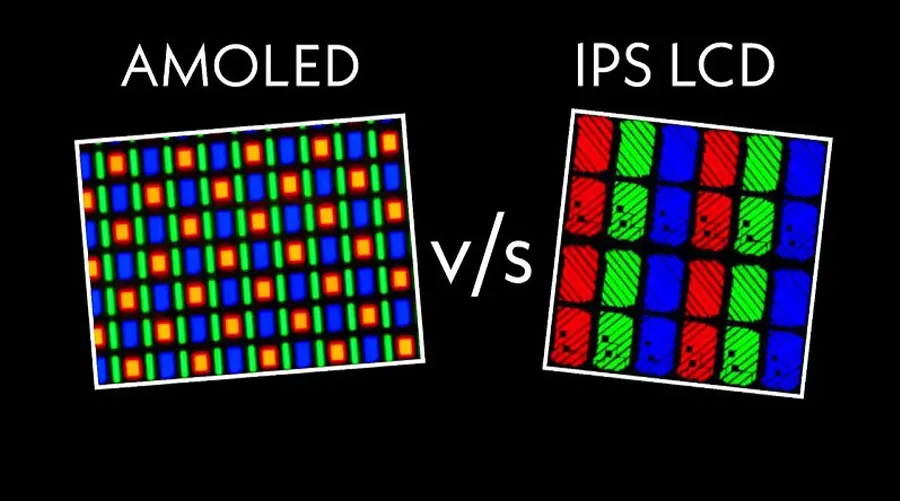
OLED vs LCD Display: A Comprehensive Comparison for 2025
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) are two dominant technologies shaping modern display systems. This article provides an in-depth comparison covering their working principles, performance metrics, use cases, and future trends.
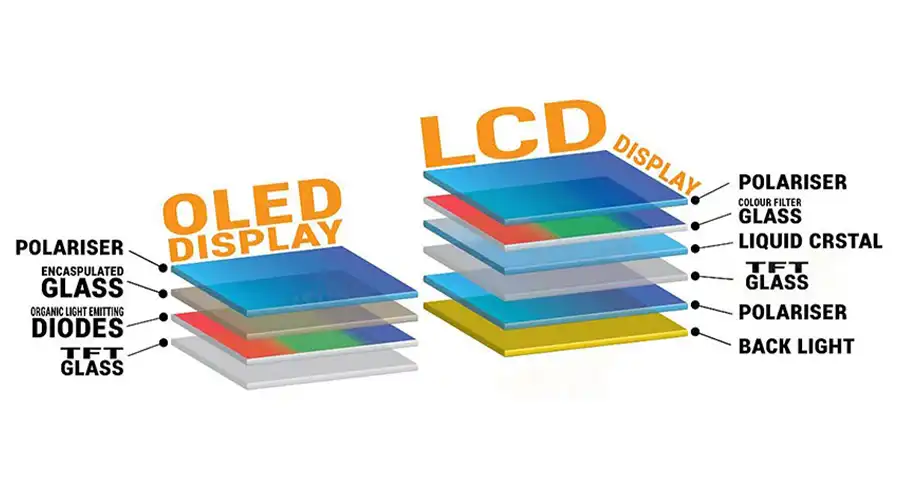
1. Technical Principles: How OLED and LCD Work
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode)
-
Self-Emitting Pixels: Each pixel emits its own light via organic materials.
-
Thin & Flexible: Ultra-thin structure enables curved or rollable designs.
-
Fast Response Time: Up to 0.1ms for smooth motion rendering.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
-
Backlight Dependent: Requires LED backlighting for visibility.
-
Thicker Design: Multiple layers including filters and backlight modules.
-
Slower Response: Typically 5–10ms, which may cause motion blur.
| Feature | OLED | LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Light Source | Self-emitting | Backlight required |
| Thickness | <1mm | >3mm |
| Flexibility | Curved/Rollable | Rigid |
| Response Time | <1ms | 5–10ms |
2. Image Quality: Color Accuracy, Brightness & Contrast
Color Performance
OLED offers wider gamut coverage (98%+ DCI-P3), while LCDs vary based on panel type (IPS vs TN).
Brightness and Contrast
OLED achieves infinite contrast due to true blacks, whereas LCD relies on local dimming to simulate similar effects.
Viewing Angles
OLED maintains consistent brightness at 178°, while standard LCDs may suffer from color distortion at wide angles.

3. Energy Efficiency & Lifespan: Which is More Durable?
Power Consumption
OLED saves energy in dark scenes, but uses more power during full-white displays. LCD consumes power consistently regardless of content.
Lifespan and Aging
OLED may experience burn-in over time (~50,000 hours), while LCD has no such risk but requires backlight replacements after ~50,000 hours.
4. Applications: From Smartphones to Industrial Displays
Consumer Electronics
OLED dominates smartphones (e.g., iPhone 15 Pro, Galaxy S24 Ultra). LCD remains cost-effective for budget laptops and tablets.
Professional & Industrial Use
OLED used in medical imaging and automotive dashboards. LCD preferred for industrial control panels and outdoor signage.
Future Trends
Foldable phones and AR/VR headsets leverage micro-OLED. LCD evolves with Mini-LED and Quantum Dot enhancements.
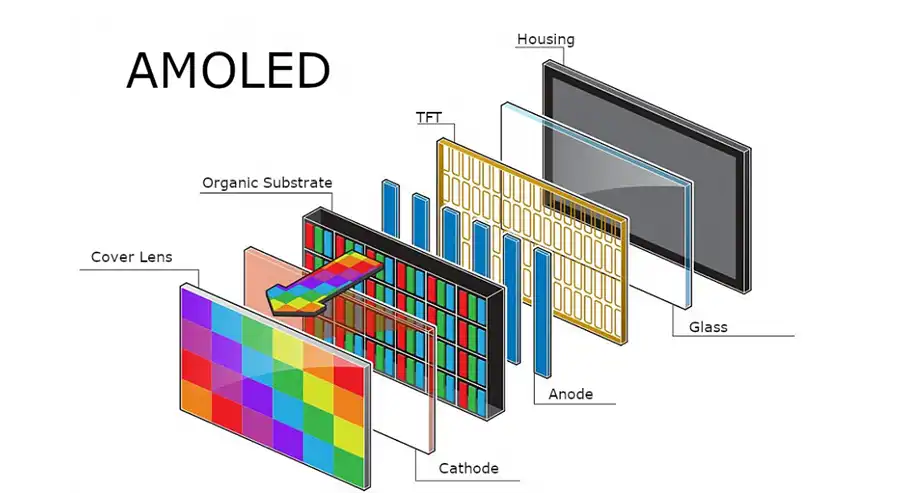
5. Cost & Market Trends: Future of Display Technology
Production Costs
OLED costs higher due to complex manufacturing, though mass production reduces prices for small modules like BrownOPTO’s 2.06" AMOLED screen.
Market Growth Forecasts
OLED market projected to reach $60B by 2025. LCD remains strong at $40B with continued demand in mid-range and industrial sectors.
6. FAQ: Common Questions About OLED and LCD
Q1: Can OLED displays avoid burn-in?
A: Modern OLEDs use pixel shifting and reduced static icon brightness to minimize burn-in risks.
Q2: Are LCDs capable of flexible designs?
A: No. LCDs require rigid backlight structures, though experimental "bendable LCDs" exist.
Q3: How to choose between OLED and LCD?
A: Choose OLED for high contrast, dynamic visuals, or flexible design. Choose LCD for cost-effectiveness and long-term reliability.
Conclusion: The Synergy of OLED and LCD
While OLED and LCD represent distinct technological paths, they are not mutually exclusive. Innovations like Mini-LED backlit LCDs combine LCD’s durability with OLED-like contrast. Meanwhile, OLED’s flexibility is revolutionizing wearables and automotive displays. Companies like BrownOPTO offer advanced AMOLED modules that serve both consumer electronics and industrial markets. As material science advances, OLED and LCD will coexist, each dominating its niche while pushing the boundaries of display technology.
Latest articles
-
Why 1–2" AMOLEDs Are Key to AR/XR in 2025
Why 1–2 Inch AMOLED Displays Are Becoming Essential in the AR/XR Boom (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
Discover how stretched bar LCD displays enhance supermarket shelf-edge marketing, drive sales, reduc
-
Stretched LCD Solutions for Restaurants and Hospitality Venues
Stretched LCDs offer sleek, high-brightness displays perfect for restaurant menus and hospitality si
Recommended products
-
2.06-inch OLED Display | 410×502 Resolution | 600 Nits | SPI Screen
The 2.06-inch AMOLED display module is designed specifically for harsh industrial environments, feat
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Product Specifications: BRO392001AResolution: 1080x1024Operating Voltage Range: 28VScreen Size: 3.92
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Product Specifications: BRO601001ADisplayMode: AMOLED Screen Size (inch): 6.01 Resolution: 1080x2
-
4.39 INCH OLED display module I2C Interface 568×1210 Resolution
The 4.39-inch AMOLED display module (model BR439102-A1) introduced by (Shenzhen Brownopto Technology
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Product Specifications: BRO548001AResolution: 1080x1920Operating Voltage Range: 2.8VScreen Size: 5.4