Explore the intricate workings of leading display technologies, their benefits, and potential applications.
Introduction to Display Technologies
In the rapidly evolving world of electronic displays, Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD), Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLED), and MicroLEDs represent significant milestones in technological advancement. Each technology offers unique features and capabilities that cater to various applications from smartphones and televisions to medical devices and industrial control panels. Understanding these technologies helps consumers and professionals make informed decisions about which type of display best suits their needs.
An In-depth Look at LCD Technology
Liquid Crystal Displays have been a cornerstone of visual technology for decades, providing reliable performance across a wide range of products. The basic structure of an LCD includes layers such as the backlight unit, polarizers, liquid crystal layer, and color filters. These components work together to manipulate light and create images on the screen.

The Core Components of LCD Screens
The core components of an LCD screen include the backlight unit, which provides the necessary illumination, polarizing films that control light passage, and the liquid crystal layer that modulates the light based on electrical signals. Additionally, color filters are used to produce the red, green, and blue colors needed for full-color displays.
LCDs are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability. However, they have limitations in terms of contrast ratios and viewing angles compared to newer technologies like OLED and MicroLED.
Förstå OLED-skärmar
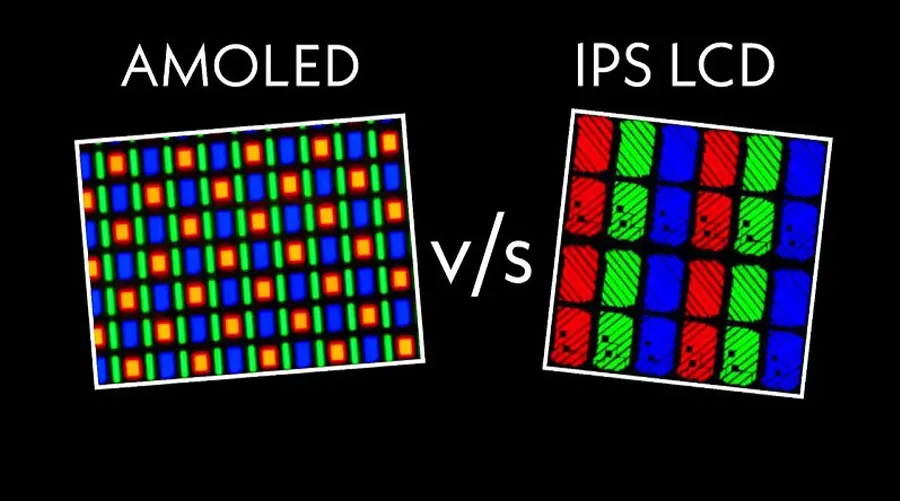
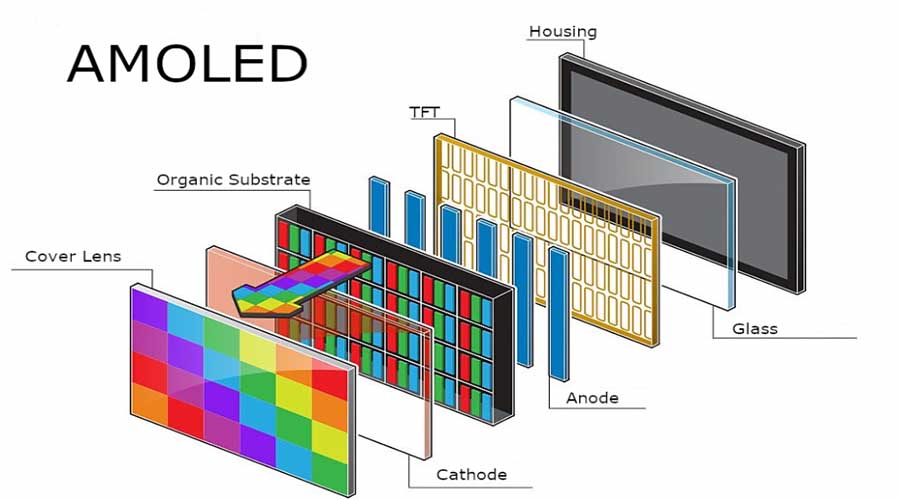
OLED technology has revolutionized display capabilities by offering superior contrast ratios and vibrant colors. Unlike LCDs, OLED displays do not require a backlight because each pixel emits its own light. This self-emissive nature allows OLED screens to achieve true blacks and infinite contrast ratios, making them ideal for high-end applications where picture quality is paramount.
Advantages of OLED Over Traditional LCDs
One of the most notable advantages of OLED is its ability to achieve true blacks and infinite contrast ratios. Since OLED pixels emit their own light, they can be turned off completely, resulting in deep blacks and enhanced picture quality. OLED also offers faster response times and wider viewing angles compared to LCDs, making it suitable for dynamic content like movies and games.
Burn-In Issues in OLED Displays
A common issue with OLED displays is burn-in, where static images left on the screen for extended periods may leave permanent marks. This occurs due to differential lifespans among red, green, and blue subpixels. Software solutions can mitigate this problem by adjusting current levels across different areas of the screen.
The Future with MicroLED Technology
MicroLED is poised to be the next big leap in display technology, offering unparalleled brightness and energy efficiency. By using microscopic LEDs that can emit light independently, MicroLED displays provide superior performance compared to both LCD and OLED technologies. MicroLED uses inorganic materials, making it more durable and less prone to degradation over time.

Key Features of MicroLED Displays
MicroLED displays are characterized by their use of microscopic LEDs that can emit light independently. These LEDs are made from inorganic materials, making them more durable and less prone to degradation over time. MicroLED technology also offers higher brightness levels and lower power consumption compared to OLED, making it ideal for outdoor and high-brightness environments.
Challenges in MicroLED Production
Despite its promising features, MicroLED faces challenges related to manufacturing complexity and cost. The process of assembling millions of tiny LEDs onto a substrate requires precise alignment and bonding techniques. As research and development continue, these challenges are expected to diminish, paving the way for widespread adoption of MicroLED technology.
Comparing LCD, OLED, and MicroLED
When comparing these three display technologies, it's clear that each has its strengths and weaknesses. LCDs offer reliability and cost-effectiveness but lag behind in terms of contrast and response time. OLEDs provide superior picture quality and flexibility but suffer from issues like burn-in. MicroLED combines the best aspects of both technologies, offering high brightness, low power consumption, and durability, though it currently faces production challenges.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
As we look towards the future, MicroLED is expected to play a significant role in shaping the next generation of displays. With ongoing research and development efforts, the cost and production challenges associated with MicroLED are likely to diminish, paving the way for widespread adoption. Meanwhile, OLED continues to dominate the mobile and television markets due to its superior picture quality, while LCD remains a reliable choice for budget-conscious consumers.
For tech enthusiasts and professionals, staying informed about the latest advancements in display technology is crucial. Whether you're designing a new product or simply upgrading your personal device, understanding the nuances of LCD, OLED, and MicroLED will help you make the best decision.

Senaste artiklarna
-
Varför 1–2-tums AMOLED-skärmar är nyckeln till AR/XR år 2025
Varför 1–2-tums AMOLED-skärmar blir allt viktigare i AR/XR-boomen (2025 Industry Insight) body {f
-
Understanding OLED Display Technology: Principles, Performance & Applications
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are a class of self-emissive display technology in whic
-
From Wearables to AR Glasses – How OLED Displays Are Redefining Visual Experiences in 2025
By 2025, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has transitioned from luxury smartphone disp
-
LCD-skärmar med sträckta streck för detaljhandeln: Öka försäljning och engagemang i stormarknader
Upptäck hur LCD-skärmar med utdragbar bar förbättrar marknadsföringen av hyllkanten i stormarknaden, driver försäljning, minskar
-
Utsträckta LCD-lösningar för restauranger och hotell
Sträckta LCD-skärmar erbjuder eleganta skärmar med hög ljusstyrka, perfekta för restaurangmenyer och hotellbranschen.
Recommended products
-
3.92 INCH OLED Screen I2C Interface 1080 × 1240 Resolution
Produktspecifikationer: BRO392001A Upplösning: 1080x1024 Driftspänningsområde: 28VSkärmstorlek: 3,92
-
6.01 INCH Display OLED screen | High Definition 1080x2160 | MIPI Interface
Produktspecifikationer: BRO601001ASkärmläge: AMOLED Skärmstorlek (tum): 6,01 Upplösning: 1080x2
-
1.38 INCH AMOLED Type 128x400 Low Power Wearable Display
Shenzhen Brownopto 1,38-tums AMOLED-modul: 128×400 upplösning, 600 nit ljusstyrka, MIPI/QSPI/SPI-ingång
-
5.48 INCH AMOLED Display Module - 1080x1920 I2C, MIPI DSI, Industrial
Produktspecifikationer: BRO548001A Upplösning: 1080x1920 Driftspänningsområde: 2,8 V Skärmstorlek: 5,4