambuhay, kapangyarihan at thermal stability.
Liwanag at Panlabas na Visibility
Karaniwan: 300–900 nits (depende sa APL)
Sa mga MLA / tandem stack: hanggang 2000 nits+
Mahalaga para sa medikal at automotive
Panghabambuhay na Pagkakaaasahan
| Kulay | Karaniwang LT97 Habambuhay | Mga Tala |
|---|---|---|
| Berde | 50k–120k na oras | Malakas na katatagan |
| Pula | 40k–80k oras | Napakahusay na kahusayan |
| Asul | 10k–25k na oras | Gumaganda pa rin sa pamamagitan ng TADF |
Disenyo ng UImahalaga: ang mga static na icon ay nagpapabilis ng differential aging (burn-in).
Oras ng Pagtugon
OLED na tugon na kasing bilis ng "1 μs", 100x na mas mabilis kaysa sa LCD — perpekto para sa VR/AR at HUD.
VI. Mga Pangunahing Uri ng Display ng OLED
Rigid AMOLED (Glass Substrate)
Matipid, mature na supply chain
Industrial handheld, HMI modules, medikal
Flexible at Natitiklop na OLED
Ang mga polyimide substrate ay nagbibigay-daan sa mga curves at folds
Mga nasusuot, matalinong accessory, interior ng sasakyan
Transparent na OLED
Showcase effect na may >40% transparency
Retail, museo, futuristic na UX
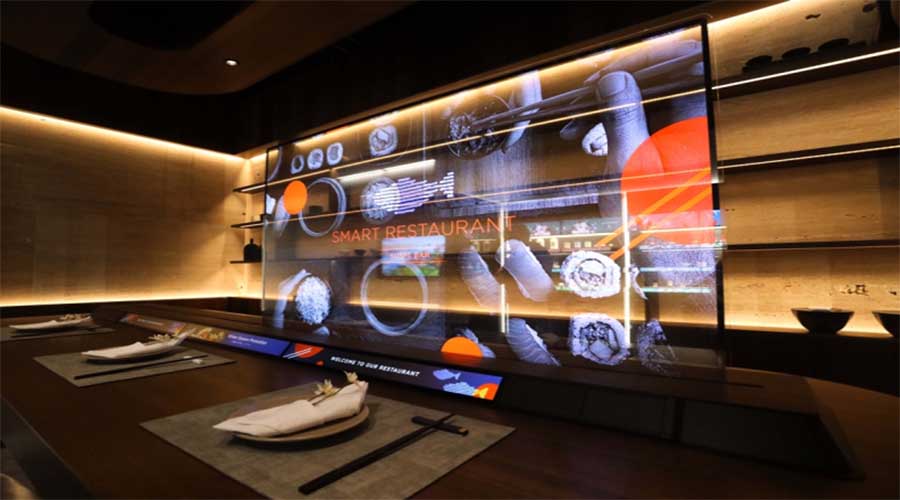

VII. Mga Application sa Industriya ng OLED Display
1) Nasusuot na Teknolohiya
Mga low power AOD mode
Kurbadong anyo para sa ginhawa
Mga pagpapabuti sa pagiging madaling mabasa sa labas
2) Industrial Human-Machine Interface
Mataas na contrast + malawak na anggulo sa pagtingin
Optical bonding para sa masungit na touch system
Kinakailangan ang diskarte sa mahabang buhay na UI
3) Retail at Transparent na Signage
Ang mga premium na graphics ay humihimok ng mga conversion
Pagpapakita ng lumulutang na impormasyon
4) Medikal at Instrumentasyon
High-data na kalinawan para sa malapit na pagbabasa
Opsyonal ang mga anti-reflection/anti-bacteria coating
VIII. OLED vs LCD vs Mini-LED vs MicroLED
| Aspeto | IKAW NA | Mini-LED (LCD) | Karaniwang LCD | MicroLED |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Itim na Antas | Perpektong itim | Mas mahusay na may lokal na dimming | Lumiwanag at dumugo | Perpektong itim |
| Contrast | Walang hanggan | Mataas | Mababa | Walang hanggan |
| Liwanag | Mabuti | Napakataas | Mataas | Napakataas |
| Kakayahang umangkop | Oo | Hindi | Hindi | Oo |
| Panganib sa Burn-in | Kailangan ng mitigation | wala | wala | Minimal |
| Gastos | Mas mataas | Higher-mid | Ibaba | Napakataas |
Conclusion:Ang OLED ang pinakamahusay na pagpipilian kapag kailangan ang premium na UX at manipis/flexible na disenyo.
IX. Mga Umuusbong na Trend at ang Hinaharap ng OLED
QD-OLED at Hybrid Approaches
Pinagsasama ng Quantum-dot OLED (QD-OLED) at iba pang hybrid approach ang mga OLED emissive layer na may quantum-dot color conversion o enhancement films upang mapataas ang nakikitang liwanag at dami ng kulay. Nilalayon ng QD-OLED na mapanatili ang pixel-level contrast ng OLED habang pinapahusay ang peak luminance at color saturation — isang nakakahimok na trade-off para sa mga premium na TV at propesyonal na monitor.
Tandem OLED at Stacked Architectures
Ang mga tandem OLED stack ay naglalagay ng maraming emissive unit sa serye upang ibahagi ang kasalukuyang at bawasan ang per-emitter stress. Ang mga tandem na arkitektura ay nagpapabuti sa buhay, nagpapataas ng magagamit na liwanag at nagpapagaan ng pagkakaiba-iba ng pagtanda na humahantong sa pagkasunog. Ang mga stack na ito, na sinamahan ng mga pinahusay na asul na chemistries, ay sentro ng pangmatagalang komersyal na mga diskarte sa OLED.
Rollable, Printed at Stretchable OLEDs
Ang mga advance sa printed electronics at thin-film encapsulation ay nagbibigay-daan sa mga rollable na telebisyon, conformal signage, at textile-embedded na mga display. Ang mga naka-print na OLED ay nagpapababa ng CAPEX sa pagmamanupaktura sa pamamagitan ng pag-alis ng ilang hakbang sa pag-deposito ng vacuum, habang ang nababanat na OLED na pananaliksik ay nagta-target ng naisusuot at medikal na pagsasama kung saan ang mga display ay umaayon sa balat o tela.
Mga MicroOLED / Near-Eye Display at AR
Ang mga MicroOLED display (microdisplays) na may silicon o CMOS na mga backplane ay naghahatid ng napakataas na pixel density para sa mga AR/VR headset. Pinaliit ng mga OLED microdisplay ang latency at sinusuportahan ang mataas na dynamic na hanay, mga pangunahing sukatan para sa mga nakaka-engganyong near-eye system.
Sustainability at Material Efficiency
Ang industriya ay aktibong binabawasan ang paggamit ng bihirang-materyal, pagpapabuti ng recyclability ng mga substrate at layer, at pag-optimize ng drive electronics para sa pagtitipid ng enerhiya. Ang mga pagtatasa ng lifecycle at eco-design ay nagiging mga pagsasaalang-alang sa pagbili para sa mga OEM na nagde-deploy ng mga display sa sukat.
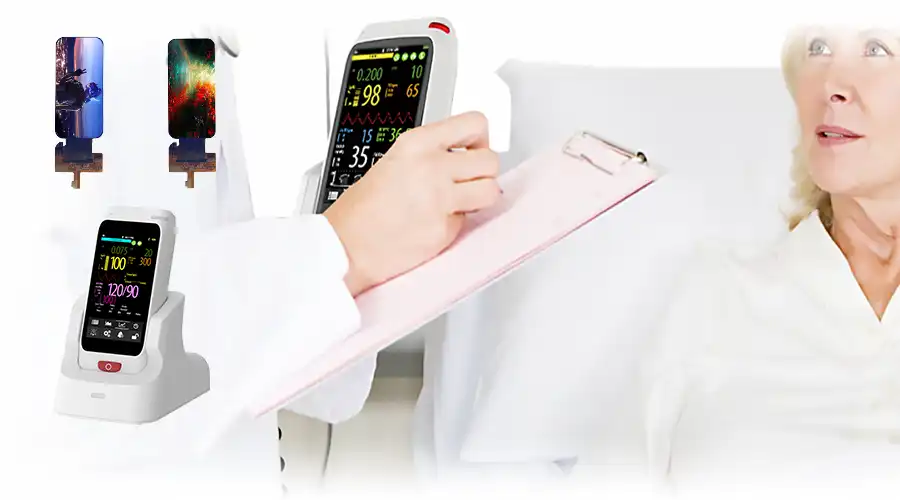
X. Pag-aaral ng Kaso — BROWNOPTO 4.4" AMOLED Integration para sa Handheld Medical Device
Pangkalahatang-ideya ng Proyekto
Ang isang medikal na aparato na OEM ay nangangailangan ng isang compact, daylight-readable na display para sa isang portable point-of-care analyzer. Kabilang sa mga pangunahing hadlang ang manipis na mekanikal na profile, hawakan na may kakayahang guwantes, mataas na contrast para sa pagiging madaling mabasa ng klinikal, at matatag na pagiging maaasahan sa field mula -20°C hanggang +70°C.
Solusyon sa Engineering
Pagpili ng panel: 4.40" LTPS AMOLED na may tandem emissive architecture upang balansehin ang liwanag at panghabambuhay.
Touch integration: On-cell projected capacitive touch na na-calibrate para sa nitrile gloves at basang kondisyon.
Mga optika: Anti-reflective polarizer at optical bonding (OCA) para sa pinahusay na contrast ng sikat ng araw at pagiging rugged.
Interface: MIPI DSI 2-lane na may naka-optimize na power sequencing para sa ligtas na start-up at low-power sleep mode.
Encapsulation: Thin-film encapsulation (TFE) na naghahatid ng WVTR < 1e-6 g/m²/araw para sa pinahabang field lifetime.
Naihatid ang Mga Pangunahing Detalye
| Parameter | Halaga |
|---|---|
| dayagonal | 4.40 pulgada |
| Resolusyon | 568 × 1210 |
| Karaniwang Liwanag | 600 cd/m² |
| Contrast | ~100,000:1 (typ.) |
| Interface | MIPI DSI (2 lane) |
| Operating Temp | -20 °C hanggang +70 °C |
| Encapsulation | Thin-film encapsulation (TFE) |
Mga Resulta at Feedback sa Field
Ang device ay pumasok sa isang 12-buwang pilot sa mga klinika at mobile unit. Itinampok ng feedback ang pambihirang pagiging madaling mabasa sa ilalim ng iba't ibang ilaw at pare-parehong pag-uugali sa pagpindot gamit ang mga guwantes. Walang mga pagkabigo sa field na may kaugnayan sa pagganap ng display ang naitala; ang tandem na OLED na diskarte at naka-calibrate na mga diskarte sa UI ay nagpapagaan ng panganib sa pagkasunog.

XI. Mga Madalas Itanong
Ano ang pagkakaiba sa pagitan ng OLED at AMOLED?
Ang OLED ay ang pangkalahatang klase ng mga organic light-emitting diode display. Gumagamit ang AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED) ng thin-film transistor (TFT) na backplane upang aktibong tugunan ang mga pixel at sumusuporta sa mga panel na may mataas na resolution at malalaking format na angkop para sa mga smartphone, TV at mga pang-industriyang display; Ang PMOLED ay isang passive matrix na variant na angkop para sa maliliit at murang mga screen.
Gaano katagal karaniwang tumatagal ang mga OLED display?
Nakadepende ang buhay sa emitter chemistry, liwanag ng panel, thermal design at operating patterns. Ang karaniwang pang-komersyal na buhay ng AMOLED ay mula sa sampu-sampung libo hanggang 100,000+ na oras para sa mga kulay maliban sa asul; Ang blue emitter lifetime ay nananatiling limiting factor at aktibong pinapabuti sa pamamagitan ng mga materyales na pananaliksik at mga istruktura ng tandem.
Angkop ba ang mga OLED display para sa panlabas na signage?
Maaaring gamitin ang mga OLED sa labas kapag idinisenyo para sa mataas na peak luminance at ipinares sa mga anti-reflective optics. Gayunpaman, para sa matinding direktang liwanag ng araw, ang mataas na liwanag na LCD/mini-LED na solusyon ay maaaring mas gusto pa rin dahil sa mas mataas na pinapanatili na peak brightness at mas mababang susceptibility sa solar washout.
Ano ang sanhi ng burn-in at paano ito maiiwasan?
Ang burn-in ay nagmumula sa hindi pantay na pagtanda ng mga organic na naglalabas kapag ang static na high-contrast na nilalaman ay ipinapakita sa mahabang panahon. Kasama sa mga diskarte sa pagpapagaan ang disenyo ng UI para bawasan ang mga static na elemento, paglilipat ng pixel, mga limitasyon sa liwanag para sa patuloy na mga elemento ng UI, naka-iskedyul na paggalaw ng content, at paggamit ng mga tandem emissive stack para sa pinahusay na mahabang buhay.
Maaari bang suportahan ng mga OLED display ang touch at masungit na paggamit?
Oo. Ang mga on-cell at in-cell touch architecture ay karaniwan. Para sa masungit na kagamitan, ang optical bonding at matibay na cover lens (chemically strengthened glass, AR/AG coatings) kasama ng conformal sealing ay ginagamit upang matugunan ang mga environmental at mechanical specs.
Paano maihahambing ang OLED sa MicroLED?
Kailangan ng custom na OLED display solution?Ang mga inhinyero ng BROWNOPTO ay kasosyo sa mga OEM upang maghatid ng mga pinasadyang AMOLED na module para sa mga naisusuot, medikal, pang-industriya at tingian na mga produkto.Makipag-ugnayan sa aminpara sa mga sample, datasheet at suporta sa NPI.
Mga pinakabagong artikulo
-
Bakit 1–2" na AMOLED ang Susi sa AR/XR sa 2025
Bakit Nagiging Mahalaga ang 1–2 Inch AMOLED Display sa AR/XR Boom (2025 Industry Insight) body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Mga Stretched Bar LCD Display para sa Retail: Palakasin ang Benta at Pakikipag-ugnayan sa Mga Supermarket
Tuklasin kung paano pinahusay ng mga stretched bar LCD display ang shelf-edge marketing ng supermarket, humimok ng mga benta, at bawasan
-
Naka-stretch na LCD Solutions para sa Mga Restaurant at Hospitality Venues
Stretched LCDs offer sleek, high-brightness displays perfect for restaurant menus and hospitality si
Inirerekomendang mga produkto
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Mga Detalye ng Produkto: BRO392001AResolution: 1080x1024Sinakop ng Operating Voltage: 28VSLaki ng Screen: 3.92
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Mga Detalye ng Produkto: BRO601001ADiplayMode: AMOLED na Laki ng Screen (pulgada): 6.01 Resolution: 1080x2
-
1.43 INCH Circular OLED 466x466 MIPI for Smartwatches/Industrial
1.43-inch AMOLED displayAng 1.43-inch AMOLED circular display module ay idinisenyo para sa compact smart d
-
6.39 INCH Outdoor AMOLED, 1080x2340, HD, High Brightness
Mga Detalye ng Produkto: BRO639001AResolution: 1080x2340Voltage: 2.8VSlaki: 6.39 pulgadaDriver IC: SD52
-
4.39 INCH OLED display module I2C Interface 568×1210 Resolution
Ang 4.39-inch AMOLED display module (modelo BR439102-A1) na ipinakilala ni (Shenzhen Brownopto Technology
-
2.08 INCH AMOLED Display 320×680 MIPI LTPS Module
2.08 INCH AMOLED 320×680 display, MIPI interface, 600nit brightness, wide viewing angle. Ideal for w