Introduction
In an era where vibrant colors, razor-thin screens, and energy efficiency dominate consumer demands, Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) have emerged as a revolutionary technology. From smartphones to televisions, OLEDs are redefining how we experience visual content. This article dives deep into the science, applications, and future of OLED technology, offering insights that go beyond basic explanations to explore its societal and environmental impact.
The Basics of OLED Technology
What Does OLED Stand For?
OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Unlike traditional LEDs, OLEDs use carbon-based organic compounds to emit light when an electric current flows through them. This enables unique advantages like flexibility, deeper blacks, and ultra-thin designs.
The Anatomy of an OLED
Substrate: Rigid (glass) or flexible (plastic) base.
Anode: Transparent layer (e.g., indium tin oxide).
Organic Layers:
Hole Transport Layer (HTL)
Emissive Layer (EML)
Electron Transport Layer (ETL)
Cathode: Metal layer (e.g., aluminum).
When voltage is applied, electrons and holes combine in the emissive layer to produce electroluminescence.
How Do OLEDs Work? The Science Simplified
OLEDs use self-emissive pixels, eliminating the need for a backlight (as in LCDs). This enables:
True Blacks: Individual pixels can turn off completely.
Infinite Contrast Ratios: Coexistence of darkest blacks and brightest whites.
Faster Response Times: Ideal for gaming and high-speed video.
Fun Fact: The color of light emitted depends on the organic material used in the emissive layer. Red, green, and blue (RGB) subpixels combine to create the full color spectrum.
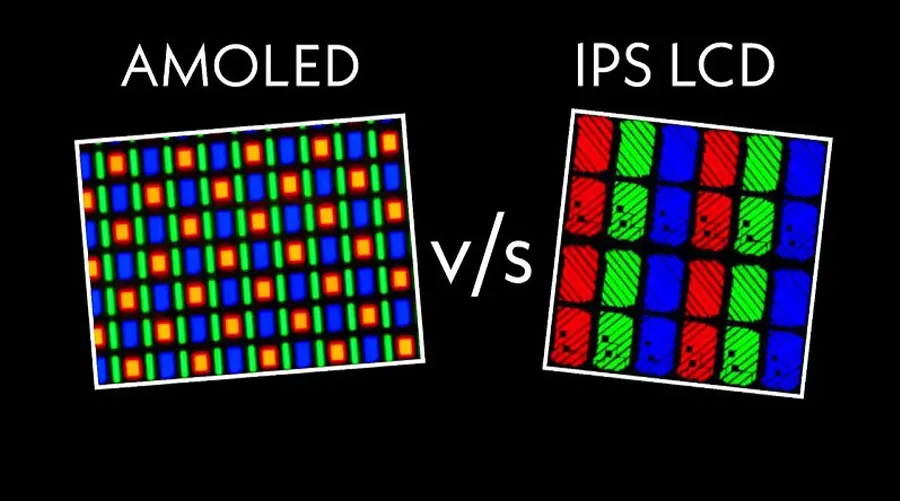
OLED vs. LCD/LED: Why OLEDs Dominate
| Feature | OLED | LCD/LED |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight | Self-emissive pixels | Requires external backlight |
| Thickness | As thin as 0.3 mm | Bulkier due to backlight layers |
| Viewing Angles | Near 180° without color shift | Limited by backlight leakage |
Applications of OLEDs Beyond Screens
Lighting
OLED panels are used for ambient lighting due to their soft, glare-free illumination. Companies like LG and Philips offer designer OLED lamps.
Healthcare
Wearable Sensors: Monitor vital signs in real time.
Photodynamic Therapy: Treat skin conditions with targeted light.
Challenges and Innovations
Burn-in and Lifespan
Blue OLED materials degrade faster than red/green. Solutions include:
Pixel Shifting: Subtly move static images to spread wear.
Improved Materials: TADF and Hyperfluorescence technologies extend blue OLED lifespan.
The Future of OLEDs
MicroLED vs. OLED
MicroLEDs offer higher brightness but face manufacturing hurdles. OLEDs will dominate consumer electronics, while MicroLEDs excel in large-format displays.
Quantum Dot-OLED (QD-OLED)
Samsung’s QD-OLED TVs combine OLED’s perfect blacks with quantum dots’ vibrant colors, representing the next evolution in home entertainment.

FAQ Section
Can OLED screens burn in?
Yes, but modern devices use software safeguards to minimize risk. Avoid static images at maximum brightness for extended periods.
Are OLEDs better for your eyes?
OLEDs emit less blue light than LCDs and lack flickering backlights, reducing eye strain.
Conclusion
OLEDs represent a paradigm shift in how we interact with light. From foldable phones to sustainable lighting, their potential is limitless. As research tackles current limitations, OLEDs will continue to shape industries, blending science with artistry to create a brighter—and more flexible—future.
Latest articles
-
Why 1–2" AMOLEDs Are Key to AR/XR in 2025
Why 1–2 Inch AMOLED Displays Are Becoming Essential in the AR/XR Boom (2025 Industry Insight)body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Retail: Boost Sales & Engagement in Supermarkets
Discover how stretched bar LCD displays enhance supermarket shelf-edge marketing, drive sales, reduc
-
Stretched LCD Solutions for Restaurants and Hospitality Venues
Stretched LCDs offer sleek, high-brightness displays perfect for restaurant menus and hospitality si
Recommended products
-
2.06-inch OLED Display | 410×502 Resolution | 600 Nits | SPI Screen
The 2.06-inch AMOLED display module is designed specifically for harsh industrial environments, feat
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Product Specifications: BRO601001ADisplayMode: AMOLED Screen Size (inch): 6.01 Resolution: 1080x2
-
4.39 INCH OLED display module I2C Interface 568×1210 Resolution
The 4.39-inch AMOLED display module (model BR439102-A1) introduced by (Shenzhen Brownopto Technology
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Product Specifications: BRO548001AResolution: 1080x1920Operating Voltage Range: 2.8VScreen Size: 5.4